Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder.
Restricted Boltzmann Machine features for digit classification#
For greyscale image data where pixel values can be interpreted as degrees of
blackness on a white background, like handwritten digit recognition, the
Bernoulli Restricted Boltzmann machine model (BernoulliRBM) can perform effective non-linear
feature extraction.
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
Generate data#
In order to learn good latent representations from a small dataset, we artificially generate more labeled data by perturbing the training data with linear shifts of 1 pixel in each direction.
import numpy as np
from scipy.ndimage import convolve
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import minmax_scale
def nudge_dataset(X, Y):
"""
This produces a dataset 5 times bigger than the original one,
by moving the 8x8 images in X around by 1px to left, right, down, up
"""
direction_vectors = [
[[0, 1, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]],
[[0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]],
[[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1], [0, 0, 0]],
[[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0]],
]
def shift(x, w):
return convolve(x.reshape((8, 8)), mode="constant", weights=w).ravel()
X = np.concatenate(
[X] + [np.apply_along_axis(shift, 1, X, vector) for vector in direction_vectors]
)
Y = np.concatenate([Y for _ in range(5)], axis=0)
return X, Y
X, y = datasets.load_digits(return_X_y=True)
X = np.asarray(X, "float32")
X, Y = nudge_dataset(X, y)
X = minmax_scale(X, feature_range=(0, 1)) # 0-1 scaling
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
Models definition#
We build a classification pipeline with a BernoulliRBM feature extractor and
a LogisticRegression
classifier.
from sklearn import linear_model
from sklearn.neural_network import BernoulliRBM
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
logistic = linear_model.LogisticRegression(solver="newton-cg", tol=1)
rbm = BernoulliRBM(random_state=0, verbose=True)
rbm_features_classifier = Pipeline(steps=[("rbm", rbm), ("logistic", logistic)])
Training#
The hyperparameters of the entire model (learning rate, hidden layer size, regularization) were optimized by grid search, but the search is not reproduced here because of runtime constraints.
from sklearn.base import clone
# Hyper-parameters. These were set by cross-validation,
# using a GridSearchCV. Here we are not performing cross-validation to
# save time.
rbm.learning_rate = 0.06
rbm.n_iter = 10
# More components tend to give better prediction performance, but larger
# fitting time
rbm.n_components = 100
logistic.C = 6000
# Training RBM-Logistic Pipeline
rbm_features_classifier.fit(X_train, Y_train)
# Training the Logistic regression classifier directly on the pixel
raw_pixel_classifier = clone(logistic)
raw_pixel_classifier.C = 100.0
raw_pixel_classifier.fit(X_train, Y_train)
[BernoulliRBM] Iteration 1, pseudo-likelihood = -25.57, time = 0.09s
[BernoulliRBM] Iteration 2, pseudo-likelihood = -23.68, time = 0.13s
[BernoulliRBM] Iteration 3, pseudo-likelihood = -22.88, time = 0.13s
[BernoulliRBM] Iteration 4, pseudo-likelihood = -21.91, time = 0.12s
[BernoulliRBM] Iteration 5, pseudo-likelihood = -21.79, time = 0.12s
[BernoulliRBM] Iteration 6, pseudo-likelihood = -20.96, time = 0.12s
[BernoulliRBM] Iteration 7, pseudo-likelihood = -20.88, time = 0.12s
[BernoulliRBM] Iteration 8, pseudo-likelihood = -20.50, time = 0.12s
[BernoulliRBM] Iteration 9, pseudo-likelihood = -20.34, time = 0.12s
[BernoulliRBM] Iteration 10, pseudo-likelihood = -20.21, time = 0.12s
Evaluation#
from sklearn import metrics
Y_pred = rbm_features_classifier.predict(X_test)
print(
"Logistic regression using RBM features:\n%s\n"
% (metrics.classification_report(Y_test, Y_pred))
)
/home/circleci/project/sklearn/metrics/_classification.py:1833: UndefinedMetricWarning:
Precision is ill-defined and being set to 0.0 in labels with no predicted samples. Use `zero_division` parameter to control this behavior.
/home/circleci/project/sklearn/metrics/_classification.py:1833: UndefinedMetricWarning:
Precision is ill-defined and being set to 0.0 in labels with no predicted samples. Use `zero_division` parameter to control this behavior.
/home/circleci/project/sklearn/metrics/_classification.py:1833: UndefinedMetricWarning:
Precision is ill-defined and being set to 0.0 in labels with no predicted samples. Use `zero_division` parameter to control this behavior.
Logistic regression using RBM features:
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.10 1.00 0.18 174
1 0.00 0.00 0.00 184
2 0.00 0.00 0.00 166
3 0.00 0.00 0.00 194
4 0.00 0.00 0.00 186
5 0.00 0.00 0.00 181
6 0.00 0.00 0.00 207
7 0.00 0.00 0.00 154
8 0.00 0.00 0.00 182
9 0.00 0.00 0.00 169
accuracy 0.10 1797
macro avg 0.01 0.10 0.02 1797
weighted avg 0.01 0.10 0.02 1797
Y_pred = raw_pixel_classifier.predict(X_test)
print(
"Logistic regression using raw pixel features:\n%s\n"
% (metrics.classification_report(Y_test, Y_pred))
)
/home/circleci/project/sklearn/metrics/_classification.py:1833: UndefinedMetricWarning:
Precision is ill-defined and being set to 0.0 in labels with no predicted samples. Use `zero_division` parameter to control this behavior.
/home/circleci/project/sklearn/metrics/_classification.py:1833: UndefinedMetricWarning:
Precision is ill-defined and being set to 0.0 in labels with no predicted samples. Use `zero_division` parameter to control this behavior.
/home/circleci/project/sklearn/metrics/_classification.py:1833: UndefinedMetricWarning:
Precision is ill-defined and being set to 0.0 in labels with no predicted samples. Use `zero_division` parameter to control this behavior.
Logistic regression using raw pixel features:
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.10 1.00 0.18 174
1 0.00 0.00 0.00 184
2 0.00 0.00 0.00 166
3 0.00 0.00 0.00 194
4 0.00 0.00 0.00 186
5 0.00 0.00 0.00 181
6 0.00 0.00 0.00 207
7 0.00 0.00 0.00 154
8 0.00 0.00 0.00 182
9 0.00 0.00 0.00 169
accuracy 0.10 1797
macro avg 0.01 0.10 0.02 1797
weighted avg 0.01 0.10 0.02 1797
The features extracted by the BernoulliRBM help improve the classification accuracy with respect to the logistic regression on raw pixels.
Plotting#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(4.2, 4))
for i, comp in enumerate(rbm.components_):
plt.subplot(10, 10, i + 1)
plt.imshow(comp.reshape((8, 8)), cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation="nearest")
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.suptitle("100 components extracted by RBM", fontsize=16)
plt.subplots_adjust(0.08, 0.02, 0.92, 0.85, 0.08, 0.23)
plt.show()

Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.205 seconds)
Related examples
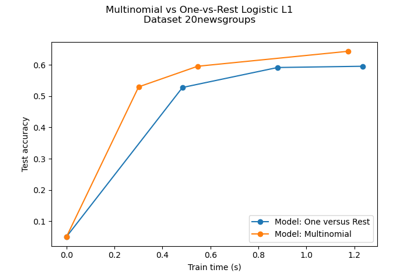
Multiclass sparse logistic regression on 20newgroups
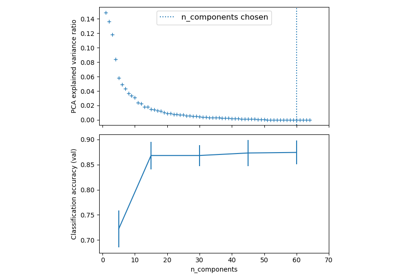
Pipelining: chaining a PCA and a logistic regression
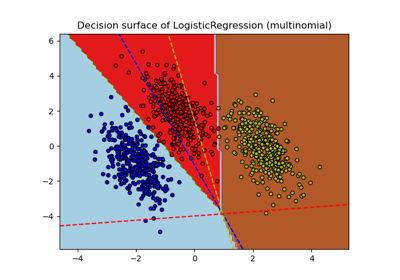
Decision Boundaries of Multinomial and One-vs-Rest Logistic Regression