sklearn.pipeline.Pipeline¶
- class sklearn.pipeline.Pipeline(steps, *, memory=None, verbose=False)[source]¶
Pipeline of transforms with a final estimator.
Sequentially apply a list of transforms and a final estimator. Intermediate steps of the pipeline must be ‘transforms’, that is, they must implement
fitandtransformmethods. The final estimator only needs to implementfit. The transformers in the pipeline can be cached usingmemoryargument.The purpose of the pipeline is to assemble several steps that can be cross-validated together while setting different parameters. For this, it enables setting parameters of the various steps using their names and the parameter name separated by a
'__', as in the example below. A step’s estimator may be replaced entirely by setting the parameter with its name to another estimator, or a transformer removed by setting it to'passthrough'orNone.For an example use case of
Pipelinecombined withGridSearchCV, refer to Selecting dimensionality reduction with Pipeline and GridSearchCV. The example Pipelining: chaining a PCA and a logistic regression shows how to grid search on a pipeline using'__'as a separator in the parameter names.Read more in the User Guide.
New in version 0.5.
- Parameters:
- stepslist of tuple
List of (name, transform) tuples (implementing
fit/transform) that are chained in sequential order. The last transform must be an estimator.- memorystr or object with the joblib.Memory interface, default=None
Used to cache the fitted transformers of the pipeline. The last step will never be cached, even if it is a transformer. By default, no caching is performed. If a string is given, it is the path to the caching directory. Enabling caching triggers a clone of the transformers before fitting. Therefore, the transformer instance given to the pipeline cannot be inspected directly. Use the attribute
named_stepsorstepsto inspect estimators within the pipeline. Caching the transformers is advantageous when fitting is time consuming.- verbosebool, default=False
If True, the time elapsed while fitting each step will be printed as it is completed.
- Attributes:
named_stepsBunchAccess the steps by name.
classes_ndarray of shape (n_classes,)The classes labels.
n_features_in_intNumber of features seen during first step
fitmethod.feature_names_in_ndarray of shape (n_features_in_,)Names of features seen during first step
fitmethod.
See also
make_pipelineConvenience function for simplified pipeline construction.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.svm import SVC >>> from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler >>> from sklearn.datasets import make_classification >>> from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split >>> from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline >>> X, y = make_classification(random_state=0) >>> X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, ... random_state=0) >>> pipe = Pipeline([('scaler', StandardScaler()), ('svc', SVC())]) >>> # The pipeline can be used as any other estimator >>> # and avoids leaking the test set into the train set >>> pipe.fit(X_train, y_train).score(X_test, y_test) 0.88 >>> # An estimator's parameter can be set using '__' syntax >>> pipe.set_params(svc__C=10).fit(X_train, y_train).score(X_test, y_test) 0.76
Methods
Transform the data, and apply
decision_functionwith the final estimator.fit(X[, y])Fit the model.
fit_predict(X[, y])Transform the data, and apply
fit_predictwith the final estimator.fit_transform(X[, y])Fit the model and transform with the final estimator.
get_feature_names_out([input_features])Get output feature names for transformation.
Get metadata routing of this object.
get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator.
Apply
inverse_transformfor each step in a reverse order.predict(X, **predict_params)Transform the data, and apply
predictwith the final estimator.predict_log_proba(X, **predict_log_proba_params)Transform the data, and apply
predict_log_probawith the final estimator.predict_proba(X, **predict_proba_params)Transform the data, and apply
predict_probawith the final estimator.score(X[, y, sample_weight])Transform the data, and apply
scorewith the final estimator.Transform the data, and apply
score_sampleswith the final estimator.set_output(*[, transform])Set the output container when
"transform"and"fit_transform"are called.set_params(**kwargs)Set the parameters of this estimator.
set_score_request(*[, sample_weight])Request metadata passed to the
scoremethod.transform(X)Transform the data, and apply
transformwith the final estimator.- property classes_¶
The classes labels. Only exist if the last step is a classifier.
- decision_function(X)[source]¶
Transform the data, and apply
decision_functionwith the final estimator.Call
transformof each transformer in the pipeline. The transformed data are finally passed to the final estimator that callsdecision_functionmethod. Only valid if the final estimator implementsdecision_function.- Parameters:
- Xiterable
Data to predict on. Must fulfill input requirements of first step of the pipeline.
- Returns:
- y_scorendarray of shape (n_samples, n_classes)
Result of calling
decision_functionon the final estimator.
- property feature_names_in_¶
Names of features seen during first step
fitmethod.
- fit(X, y=None, **fit_params)[source]¶
Fit the model.
Fit all the transformers one after the other and transform the data. Finally, fit the transformed data using the final estimator.
- Parameters:
- Xiterable
Training data. Must fulfill input requirements of first step of the pipeline.
- yiterable, default=None
Training targets. Must fulfill label requirements for all steps of the pipeline.
- **fit_paramsdict of string -> object
Parameters passed to the
fitmethod of each step, where each parameter name is prefixed such that parameterpfor stepshas keys__p.
- Returns:
- selfobject
Pipeline with fitted steps.
- fit_predict(X, y=None, **fit_params)[source]¶
Transform the data, and apply
fit_predictwith the final estimator.Call
fit_transformof each transformer in the pipeline. The transformed data are finally passed to the final estimator that callsfit_predictmethod. Only valid if the final estimator implementsfit_predict.- Parameters:
- Xiterable
Training data. Must fulfill input requirements of first step of the pipeline.
- yiterable, default=None
Training targets. Must fulfill label requirements for all steps of the pipeline.
- **fit_paramsdict of string -> object
Parameters passed to the
fitmethod of each step, where each parameter name is prefixed such that parameterpfor stepshas keys__p.
- Returns:
- y_predndarray
Result of calling
fit_predicton the final estimator.
- fit_transform(X, y=None, **fit_params)[source]¶
Fit the model and transform with the final estimator.
Fits all the transformers one after the other and transform the data. Then uses
fit_transformon transformed data with the final estimator.- Parameters:
- Xiterable
Training data. Must fulfill input requirements of first step of the pipeline.
- yiterable, default=None
Training targets. Must fulfill label requirements for all steps of the pipeline.
- **fit_paramsdict of string -> object
Parameters passed to the
fitmethod of each step, where each parameter name is prefixed such that parameterpfor stepshas keys__p.
- Returns:
- Xtndarray of shape (n_samples, n_transformed_features)
Transformed samples.
- get_feature_names_out(input_features=None)[source]¶
Get output feature names for transformation.
Transform input features using the pipeline.
- Parameters:
- input_featuresarray-like of str or None, default=None
Input features.
- Returns:
- feature_names_outndarray of str objects
Transformed feature names.
- get_metadata_routing()[source]¶
Get metadata routing of this object.
Please check User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.
- Returns:
- routingMetadataRequest
A
MetadataRequestencapsulating routing information.
- get_params(deep=True)[source]¶
Get parameters for this estimator.
Returns the parameters given in the constructor as well as the estimators contained within the
stepsof thePipeline.- Parameters:
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns:
- paramsmapping of string to any
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- inverse_transform(Xt)[source]¶
Apply
inverse_transformfor each step in a reverse order.All estimators in the pipeline must support
inverse_transform.- Parameters:
- Xtarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_transformed_features)
Data samples, where
n_samplesis the number of samples andn_featuresis the number of features. Must fulfill input requirements of last step of pipeline’sinverse_transformmethod.
- Returns:
- Xtndarray of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Inverse transformed data, that is, data in the original feature space.
- property n_features_in_¶
Number of features seen during first step
fitmethod.
- property named_steps¶
Access the steps by name.
Read-only attribute to access any step by given name. Keys are steps names and values are the steps objects.
- predict(X, **predict_params)[source]¶
Transform the data, and apply
predictwith the final estimator.Call
transformof each transformer in the pipeline. The transformed data are finally passed to the final estimator that callspredictmethod. Only valid if the final estimator implementspredict.- Parameters:
- Xiterable
Data to predict on. Must fulfill input requirements of first step of the pipeline.
- **predict_paramsdict of string -> object
Parameters to the
predictcalled at the end of all transformations in the pipeline. Note that while this may be used to return uncertainties from some models with return_std or return_cov, uncertainties that are generated by the transformations in the pipeline are not propagated to the final estimator.New in version 0.20.
- Returns:
- y_predndarray
Result of calling
predicton the final estimator.
- predict_log_proba(X, **predict_log_proba_params)[source]¶
Transform the data, and apply
predict_log_probawith the final estimator.Call
transformof each transformer in the pipeline. The transformed data are finally passed to the final estimator that callspredict_log_probamethod. Only valid if the final estimator implementspredict_log_proba.- Parameters:
- Xiterable
Data to predict on. Must fulfill input requirements of first step of the pipeline.
- **predict_log_proba_paramsdict of string -> object
Parameters to the
predict_log_probacalled at the end of all transformations in the pipeline.
- Returns:
- y_log_probandarray of shape (n_samples, n_classes)
Result of calling
predict_log_probaon the final estimator.
- predict_proba(X, **predict_proba_params)[source]¶
Transform the data, and apply
predict_probawith the final estimator.Call
transformof each transformer in the pipeline. The transformed data are finally passed to the final estimator that callspredict_probamethod. Only valid if the final estimator implementspredict_proba.- Parameters:
- Xiterable
Data to predict on. Must fulfill input requirements of first step of the pipeline.
- **predict_proba_paramsdict of string -> object
Parameters to the
predict_probacalled at the end of all transformations in the pipeline.
- Returns:
- y_probandarray of shape (n_samples, n_classes)
Result of calling
predict_probaon the final estimator.
- score(X, y=None, sample_weight=None)[source]¶
Transform the data, and apply
scorewith the final estimator.Call
transformof each transformer in the pipeline. The transformed data are finally passed to the final estimator that callsscoremethod. Only valid if the final estimator implementsscore.- Parameters:
- Xiterable
Data to predict on. Must fulfill input requirements of first step of the pipeline.
- yiterable, default=None
Targets used for scoring. Must fulfill label requirements for all steps of the pipeline.
- sample_weightarray-like, default=None
If not None, this argument is passed as
sample_weightkeyword argument to thescoremethod of the final estimator.
- Returns:
- scorefloat
Result of calling
scoreon the final estimator.
- score_samples(X)[source]¶
Transform the data, and apply
score_sampleswith the final estimator.Call
transformof each transformer in the pipeline. The transformed data are finally passed to the final estimator that callsscore_samplesmethod. Only valid if the final estimator implementsscore_samples.- Parameters:
- Xiterable
Data to predict on. Must fulfill input requirements of first step of the pipeline.
- Returns:
- y_scorendarray of shape (n_samples,)
Result of calling
score_sampleson the final estimator.
- set_output(*, transform=None)[source]¶
Set the output container when
"transform"and"fit_transform"are called.Calling
set_outputwill set the output of all estimators insteps.- Parameters:
- transform{“default”, “pandas”}, default=None
Configure output of
transformandfit_transform."default": Default output format of a transformer"pandas": DataFrame outputNone: Transform configuration is unchanged
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
- set_params(**kwargs)[source]¶
Set the parameters of this estimator.
Valid parameter keys can be listed with
get_params(). Note that you can directly set the parameters of the estimators contained insteps.- Parameters:
- **kwargsdict
Parameters of this estimator or parameters of estimators contained in
steps. Parameters of the steps may be set using its name and the parameter name separated by a ‘__’.
- Returns:
- selfobject
Pipeline class instance.
- set_score_request(*, sample_weight: Union[bool, None, str] = '$UNCHANGED$') Pipeline[source]¶
Request metadata passed to the
scoremethod.Note that this method is only relevant if
enable_metadata_routing=True(seesklearn.set_config). Please see User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.The options for each parameter are:
True: metadata is requested, and passed toscoreif provided. The request is ignored if metadata is not provided.False: metadata is not requested and the meta-estimator will not pass it toscore.None: metadata is not requested, and the meta-estimator will raise an error if the user provides it.str: metadata should be passed to the meta-estimator with this given alias instead of the original name.
The default (
sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED) retains the existing request. This allows you to change the request for some parameters and not others.New in version 1.3.
Note
This method is only relevant if this estimator is used as a sub-estimator of a meta-estimator, e.g. used inside a
Pipeline. Otherwise it has no effect.- Parameters:
- sample_weightstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
sample_weightparameter inscore.
- Returns:
- selfobject
The updated object.
- transform(X)[source]¶
Transform the data, and apply
transformwith the final estimator.Call
transformof each transformer in the pipeline. The transformed data are finally passed to the final estimator that callstransformmethod. Only valid if the final estimator implementstransform.This also works where final estimator is
Nonein which case all prior transformations are applied.- Parameters:
- Xiterable
Data to transform. Must fulfill input requirements of first step of the pipeline.
- Returns:
- Xtndarray of shape (n_samples, n_transformed_features)
Transformed data.
Examples using sklearn.pipeline.Pipeline¶
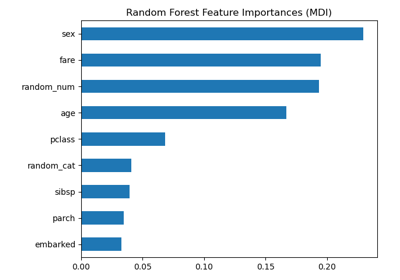
Permutation Importance vs Random Forest Feature Importance (MDI)
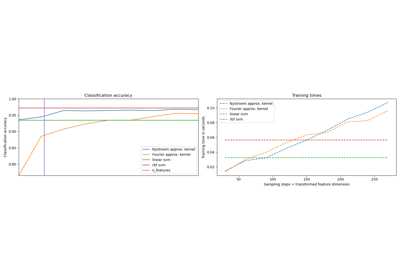
Explicit feature map approximation for RBF kernels
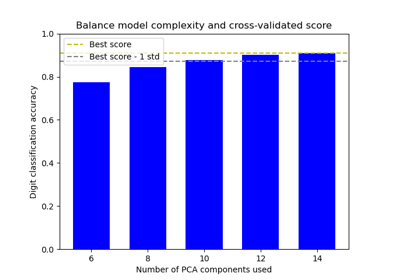
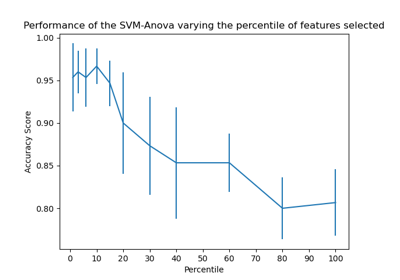
Balance model complexity and cross-validated score
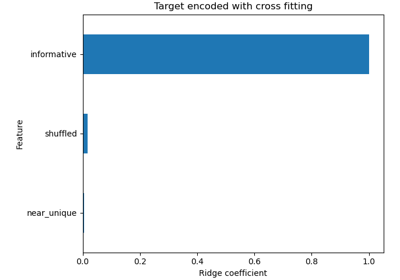
Sample pipeline for text feature extraction and evaluation
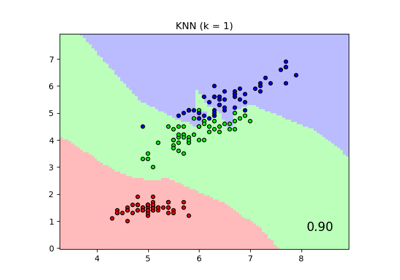
Comparing Nearest Neighbors with and without Neighborhood Components Analysis

Restricted Boltzmann Machine features for digit classification
Column Transformer with Heterogeneous Data Sources
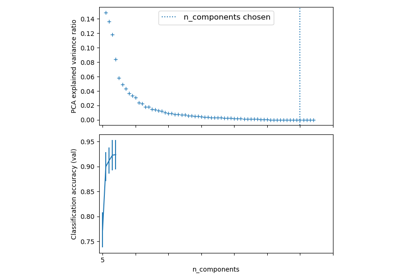
Pipelining: chaining a PCA and a logistic regression
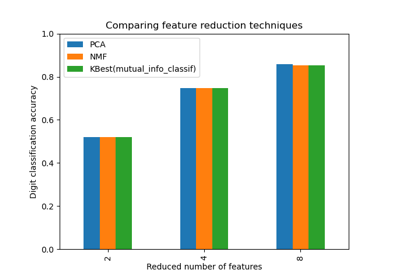
Selecting dimensionality reduction with Pipeline and GridSearchCV