Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder.
SVM Margins Example#
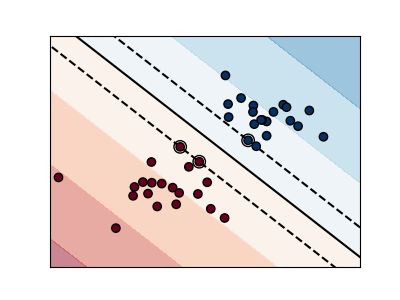
The plots below illustrate the effect the parameter C has
on the separation line. A large value of C basically tells
our model that we do not have that much faith in our data’s
distribution, and will only consider points close to line
of separation.
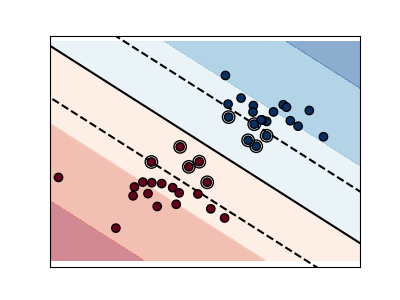
A small value of C includes more/all the observations, allowing
the margins to be calculated using all the data in the area.
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import svm
# we create 40 separable points
np.random.seed(0)
X = np.r_[np.random.randn(20, 2) - [2, 2], np.random.randn(20, 2) + [2, 2]]
Y = [0] * 20 + [1] * 20
# figure number
fignum = 1
# fit the model
for name, penalty in (("unreg", 1), ("reg", 0.05)):
clf = svm.SVC(kernel="linear", C=penalty)
clf.fit(X, Y)
# get the separating hyperplane
w = clf.coef_[0]
a = -w[0] / w[1]
xx = np.linspace(-5, 5)
yy = a * xx - (clf.intercept_[0]) / w[1]
# plot the parallels to the separating hyperplane that pass through the
# support vectors (margin away from hyperplane in direction
# perpendicular to hyperplane). This is sqrt(1+a^2) away vertically in
# 2-d.
margin = 1 / np.sqrt(np.sum(clf.coef_**2))
yy_down = yy - np.sqrt(1 + a**2) * margin
yy_up = yy + np.sqrt(1 + a**2) * margin
# plot the line, the points, and the nearest vectors to the plane
plt.figure(fignum, figsize=(4, 3))
plt.clf()
plt.plot(xx, yy, "k-")
plt.plot(xx, yy_down, "k--")
plt.plot(xx, yy_up, "k--")
plt.scatter(
clf.support_vectors_[:, 0],
clf.support_vectors_[:, 1],
s=80,
facecolors="none",
zorder=10,
edgecolors="k",
)
plt.scatter(
X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=Y, zorder=10, cmap=plt.get_cmap("RdBu"), edgecolors="k"
)
plt.axis("tight")
x_min = -4.8
x_max = 4.2
y_min = -6
y_max = 6
YY, XX = np.meshgrid(yy, xx)
xy = np.vstack([XX.ravel(), YY.ravel()]).T
Z = clf.decision_function(xy).reshape(XX.shape)
# Put the result into a contour plot
plt.contourf(XX, YY, Z, cmap=plt.get_cmap("RdBu"), alpha=0.5, linestyles=["-"])
plt.xlim(x_min, x_max)
plt.ylim(y_min, y_max)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
fignum = fignum + 1
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.053 seconds)
Related examples
Illustration of Gaussian process classification (GPC) on the XOR dataset
Illustration of Gaussian process classification (GPC) on the XOR dataset
Gaussian process classification (GPC) on iris dataset
Gaussian process classification (GPC) on iris dataset