Note
Click here to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
Sparsity Example: Fitting only features 1 and 2¶
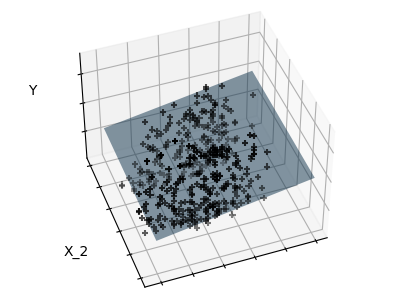
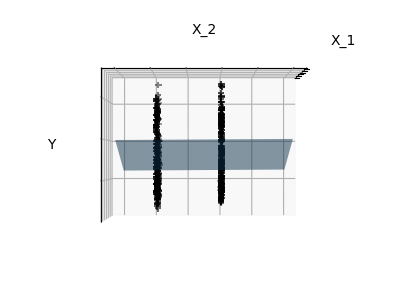
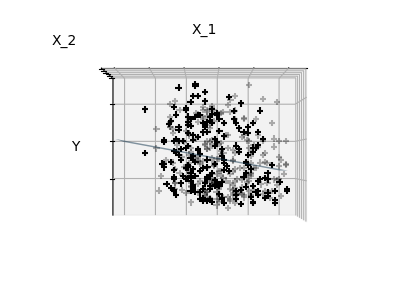
Features 1 and 2 of the diabetes-dataset are fitted and
plotted below. It illustrates that although feature 2
has a strong coefficient on the full model, it does not
give us much regarding y when compared to just feature 1
Out:
/home/circleci/project/examples/linear_model/plot_ols_3d.py:41: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: Axes3D(fig) adding itself to the figure is deprecated since 3.4. Pass the keyword argument auto_add_to_figure=False and use fig.add_axes(ax) to suppress this warning. The default value of auto_add_to_figure will change to False in mpl3.5 and True values will no longer work in 3.6. This is consistent with other Axes classes.
ax = Axes3D(fig, elev=elev, azim=azim)
/home/circleci/project/examples/linear_model/plot_ols_3d.py:41: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: Axes3D(fig) adding itself to the figure is deprecated since 3.4. Pass the keyword argument auto_add_to_figure=False and use fig.add_axes(ax) to suppress this warning. The default value of auto_add_to_figure will change to False in mpl3.5 and True values will no longer work in 3.6. This is consistent with other Axes classes.
ax = Axes3D(fig, elev=elev, azim=azim)
/home/circleci/project/examples/linear_model/plot_ols_3d.py:41: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: Axes3D(fig) adding itself to the figure is deprecated since 3.4. Pass the keyword argument auto_add_to_figure=False and use fig.add_axes(ax) to suppress this warning. The default value of auto_add_to_figure will change to False in mpl3.5 and True values will no longer work in 3.6. This is consistent with other Axes classes.
ax = Axes3D(fig, elev=elev, azim=azim)
# Code source: Gaël Varoquaux
# Modified for documentation by Jaques Grobler
# License: BSD 3 clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from sklearn import datasets, linear_model
X, y = datasets.load_diabetes(return_X_y=True)
indices = (0, 1)
X_train = X[:-20, indices]
X_test = X[-20:, indices]
y_train = y[:-20]
y_test = y[-20:]
ols = linear_model.LinearRegression()
ols.fit(X_train, y_train)
# #############################################################################
# Plot the figure
def plot_figs(fig_num, elev, azim, X_train, clf):
fig = plt.figure(fig_num, figsize=(4, 3))
plt.clf()
ax = Axes3D(fig, elev=elev, azim=azim)
ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], y_train, c="k", marker="+")
ax.plot_surface(
np.array([[-0.1, -0.1], [0.15, 0.15]]),
np.array([[-0.1, 0.15], [-0.1, 0.15]]),
clf.predict(
np.array([[-0.1, -0.1, 0.15, 0.15], [-0.1, 0.15, -0.1, 0.15]]).T
).reshape((2, 2)),
alpha=0.5,
)
ax.set_xlabel("X_1")
ax.set_ylabel("X_2")
ax.set_zlabel("Y")
ax.w_xaxis.set_ticklabels([])
ax.w_yaxis.set_ticklabels([])
ax.w_zaxis.set_ticklabels([])
# Generate the three different figures from different views
elev = 43.5
azim = -110
plot_figs(1, elev, azim, X_train, ols)
elev = -0.5
azim = 0
plot_figs(2, elev, azim, X_train, ols)
elev = -0.5
azim = 90
plot_figs(3, elev, azim, X_train, ols)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.181 seconds)