EmpiricalCovariance#
- class sklearn.covariance.EmpiricalCovariance(*, store_precision=True, assume_centered=False)[source]#
Maximum likelihood covariance estimator.
Read more in the User Guide.
- Parameters:
- store_precisionbool, default=True
Specifies if the estimated precision is stored.
- assume_centeredbool, default=False
If True, data are not centered before computation. Useful when working with data whose mean is almost, but not exactly zero. If False (default), data are centered before computation.
- Attributes:
- location_ndarray of shape (n_features,)
Estimated location, i.e. the estimated mean.
- covariance_ndarray of shape (n_features, n_features)
Estimated covariance matrix
- precision_ndarray of shape (n_features, n_features)
Estimated pseudo-inverse matrix. (stored only if store_precision is True)
- n_features_in_int
Number of features seen during fit.
Added in version 0.24.
- feature_names_in_ndarray of shape (
n_features_in_,) Names of features seen during fit. Defined only when
Xhas feature names that are all strings.Added in version 1.0.
See also
EllipticEnvelopeAn object for detecting outliers in a Gaussian distributed dataset.
GraphicalLassoSparse inverse covariance estimation with an l1-penalized estimator.
LedoitWolfLedoitWolf Estimator.
MinCovDetMinimum Covariance Determinant (robust estimator of covariance).
OASOracle Approximating Shrinkage Estimator.
ShrunkCovarianceCovariance estimator with shrinkage.
Examples
>>> import numpy as np >>> from sklearn.covariance import EmpiricalCovariance >>> from sklearn.datasets import make_gaussian_quantiles >>> real_cov = np.array([[.8, .3], ... [.3, .4]]) >>> rng = np.random.RandomState(0) >>> X = rng.multivariate_normal(mean=[0, 0], ... cov=real_cov, ... size=500) >>> cov = EmpiricalCovariance().fit(X) >>> cov.covariance_ array([[0.7569..., 0.2818...], [0.2818..., 0.3928...]]) >>> cov.location_ array([0.0622..., 0.0193...])
- error_norm(comp_cov, norm='frobenius', scaling=True, squared=True)[source]#
Compute the Mean Squared Error between two covariance estimators.
- Parameters:
- comp_covarray-like of shape (n_features, n_features)
The covariance to compare with.
- norm{“frobenius”, “spectral”}, default=”frobenius”
The type of norm used to compute the error. Available error types: - ‘frobenius’ (default): sqrt(tr(A^t.A)) - ‘spectral’: sqrt(max(eigenvalues(A^t.A)) where A is the error
(comp_cov - self.covariance_).- scalingbool, default=True
If True (default), the squared error norm is divided by n_features. If False, the squared error norm is not rescaled.
- squaredbool, default=True
Whether to compute the squared error norm or the error norm. If True (default), the squared error norm is returned. If False, the error norm is returned.
- Returns:
- resultfloat
The Mean Squared Error (in the sense of the Frobenius norm) between
selfandcomp_covcovariance estimators.
- fit(X, y=None)[source]#
Fit the maximum likelihood covariance estimator to X.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Training data, where
n_samplesis the number of samples andn_featuresis the number of features.- yIgnored
Not used, present for API consistency by convention.
- Returns:
- selfobject
Returns the instance itself.
- get_metadata_routing()[source]#
Get metadata routing of this object.
Please check User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.
- Returns:
- routingMetadataRequest
A
MetadataRequestencapsulating routing information.
- get_params(deep=True)[source]#
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters:
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns:
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- get_precision()[source]#
Getter for the precision matrix.
- Returns:
- precision_array-like of shape (n_features, n_features)
The precision matrix associated to the current covariance object.
- mahalanobis(X)[source]#
Compute the squared Mahalanobis distances of given observations.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The observations, the Mahalanobis distances of the which we compute. Observations are assumed to be drawn from the same distribution than the data used in fit.
- Returns:
- distndarray of shape (n_samples,)
Squared Mahalanobis distances of the observations.
- score(X_test, y=None)[source]#
Compute the log-likelihood of
X_testunder the estimated Gaussian model.The Gaussian model is defined by its mean and covariance matrix which are represented respectively by
self.location_andself.covariance_.- Parameters:
- X_testarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Test data of which we compute the likelihood, where
n_samplesis the number of samples andn_featuresis the number of features.X_testis assumed to be drawn from the same distribution than the data used in fit (including centering).- yIgnored
Not used, present for API consistency by convention.
- Returns:
- resfloat
The log-likelihood of
X_testwithself.location_andself.covariance_as estimators of the Gaussian model mean and covariance matrix respectively.
- set_params(**params)[source]#
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters:
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
Gallery examples#
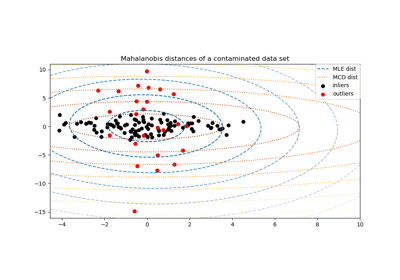
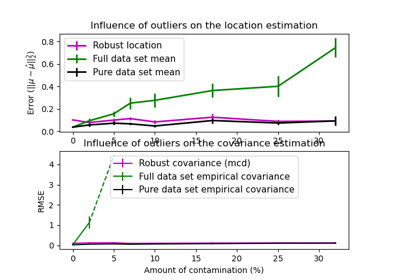
Robust covariance estimation and Mahalanobis distances relevance
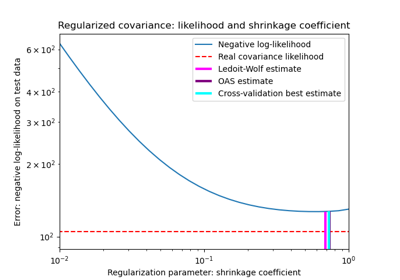
Shrinkage covariance estimation: LedoitWolf vs OAS and max-likelihood