sklearn.datasets.make_circles¶
- sklearn.datasets.make_circles(n_samples=100, *, shuffle=True, noise=None, random_state=None, factor=0.8)[source]¶
Make a large circle containing a smaller circle in 2d.
A simple toy dataset to visualize clustering and classification algorithms.
Read more in the User Guide.
- Parameters:
- n_samplesint or tuple of shape (2,), dtype=int, default=100
If int, it is the total number of points generated. For odd numbers, the inner circle will have one point more than the outer circle. If two-element tuple, number of points in outer circle and inner circle.
Changed in version 0.23: Added two-element tuple.
- shufflebool, default=True
Whether to shuffle the samples.
- noisefloat, default=None
Standard deviation of Gaussian noise added to the data.
- random_stateint, RandomState instance or None, default=None
Determines random number generation for dataset shuffling and noise. Pass an int for reproducible output across multiple function calls. See Glossary.
- factorfloat, default=.8
Scale factor between inner and outer circle in the range
[0, 1).
- Returns:
- Xndarray of shape (n_samples, 2)
The generated samples.
- yndarray of shape (n_samples,)
The integer labels (0 or 1) for class membership of each sample.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.datasets import make_circles >>> X, y = make_circles(random_state=42) >>> X.shape (100, 2) >>> y.shape (100,) >>> list(y[:5]) [1, 1, 1, 0, 0]
Examples using sklearn.datasets.make_circles¶
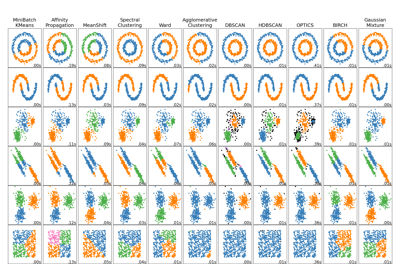
Comparing different clustering algorithms on toy datasets
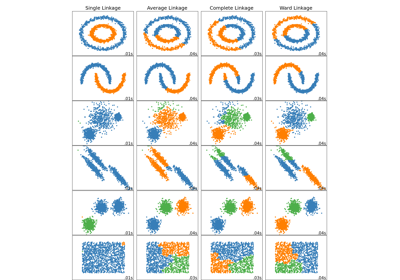
Comparing different hierarchical linkage methods on toy datasets
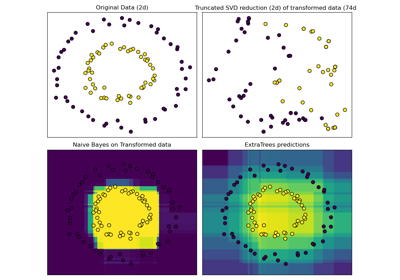
Hashing feature transformation using Totally Random Trees
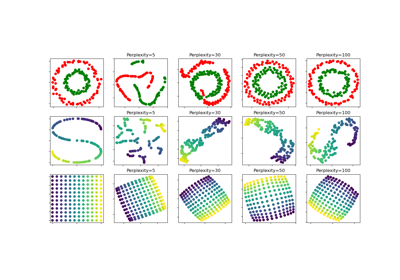
t-SNE: The effect of various perplexity values on the shape
Compare Stochastic learning strategies for MLPClassifier