sklearn.linear_model.RANSACRegressor¶
- class sklearn.linear_model.RANSACRegressor(base_estimator=None, *, min_samples=None, residual_threshold=None, is_data_valid=None, is_model_valid=None, max_trials=100, max_skips=inf, stop_n_inliers=inf, stop_score=inf, stop_probability=0.99, loss='absolute_error', random_state=None)[source]¶
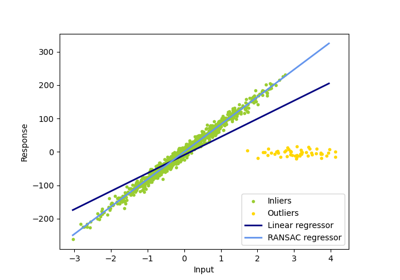
RANSAC (RANdom SAmple Consensus) algorithm.
RANSAC is an iterative algorithm for the robust estimation of parameters from a subset of inliers from the complete data set.
Read more in the User Guide.
- Parameters
- base_estimatorobject, default=None
Base estimator object which implements the following methods:
fit(X, y): Fit model to given training data and target values.score(X, y): Returns the mean accuracy on the given test data, which is used for the stop criterion defined bystop_score. Additionally, the score is used to decide which of two equally large consensus sets is chosen as the better one.predict(X): Returns predicted values using the linear model, which is used to compute residual error using loss function.
If
base_estimatoris None, thenLinearRegressionis used for target values of dtype float.Note that the current implementation only supports regression estimators.
- min_samplesint (>= 1) or float ([0, 1]), default=None
Minimum number of samples chosen randomly from original data. Treated as an absolute number of samples for
min_samples >= 1, treated as a relative numberceil(min_samples * X.shape[0])formin_samples < 1. This is typically chosen as the minimal number of samples necessary to estimate the givenbase_estimator. By default asklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression()estimator is assumed andmin_samplesis chosen asX.shape[1] + 1. This parameter is highly dependent upon the model, so if abase_estimatorother thanlinear_model.LinearRegressionis used, the user is encouraged to provide a value.Deprecated since version 1.0: Not setting
min_samplesexplicitly will raise an error in version 1.2 for models other thanLinearRegression. To keep the old default behavior, setmin_samples=X.shape[1] + 1explicitly.- residual_thresholdfloat, default=None
Maximum residual for a data sample to be classified as an inlier. By default the threshold is chosen as the MAD (median absolute deviation) of the target values
y. Points whose residuals are strictly equal to the threshold are considered as inliers.- is_data_validcallable, default=None
This function is called with the randomly selected data before the model is fitted to it:
is_data_valid(X, y). If its return value is False the current randomly chosen sub-sample is skipped.- is_model_validcallable, default=None
This function is called with the estimated model and the randomly selected data:
is_model_valid(model, X, y). If its return value is False the current randomly chosen sub-sample is skipped. Rejecting samples with this function is computationally costlier than withis_data_valid.is_model_validshould therefore only be used if the estimated model is needed for making the rejection decision.- max_trialsint, default=100
Maximum number of iterations for random sample selection.
- max_skipsint, default=np.inf
Maximum number of iterations that can be skipped due to finding zero inliers or invalid data defined by
is_data_validor invalid models defined byis_model_valid.New in version 0.19.
- stop_n_inliersint, default=np.inf
Stop iteration if at least this number of inliers are found.
- stop_scorefloat, default=np.inf
Stop iteration if score is greater equal than this threshold.
- stop_probabilityfloat in range [0, 1], default=0.99
RANSAC iteration stops if at least one outlier-free set of the training data is sampled in RANSAC. This requires to generate at least N samples (iterations):
N >= log(1 - probability) / log(1 - e**m)
where the probability (confidence) is typically set to high value such as 0.99 (the default) and e is the current fraction of inliers w.r.t. the total number of samples.
- lossstr, callable, default=’absolute_error’
String inputs, ‘absolute_error’ and ‘squared_error’ are supported which find the absolute error and squared error per sample respectively.
If
lossis a callable, then it should be a function that takes two arrays as inputs, the true and predicted value and returns a 1-D array with the i-th value of the array corresponding to the loss onX[i].If the loss on a sample is greater than the
residual_threshold, then this sample is classified as an outlier.New in version 0.18.
Deprecated since version 1.0: The loss ‘squared_loss’ was deprecated in v1.0 and will be removed in version 1.2. Use
loss='squared_error'which is equivalent.Deprecated since version 1.0: The loss ‘absolute_loss’ was deprecated in v1.0 and will be removed in version 1.2. Use
loss='absolute_error'which is equivalent.- random_stateint, RandomState instance, default=None
The generator used to initialize the centers. Pass an int for reproducible output across multiple function calls. See Glossary.
- Attributes
- estimator_object
Best fitted model (copy of the
base_estimatorobject).- n_trials_int
Number of random selection trials until one of the stop criteria is met. It is always
<= max_trials.- inlier_mask_bool array of shape [n_samples]
Boolean mask of inliers classified as
True.- n_skips_no_inliers_int
Number of iterations skipped due to finding zero inliers.
New in version 0.19.
- n_skips_invalid_data_int
Number of iterations skipped due to invalid data defined by
is_data_valid.New in version 0.19.
- n_skips_invalid_model_int
Number of iterations skipped due to an invalid model defined by
is_model_valid.New in version 0.19.
- n_features_in_int
Number of features seen during fit.
New in version 0.24.
- feature_names_in_ndarray of shape (
n_features_in_,) Names of features seen during fit. Defined only when
Xhas feature names that are all strings.New in version 1.0.
See also
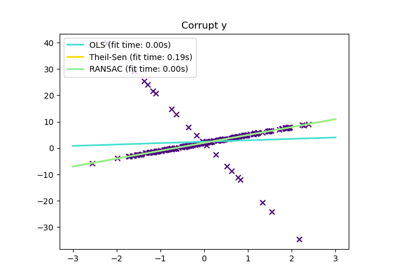
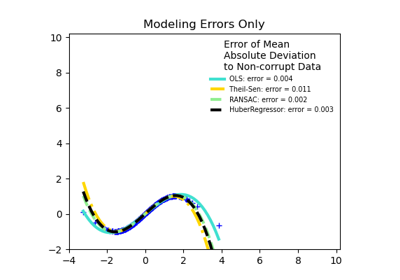
HuberRegressorLinear regression model that is robust to outliers.
TheilSenRegressorTheil-Sen Estimator robust multivariate regression model.
SGDRegressorFitted by minimizing a regularized empirical loss with SGD.
References
Examples
>>> from sklearn.linear_model import RANSACRegressor >>> from sklearn.datasets import make_regression >>> X, y = make_regression( ... n_samples=200, n_features=2, noise=4.0, random_state=0) >>> reg = RANSACRegressor(random_state=0).fit(X, y) >>> reg.score(X, y) 0.9885... >>> reg.predict(X[:1,]) array([-31.9417...])
Methods
fit(X, y[, sample_weight])Fit estimator using RANSAC algorithm.
get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator.
predict(X)Predict using the estimated model.
score(X, y)Return the score of the prediction.
set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator.
- fit(X, y, sample_weight=None)[source]¶
Fit estimator using RANSAC algorithm.
- Parameters
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Training data.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_targets)
Target values.
- sample_weightarray-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None
Individual weights for each sample raises error if sample_weight is passed and base_estimator fit method does not support it.
New in version 0.18.
- Returns
- selfobject
Fitted
RANSACRegressorestimator.
- Raises
- ValueError
If no valid consensus set could be found. This occurs if
is_data_validandis_model_validreturn False for allmax_trialsrandomly chosen sub-samples.
- get_params(deep=True)[source]¶
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- predict(X)[source]¶
Predict using the estimated model.
This is a wrapper for
estimator_.predict(X).- Parameters
- X{array-like or sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Input data.
- Returns
- yarray, shape = [n_samples] or [n_samples, n_targets]
Returns predicted values.
- score(X, y)[source]¶
Return the score of the prediction.
This is a wrapper for
estimator_.score(X, y).- Parameters
- X(array-like or sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Training data.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_targets)
Target values.
- Returns
- zfloat
Score of the prediction.
- set_params(**params)[source]¶
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.