Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
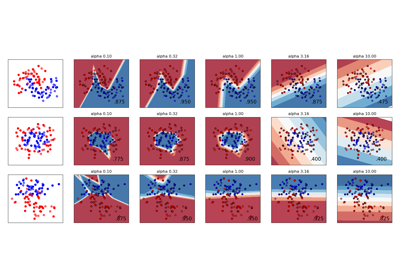
Demonstrating the different strategies of KBinsDiscretizer¶
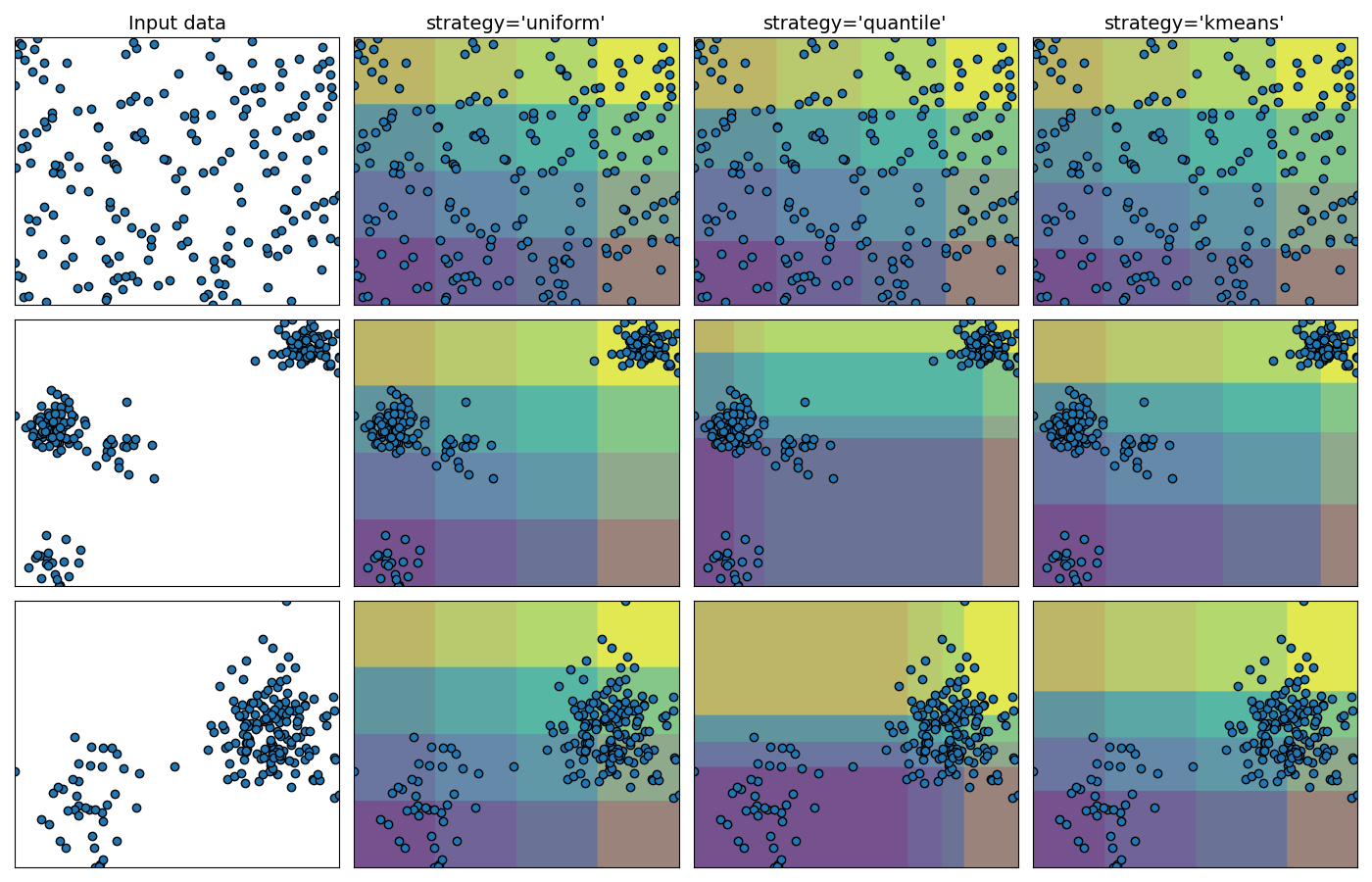
This example presents the different strategies implemented in KBinsDiscretizer:
‘uniform’: The discretization is uniform in each feature, which means that the bin widths are constant in each dimension.
quantile’: The discretization is done on the quantiled values, which means that each bin has approximately the same number of samples.
‘kmeans’: The discretization is based on the centroids of a KMeans clustering procedure.
The plot shows the regions where the discretized encoding is constant.
# Author: Tom Dupré la Tour
# License: BSD 3 clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
from sklearn.preprocessing import KBinsDiscretizer
strategies = ["uniform", "quantile", "kmeans"]
n_samples = 200
centers_0 = np.array([[0, 0], [0, 5], [2, 4], [8, 8]])
centers_1 = np.array([[0, 0], [3, 1]])
# construct the datasets
random_state = 42
X_list = [
np.random.RandomState(random_state).uniform(-3, 3, size=(n_samples, 2)),
make_blobs(
n_samples=[
n_samples // 10,
n_samples * 4 // 10,
n_samples // 10,
n_samples * 4 // 10,
],
cluster_std=0.5,
centers=centers_0,
random_state=random_state,
)[0],
make_blobs(
n_samples=[n_samples // 5, n_samples * 4 // 5],
cluster_std=0.5,
centers=centers_1,
random_state=random_state,
)[0],
]
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(14, 9))
i = 1
for ds_cnt, X in enumerate(X_list):
ax = plt.subplot(len(X_list), len(strategies) + 1, i)
ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], edgecolors="k")
if ds_cnt == 0:
ax.set_title("Input data", size=14)
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(X[:, 0].min(), X[:, 0].max(), 300),
np.linspace(X[:, 1].min(), X[:, 1].max(), 300),
)
grid = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
i += 1
# transform the dataset with KBinsDiscretizer
for strategy in strategies:
enc = KBinsDiscretizer(
n_bins=4, encode="ordinal", strategy=strategy, subsample=200_000
)
enc.fit(X)
grid_encoded = enc.transform(grid)
ax = plt.subplot(len(X_list), len(strategies) + 1, i)
# horizontal stripes
horizontal = grid_encoded[:, 0].reshape(xx.shape)
ax.contourf(xx, yy, horizontal, alpha=0.5)
# vertical stripes
vertical = grid_encoded[:, 1].reshape(xx.shape)
ax.contourf(xx, yy, vertical, alpha=0.5)
ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], edgecolors="k")
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
if ds_cnt == 0:
ax.set_title("strategy='%s'" % (strategy,), size=14)
i += 1
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.652 seconds)
Related examples
Illustration of Gaussian process classification (GPC) on the XOR dataset