sklearn.metrics.plot_roc_curve¶
-
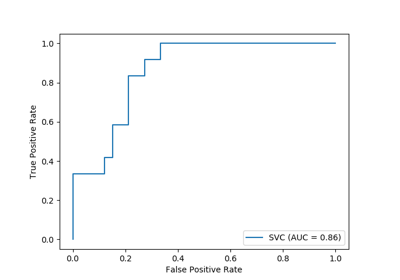
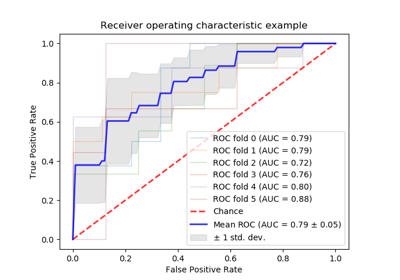
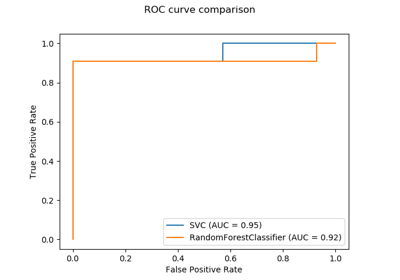
sklearn.metrics.plot_roc_curve(estimator, X, y, sample_weight=None, drop_intermediate=True, response_method='auto', name=None, ax=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Plot Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
Extra keyword arguments will be passed to matplotlib’s
plot.Read more in the User Guide.
- Parameters
- estimatorestimator instance
Trained classifier.
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Input values.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,)
Target values.
- sample_weightarray-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None
Sample weights.
- drop_intermediateboolean, default=True
Whether to drop some suboptimal thresholds which would not appear on a plotted ROC curve. This is useful in order to create lighter ROC curves.
- response_method{‘predict_proba’, ‘decision_function’, ‘auto’} default=’auto’
Specifies whether to use predict_proba or decision_function as the target response. If set to ‘auto’, predict_proba is tried first and if it does not exist decision_function is tried next.
- namestr, default=None
Name of ROC Curve for labeling. If
None, use the name of the estimator.- axmatplotlib axes, default=None
Axes object to plot on. If
None, a new figure and axes is created.
- Returns
- display
RocCurveDisplay Object that stores computed values.
- display
Examples
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # doctest: +SKIP >>> from sklearn import datasets, metrics, model_selection, svm >>> X, y = datasets.make_classification(random_state=0) >>> X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = model_selection.train_test_split( X, y, random_state=0) >>> clf = svm.SVC(random_state=0) >>> clf.fit(X_train, y_train) SVC(random_state=0) >>> metrics.plot_roc_curve(clf, X_test, y_test) # doctest: +SKIP >>> plt.show() # doctest: +SKIP