Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder.
Recursive feature elimination#
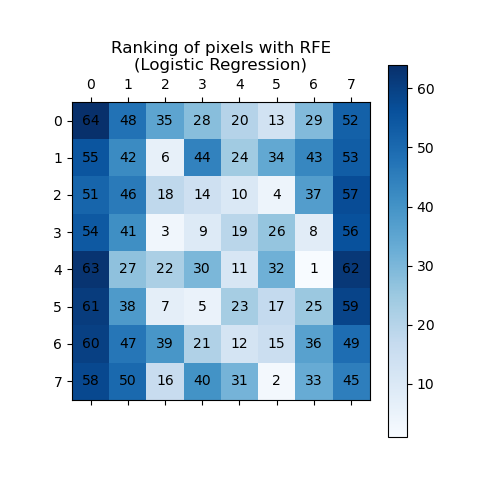
This example demonstrates how Recursive Feature Elimination
(RFE) can be used to determine the
importance of individual pixels for classifying handwritten digits.
RFE recursively removes the least
significant features, assigning ranks based on their importance, where higher
ranking_ values denote lower importance. The ranking is visualized using both
shades of blue and pixel annotations for clarity. As expected, pixels positioned
at the center of the image tend to be more predictive than those near the edges.
Note
See also Recursive feature elimination with cross-validation
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFE
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
# Load the digits dataset
digits = load_digits()
X = digits.images.reshape((len(digits.images), -1))
y = digits.target
pipe = Pipeline(
[
("scaler", MinMaxScaler()),
("rfe", RFE(estimator=LogisticRegression(), n_features_to_select=1, step=1)),
]
)
pipe.fit(X, y)
ranking = pipe.named_steps["rfe"].ranking_.reshape(digits.images[0].shape)
# Plot pixel ranking
plt.matshow(ranking, cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
# Add annotations for pixel numbers
for i in range(ranking.shape[0]):
for j in range(ranking.shape[1]):
plt.text(j, i, str(ranking[i, j]), ha="center", va="center", color="black")
plt.colorbar()
plt.title("Ranking of pixels with RFE\n(Logistic Regression)")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 3.193 seconds)
Related examples
Label Propagation digits: Demonstrating performance