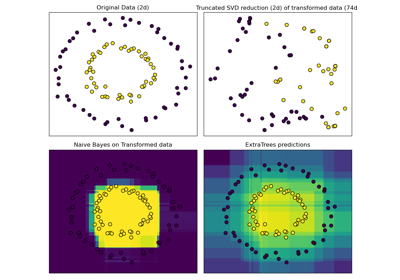
sklearn.decomposition.TruncatedSVD¶
-
class
sklearn.decomposition.TruncatedSVD(n_components=2, *, algorithm='randomized', n_iter=5, random_state=None, tol=0.0)[source]¶ Dimensionality reduction using truncated SVD (aka LSA).
This transformer performs linear dimensionality reduction by means of truncated singular value decomposition (SVD). Contrary to PCA, this estimator does not center the data before computing the singular value decomposition. This means it can work with sparse matrices efficiently.
In particular, truncated SVD works on term count/tf-idf matrices as returned by the vectorizers in
sklearn.feature_extraction.text. In that context, it is known as latent semantic analysis (LSA).This estimator supports two algorithms: a fast randomized SVD solver, and a “naive” algorithm that uses ARPACK as an eigensolver on
X * X.TorX.T * X, whichever is more efficient.Read more in the User Guide.
- Parameters
- n_componentsint, default=2
Desired dimensionality of output data. Must be strictly less than the number of features. The default value is useful for visualisation. For LSA, a value of 100 is recommended.
- algorithm{‘arpack’, ‘randomized’}, default=’randomized’
SVD solver to use. Either “arpack” for the ARPACK wrapper in SciPy (scipy.sparse.linalg.svds), or “randomized” for the randomized algorithm due to Halko (2009).
- n_iterint, default=5
Number of iterations for randomized SVD solver. Not used by ARPACK. The default is larger than the default in
randomized_svdto handle sparse matrices that may have large slowly decaying spectrum.- random_stateint, RandomState instance or None, default=None
Used during randomized svd. Pass an int for reproducible results across multiple function calls. See Glossary.
- tolfloat, default=0.
Tolerance for ARPACK. 0 means machine precision. Ignored by randomized SVD solver.
- Attributes
- components_ndarray of shape (n_components, n_features)
- explained_variance_ndarray of shape (n_components,)
The variance of the training samples transformed by a projection to each component.
- explained_variance_ratio_ndarray of shape (n_components,)
Percentage of variance explained by each of the selected components.
- singular_values_ndarray od shape (n_components,)
The singular values corresponding to each of the selected components. The singular values are equal to the 2-norms of the
n_componentsvariables in the lower-dimensional space.
See also
Notes
SVD suffers from a problem called “sign indeterminacy”, which means the sign of the
components_and the output from transform depend on the algorithm and random state. To work around this, fit instances of this class to data once, then keep the instance around to do transformations.References
Finding structure with randomness: Stochastic algorithms for constructing approximate matrix decompositions Halko, et al., 2009 (arXiv:909) https://arxiv.org/pdf/0909.4061.pdf
Examples
>>> from sklearn.decomposition import TruncatedSVD >>> from scipy.sparse import random as sparse_random >>> X = sparse_random(100, 100, density=0.01, format='csr', ... random_state=42) >>> svd = TruncatedSVD(n_components=5, n_iter=7, random_state=42) >>> svd.fit(X) TruncatedSVD(n_components=5, n_iter=7, random_state=42) >>> print(svd.explained_variance_ratio_) [0.0646... 0.0633... 0.0639... 0.0535... 0.0406...] >>> print(svd.explained_variance_ratio_.sum()) 0.286... >>> print(svd.singular_values_) [1.553... 1.512... 1.510... 1.370... 1.199...]
Methods
fit(X[, y])Fit model on training data X.
fit_transform(X[, y])Fit model to X and perform dimensionality reduction on X.
get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator.
Transform X back to its original space.
set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator.
transform(X)Perform dimensionality reduction on X.
-
fit(X, y=None)[source]¶ Fit model on training data X.
- Parameters
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Training data.
- yIgnored
- Returns
- selfobject
Returns the transformer object.
-
fit_transform(X, y=None)[source]¶ Fit model to X and perform dimensionality reduction on X.
- Parameters
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Training data.
- yIgnored
- Returns
- X_newndarray of shape (n_samples, n_components)
Reduced version of X. This will always be a dense array.
-
get_params(deep=True)[source]¶ Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
-
inverse_transform(X)[source]¶ Transform X back to its original space.
Returns an array X_original whose transform would be X.
- Parameters
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_components)
New data.
- Returns
- X_originalndarray of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Note that this is always a dense array.
-
set_params(**params)[source]¶ Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.