OneHotEncoder#
- class sklearn.preprocessing.OneHotEncoder(*, categories='auto', drop=None, sparse_output=True, dtype=<class 'numpy.float64'>, handle_unknown='error', min_frequency=None, max_categories=None, feature_name_combiner='concat')[source]#
Encode categorical features as a one-hot numeric array.
The input to this transformer should be an array-like of integers or strings, denoting the values taken on by categorical (discrete) features. The features are encoded using a one-hot (aka ‘one-of-K’ or ‘dummy’) encoding scheme. This creates a binary column for each category and returns a sparse matrix or dense array (depending on the
sparse_outputparameter).By default, the encoder derives the categories based on the unique values in each feature. Alternatively, you can also specify the
categoriesmanually.This encoding is needed for feeding categorical data to many scikit-learn estimators, notably linear models and SVMs with the standard kernels.
Note: a one-hot encoding of y labels should use a LabelBinarizer instead.
Read more in the User Guide. For a comparison of different encoders, refer to: Comparing Target Encoder with Other Encoders.
- Parameters:
- categories‘auto’ or a list of array-like, default=’auto’
Categories (unique values) per feature:
‘auto’ : Determine categories automatically from the training data.
list :
categories[i]holds the categories expected in the ith column. The passed categories should not mix strings and numeric values within a single feature, and should be sorted in case of numeric values.
The used categories can be found in the
categories_attribute.Added in version 0.20.
- drop{‘first’, ‘if_binary’} or an array-like of shape (n_features,), default=None
Specifies a methodology to use to drop one of the categories per feature. This is useful in situations where perfectly collinear features cause problems, such as when feeding the resulting data into an unregularized linear regression model.
However, dropping one category breaks the symmetry of the original representation and can therefore induce a bias in downstream models, for instance for penalized linear classification or regression models.
None : retain all features (the default).
‘first’ : drop the first category in each feature. If only one category is present, the feature will be dropped entirely.
‘if_binary’ : drop the first category in each feature with two categories. Features with 1 or more than 2 categories are left intact.
array :
drop[i]is the category in featureX[:, i]that should be dropped.
When
max_categoriesormin_frequencyis configured to group infrequent categories, the dropping behavior is handled after the grouping.Added in version 0.21: The parameter
dropwas added in 0.21.Changed in version 0.23: The option
drop='if_binary'was added in 0.23.Changed in version 1.1: Support for dropping infrequent categories.
- sparse_outputbool, default=True
When
True, it returns ascipy.sparse.csr_matrix, i.e. a sparse matrix in “Compressed Sparse Row” (CSR) format.Added in version 1.2:
sparsewas renamed tosparse_output- dtypenumber type, default=np.float64
Desired dtype of output.
- handle_unknown{‘error’, ‘ignore’, ‘infrequent_if_exist’}, default=’error’
Specifies the way unknown categories are handled during
transform.‘error’ : Raise an error if an unknown category is present during transform.
‘ignore’ : When an unknown category is encountered during transform, the resulting one-hot encoded columns for this feature will be all zeros. In the inverse transform, an unknown category will be denoted as None.
‘infrequent_if_exist’ : When an unknown category is encountered during transform, the resulting one-hot encoded columns for this feature will map to the infrequent category if it exists. The infrequent category will be mapped to the last position in the encoding. During inverse transform, an unknown category will be mapped to the category denoted
'infrequent'if it exists. If the'infrequent'category does not exist, thentransformandinverse_transformwill handle an unknown category as withhandle_unknown='ignore'. Infrequent categories exist based onmin_frequencyandmax_categories. Read more in the User Guide.
Changed in version 1.1:
'infrequent_if_exist'was added to automatically handle unknown categories and infrequent categories.- min_frequencyint or float, default=None
Specifies the minimum frequency below which a category will be considered infrequent.
If
int, categories with a smaller cardinality will be considered infrequent.If
float, categories with a smaller cardinality thanmin_frequency * n_sampleswill be considered infrequent.
Added in version 1.1: Read more in the User Guide.
- max_categoriesint, default=None
Specifies an upper limit to the number of output features for each input feature when considering infrequent categories. If there are infrequent categories,
max_categoriesincludes the category representing the infrequent categories along with the frequent categories. IfNone, there is no limit to the number of output features.Added in version 1.1: Read more in the User Guide.
- feature_name_combiner“concat” or callable, default=”concat”
Callable with signature
def callable(input_feature, category)that returns a string. This is used to create feature names to be returned byget_feature_names_out."concat"concatenates encoded feature name and category withfeature + "_" + str(category).E.g. feature X with values 1, 6, 7 create feature namesX_1, X_6, X_7.Added in version 1.3.
- Attributes:
- categories_list of arrays
The categories of each feature determined during fitting (in order of the features in X and corresponding with the output of
transform). This includes the category specified indrop(if any).- drop_idx_array of shape (n_features,)
drop_idx_[i]is the index incategories_[i]of the category to be dropped for each feature.drop_idx_[i] = Noneif no category is to be dropped from the feature with indexi, e.g. whendrop='if_binary'and the feature isn’t binary.drop_idx_ = Noneif all the transformed features will be retained.
If infrequent categories are enabled by setting
min_frequencyormax_categoriesto a non-default value anddrop_idx[i]corresponds to a infrequent category, then the entire infrequent category is dropped.Changed in version 0.23: Added the possibility to contain
Nonevalues.infrequent_categories_list of ndarrayInfrequent categories for each feature.
- n_features_in_int
Number of features seen during fit.
Added in version 1.0.
- feature_names_in_ndarray of shape (
n_features_in_,) Names of features seen during fit. Defined only when
Xhas feature names that are all strings.Added in version 1.0.
- feature_name_combinercallable or None
Callable with signature
def callable(input_feature, category)that returns a string. This is used to create feature names to be returned byget_feature_names_out.Added in version 1.3.
See also
OrdinalEncoderPerforms an ordinal (integer) encoding of the categorical features.
TargetEncoderEncodes categorical features using the target.
sklearn.feature_extraction.DictVectorizerPerforms a one-hot encoding of dictionary items (also handles string-valued features).
sklearn.feature_extraction.FeatureHasherPerforms an approximate one-hot encoding of dictionary items or strings.
LabelBinarizerBinarizes labels in a one-vs-all fashion.
MultiLabelBinarizerTransforms between iterable of iterables and a multilabel format, e.g. a (samples x classes) binary matrix indicating the presence of a class label.
Examples
Given a dataset with two features, we let the encoder find the unique values per feature and transform the data to a binary one-hot encoding.
>>> from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
One can discard categories not seen during
fit:>>> enc = OneHotEncoder(handle_unknown='ignore') >>> X = [['Male', 1], ['Female', 3], ['Female', 2]] >>> enc.fit(X) OneHotEncoder(handle_unknown='ignore') >>> enc.categories_ [array(['Female', 'Male'], dtype=object), array([1, 2, 3], dtype=object)] >>> enc.transform([['Female', 1], ['Male', 4]]).toarray() array([[1., 0., 1., 0., 0.], [0., 1., 0., 0., 0.]]) >>> enc.inverse_transform([[0, 1, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1, 0]]) array([['Male', 1], [None, 2]], dtype=object) >>> enc.get_feature_names_out(['gender', 'group']) array(['gender_Female', 'gender_Male', 'group_1', 'group_2', 'group_3'], ...)
One can always drop the first column for each feature:
>>> drop_enc = OneHotEncoder(drop='first').fit(X) >>> drop_enc.categories_ [array(['Female', 'Male'], dtype=object), array([1, 2, 3], dtype=object)] >>> drop_enc.transform([['Female', 1], ['Male', 2]]).toarray() array([[0., 0., 0.], [1., 1., 0.]])
Or drop a column for feature only having 2 categories:
>>> drop_binary_enc = OneHotEncoder(drop='if_binary').fit(X) >>> drop_binary_enc.transform([['Female', 1], ['Male', 2]]).toarray() array([[0., 1., 0., 0.], [1., 0., 1., 0.]])
One can change the way feature names are created.
>>> def custom_combiner(feature, category): ... return str(feature) + "_" + type(category).__name__ + "_" + str(category) >>> custom_fnames_enc = OneHotEncoder(feature_name_combiner=custom_combiner).fit(X) >>> custom_fnames_enc.get_feature_names_out() array(['x0_str_Female', 'x0_str_Male', 'x1_int_1', 'x1_int_2', 'x1_int_3'], dtype=object)
Infrequent categories are enabled by setting
max_categoriesormin_frequency.>>> import numpy as np >>> X = np.array([["a"] * 5 + ["b"] * 20 + ["c"] * 10 + ["d"] * 3], dtype=object).T >>> ohe = OneHotEncoder(max_categories=3, sparse_output=False).fit(X) >>> ohe.infrequent_categories_ [array(['a', 'd'], dtype=object)] >>> ohe.transform([["a"], ["b"]]) array([[0., 0., 1.], [1., 0., 0.]])
- fit(X, y=None)[source]#
Fit OneHotEncoder to X.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The data to determine the categories of each feature.
- yNone
Ignored. This parameter exists only for compatibility with
Pipeline.
- Returns:
- self
Fitted encoder.
- fit_transform(X, y=None, **fit_params)[source]#
Fit to data, then transform it.
Fits transformer to
Xandywith optional parametersfit_paramsand returns a transformed version ofX.- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Input samples.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs), default=None
Target values (None for unsupervised transformations).
- **fit_paramsdict
Additional fit parameters.
- Returns:
- X_newndarray array of shape (n_samples, n_features_new)
Transformed array.
- get_feature_names_out(input_features=None)[source]#
Get output feature names for transformation.
- Parameters:
- input_featuresarray-like of str or None, default=None
Input features.
If
input_featuresisNone, thenfeature_names_in_is used as feature names in. Iffeature_names_in_is not defined, then the following input feature names are generated:["x0", "x1", ..., "x(n_features_in_ - 1)"].If
input_featuresis an array-like, theninput_featuresmust matchfeature_names_in_iffeature_names_in_is defined.
- Returns:
- feature_names_outndarray of str objects
Transformed feature names.
- get_metadata_routing()[source]#
Get metadata routing of this object.
Please check User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.
- Returns:
- routingMetadataRequest
A
MetadataRequestencapsulating routing information.
- get_params(deep=True)[source]#
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters:
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns:
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- property infrequent_categories_#
Infrequent categories for each feature.
- inverse_transform(X)[source]#
Convert the data back to the original representation.
When unknown categories are encountered (all zeros in the one-hot encoding),
Noneis used to represent this category. If the feature with the unknown category has a dropped category, the dropped category will be its inverse.For a given input feature, if there is an infrequent category, ‘infrequent_sklearn’ will be used to represent the infrequent category.
- Parameters:
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_encoded_features)
The transformed data.
- Returns:
- X_trndarray of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Inverse transformed array.
- set_output(*, transform=None)[source]#
Set output container.
See Introducing the set_output API for an example on how to use the API.
- Parameters:
- transform{“default”, “pandas”, “polars”}, default=None
Configure output of
transformandfit_transform."default": Default output format of a transformer"pandas": DataFrame output"polars": Polars outputNone: Transform configuration is unchanged
Added in version 1.4:
"polars"option was added.
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
- set_params(**params)[source]#
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters:
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
- transform(X)[source]#
Transform X using one-hot encoding.
If
sparse_output=True(default), it returns an instance ofscipy.sparse._csr.csr_matrix(CSR format).If there are infrequent categories for a feature, set by specifying
max_categoriesormin_frequency, the infrequent categories are grouped into a single category.- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The data to encode.
- Returns:
- X_out{ndarray, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_encoded_features)
Transformed input. If
sparse_output=True, a sparse matrix will be returned.
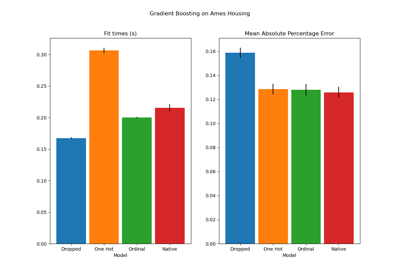
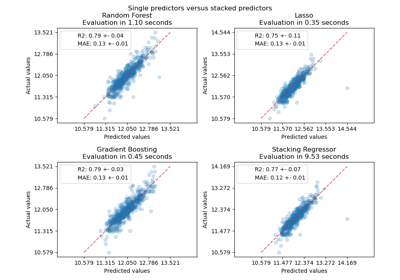
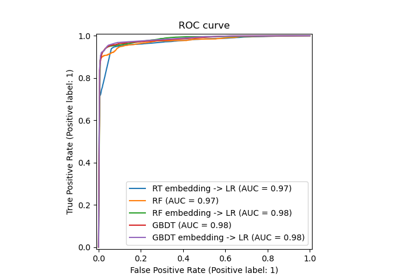
Gallery examples#
Common pitfalls in the interpretation of coefficients of linear models
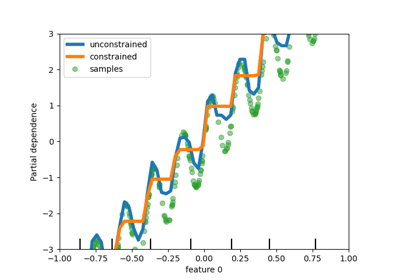
Partial Dependence and Individual Conditional Expectation Plots