HuberRegressor#
- class sklearn.linear_model.HuberRegressor(*, epsilon=1.35, max_iter=100, alpha=0.0001, warm_start=False, fit_intercept=True, tol=1e-05)[source]#
L2-regularized linear regression model that is robust to outliers.
The Huber Regressor optimizes the squared loss for the samples where
|(y - Xw - c) / sigma| < epsilonand the absolute loss for the samples where|(y - Xw - c) / sigma| > epsilon, where the model coefficientsw, the interceptcand the scalesigmaare parameters to be optimized. The parametersigmamakes sure that ifyis scaled up or down by a certain factor, one does not need to rescaleepsilonto achieve the same robustness. Note that this does not take into account the fact that the different features ofXmay be of different scales.The Huber loss function has the advantage of not being heavily influenced by the outliers while not completely ignoring their effect.
Read more in the User Guide
Added in version 0.18.
- Parameters:
- epsilonfloat, default=1.35
The parameter epsilon controls the number of samples that should be classified as outliers. The smaller the epsilon, the more robust it is to outliers. Epsilon must be in the range
[1, inf).- max_iterint, default=100
Maximum number of iterations that
scipy.optimize.minimize(method="L-BFGS-B")should run for.- alphafloat, default=0.0001
Strength of the squared L2 regularization. Note that the penalty is equal to
alpha * ||w||^2. Must be in the range[0, inf).- warm_startbool, default=False
This is useful if the stored attributes of a previously used model has to be reused. If set to False, then the coefficients will be rewritten for every call to fit. See the Glossary.
- fit_interceptbool, default=True
Whether or not to fit the intercept. This can be set to False if the data is already centered around the origin.
- tolfloat, default=1e-05
The iteration will stop when
max{|proj g_i | i = 1, ..., n}<=tolwhere pg_i is the i-th component of the projected gradient.
- Attributes:
- coef_array, shape (n_features,)
Features got by optimizing the L2-regularized Huber loss.
- intercept_float
Bias.
- scale_float
The value by which
|y - Xw - c|is scaled down.- n_features_in_int
Number of features seen during fit.
Added in version 0.24.
- feature_names_in_ndarray of shape (
n_features_in_,) Names of features seen during fit. Defined only when
Xhas feature names that are all strings.Added in version 1.0.
- n_iter_int
Number of iterations that
scipy.optimize.minimize(method="L-BFGS-B")has run for.Changed in version 0.20: In SciPy <= 1.0.0 the number of lbfgs iterations may exceed
max_iter.n_iter_will now report at mostmax_iter.- outliers_array, shape (n_samples,)
A boolean mask which is set to True where the samples are identified as outliers.
See also
RANSACRegressorRANSAC (RANdom SAmple Consensus) algorithm.
TheilSenRegressorTheil-Sen Estimator robust multivariate regression model.
SGDRegressorFitted by minimizing a regularized empirical loss with SGD.
References
[1]Peter J. Huber, Elvezio M. Ronchetti, Robust Statistics Concomitant scale estimates, p. 172
[2]Art B. Owen (2006), A robust hybrid of lasso and ridge regression.
Examples
>>> import numpy as np >>> from sklearn.linear_model import HuberRegressor, LinearRegression >>> from sklearn.datasets import make_regression >>> rng = np.random.RandomState(0) >>> X, y, coef = make_regression( ... n_samples=200, n_features=2, noise=4.0, coef=True, random_state=0) >>> X[:4] = rng.uniform(10, 20, (4, 2)) >>> y[:4] = rng.uniform(10, 20, 4) >>> huber = HuberRegressor().fit(X, y) >>> huber.score(X, y) -7.284 >>> huber.predict(X[:1,]) array([806.7200]) >>> linear = LinearRegression().fit(X, y) >>> print("True coefficients:", coef) True coefficients: [20.4923... 34.1698...] >>> print("Huber coefficients:", huber.coef_) Huber coefficients: [17.7906... 31.0106...] >>> print("Linear Regression coefficients:", linear.coef_) Linear Regression coefficients: [-1.9221... 7.0226...]
- fit(X, y, sample_weight=None)[source]#
Fit the model according to the given training data.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like, shape (n_samples, n_features)
Training vector, where
n_samplesis the number of samples andn_featuresis the number of features.- yarray-like, shape (n_samples,)
Target vector relative to X.
- sample_weightarray-like, shape (n_samples,)
Weight given to each sample.
- Returns:
- selfobject
Fitted
HuberRegressorestimator.
- get_metadata_routing()[source]#
Get metadata routing of this object.
Please check User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.
- Returns:
- routingMetadataRequest
A
MetadataRequestencapsulating routing information.
- get_params(deep=True)[source]#
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters:
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns:
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- predict(X)[source]#
Predict using the linear model.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like or sparse matrix, shape (n_samples, n_features)
Samples.
- Returns:
- Carray, shape (n_samples,)
Returns predicted values.
- score(X, y, sample_weight=None)[source]#
Return coefficient of determination on test data.
The coefficient of determination, \(R^2\), is defined as \((1 - \frac{u}{v})\), where \(u\) is the residual sum of squares
((y_true - y_pred)** 2).sum()and \(v\) is the total sum of squares((y_true - y_true.mean()) ** 2).sum(). The best possible score is 1.0 and it can be negative (because the model can be arbitrarily worse). A constant model that always predicts the expected value ofy, disregarding the input features, would get a \(R^2\) score of 0.0.- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Test samples. For some estimators this may be a precomputed kernel matrix or a list of generic objects instead with shape
(n_samples, n_samples_fitted), wheren_samples_fittedis the number of samples used in the fitting for the estimator.- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs)
True values for
X.- sample_weightarray-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None
Sample weights.
- Returns:
- scorefloat
\(R^2\) of
self.predict(X)w.r.t.y.
Notes
The \(R^2\) score used when calling
scoreon a regressor usesmultioutput='uniform_average'from version 0.23 to keep consistent with default value ofr2_score. This influences thescoremethod of all the multioutput regressors (except forMultiOutputRegressor).
- set_fit_request(*, sample_weight: bool | None | str = '$UNCHANGED$') HuberRegressor[source]#
Configure whether metadata should be requested to be passed to the
fitmethod.Note that this method is only relevant when this estimator is used as a sub-estimator within a meta-estimator and metadata routing is enabled with
enable_metadata_routing=True(seesklearn.set_config). Please check the User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.The options for each parameter are:
True: metadata is requested, and passed tofitif provided. The request is ignored if metadata is not provided.False: metadata is not requested and the meta-estimator will not pass it tofit.None: metadata is not requested, and the meta-estimator will raise an error if the user provides it.str: metadata should be passed to the meta-estimator with this given alias instead of the original name.
The default (
sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED) retains the existing request. This allows you to change the request for some parameters and not others.Added in version 1.3.
- Parameters:
- sample_weightstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
sample_weightparameter infit.
- Returns:
- selfobject
The updated object.
- set_params(**params)[source]#
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters:
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
- set_score_request(*, sample_weight: bool | None | str = '$UNCHANGED$') HuberRegressor[source]#
Configure whether metadata should be requested to be passed to the
scoremethod.Note that this method is only relevant when this estimator is used as a sub-estimator within a meta-estimator and metadata routing is enabled with
enable_metadata_routing=True(seesklearn.set_config). Please check the User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.The options for each parameter are:
True: metadata is requested, and passed toscoreif provided. The request is ignored if metadata is not provided.False: metadata is not requested and the meta-estimator will not pass it toscore.None: metadata is not requested, and the meta-estimator will raise an error if the user provides it.str: metadata should be passed to the meta-estimator with this given alias instead of the original name.
The default (
sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED) retains the existing request. This allows you to change the request for some parameters and not others.Added in version 1.3.
- Parameters:
- sample_weightstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
sample_weightparameter inscore.
- Returns:
- selfobject
The updated object.
Gallery examples#
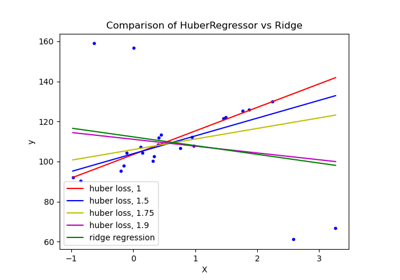
HuberRegressor vs Ridge on dataset with strong outliers
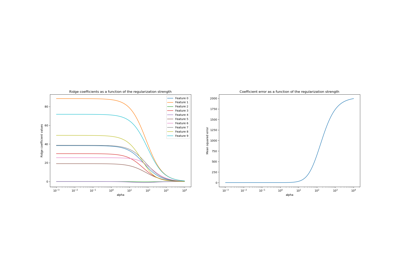
Ridge coefficients as a function of the L2 Regularization