sklearn.preprocessing.SplineTransformer¶
- class sklearn.preprocessing.SplineTransformer(n_knots=5, degree=3, *, knots='uniform', extrapolation='constant', include_bias=True, order='C')[source]¶
Generate univariate B-spline bases for features.
Generate a new feature matrix consisting of
n_splines=n_knots + degree - 1(n_knots - 1forextrapolation="periodic") spline basis functions (B-splines) of polynomial order=`degree` for each feature.Read more in the User Guide.
New in version 1.0.
- Parameters:
- n_knotsint, default=5
Number of knots of the splines if
knotsequals one of {‘uniform’, ‘quantile’}. Must be larger or equal 2. Ignored ifknotsis array-like.- degreeint, default=3
The polynomial degree of the spline basis. Must be a non-negative integer.
- knots{‘uniform’, ‘quantile’} or array-like of shape (n_knots, n_features), default=’uniform’
Set knot positions such that first knot <= features <= last knot.
If ‘uniform’,
n_knotsnumber of knots are distributed uniformly from min to max values of the features.If ‘quantile’, they are distributed uniformly along the quantiles of the features.
If an array-like is given, it directly specifies the sorted knot positions including the boundary knots. Note that, internally,
degreenumber of knots are added before the first knot, the same after the last knot.
- extrapolation{‘error’, ‘constant’, ‘linear’, ‘continue’, ‘periodic’}, default=’constant’
If ‘error’, values outside the min and max values of the training features raises a
ValueError. If ‘constant’, the value of the splines at minimum and maximum value of the features is used as constant extrapolation. If ‘linear’, a linear extrapolation is used. If ‘continue’, the splines are extrapolated as is, i.e. optionextrapolate=Trueinscipy.interpolate.BSpline. If ‘periodic’, periodic splines with a periodicity equal to the distance between the first and last knot are used. Periodic splines enforce equal function values and derivatives at the first and last knot. For example, this makes it possible to avoid introducing an arbitrary jump between Dec 31st and Jan 1st in spline features derived from a naturally periodic “day-of-year” input feature. In this case it is recommended to manually set the knot values to control the period.- include_biasbool, default=True
If True (default), then the last spline element inside the data range of a feature is dropped. As B-splines sum to one over the spline basis functions for each data point, they implicitly include a bias term, i.e. a column of ones. It acts as an intercept term in a linear models.
- order{‘C’, ‘F’}, default=’C’
Order of output array. ‘F’ order is faster to compute, but may slow down subsequent estimators.
- Attributes:
- bsplines_list of shape (n_features,)
List of BSplines objects, one for each feature.
- n_features_in_int
The total number of input features.
- feature_names_in_ndarray of shape (
n_features_in_,) Names of features seen during fit. Defined only when
Xhas feature names that are all strings.New in version 1.0.
- n_features_out_int
The total number of output features, which is computed as
n_features * n_splines, wheren_splinesis the number of bases elements of the B-splines,n_knots + degree - 1for non-periodic splines andn_knots - 1for periodic ones. Ifinclude_bias=False, then it is onlyn_features * (n_splines - 1).
See also
KBinsDiscretizerTransformer that bins continuous data into intervals.
PolynomialFeaturesTransformer that generates polynomial and interaction features.
Notes
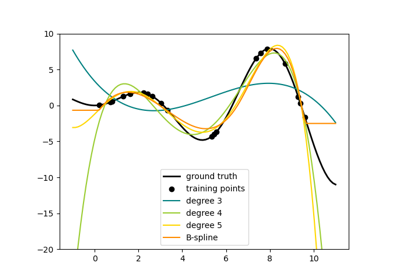
High degrees and a high number of knots can cause overfitting.
See examples/linear_model/plot_polynomial_interpolation.py.
Examples
>>> import numpy as np >>> from sklearn.preprocessing import SplineTransformer >>> X = np.arange(6).reshape(6, 1) >>> spline = SplineTransformer(degree=2, n_knots=3) >>> spline.fit_transform(X) array([[0.5 , 0.5 , 0. , 0. ], [0.18, 0.74, 0.08, 0. ], [0.02, 0.66, 0.32, 0. ], [0. , 0.32, 0.66, 0.02], [0. , 0.08, 0.74, 0.18], [0. , 0. , 0.5 , 0.5 ]])
Methods
fit(X[, y, sample_weight])Compute knot positions of splines.
fit_transform(X[, y])Fit to data, then transform it.
get_feature_names_out([input_features])Get output feature names for transformation.
get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator.
set_output(*[, transform])Set output container.
set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator.
transform(X)Transform each feature data to B-splines.
- fit(X, y=None, sample_weight=None)[source]¶
Compute knot positions of splines.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The data.
- yNone
Ignored.
- sample_weightarray-like of shape (n_samples,), default = None
Individual weights for each sample. Used to calculate quantiles if
knots="quantile". Forknots="uniform", zero weighted observations are ignored for finding the min and max ofX.
- Returns:
- selfobject
Fitted transformer.
- fit_transform(X, y=None, **fit_params)[source]¶
Fit to data, then transform it.
Fits transformer to
Xandywith optional parametersfit_paramsand returns a transformed version ofX.- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Input samples.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs), default=None
Target values (None for unsupervised transformations).
- **fit_paramsdict
Additional fit parameters.
- Returns:
- X_newndarray array of shape (n_samples, n_features_new)
Transformed array.
- get_feature_names_out(input_features=None)[source]¶
Get output feature names for transformation.
- Parameters:
- input_featuresarray-like of str or None, default=None
Input features.
If
input_featuresisNone, thenfeature_names_in_is used as feature names in. Iffeature_names_in_is not defined, then the following input feature names are generated:["x0", "x1", ..., "x(n_features_in_ - 1)"].If
input_featuresis an array-like, theninput_featuresmust matchfeature_names_in_iffeature_names_in_is defined.
- Returns:
- feature_names_outndarray of str objects
Transformed feature names.
- get_params(deep=True)[source]¶
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters:
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns:
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- set_output(*, transform=None)[source]¶
Set output container.
See Introducing the set_output API for an example on how to use the API.
- Parameters:
- transform{“default”, “pandas”}, default=None
Configure output of
transformandfit_transform."default": Default output format of a transformer"pandas": DataFrame outputNone: Transform configuration is unchanged
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
- set_params(**params)[source]¶
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters:
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
- transform(X)[source]¶
Transform each feature data to B-splines.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The data to transform.
- Returns:
- XBSndarray of shape (n_samples, n_features * n_splines)
The matrix of features, where n_splines is the number of bases elements of the B-splines, n_knots + degree - 1.