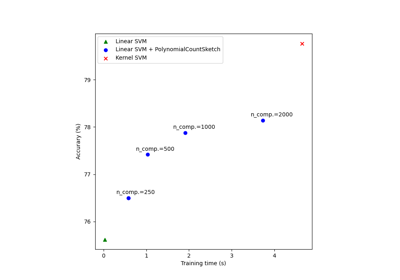
sklearn.kernel_approximation.PolynomialCountSketch¶
-
class
sklearn.kernel_approximation.PolynomialCountSketch(*, gamma=1.0, degree=2, coef0=0, n_components=100, random_state=None)[source]¶ Polynomial kernel approximation via Tensor Sketch.
Implements Tensor Sketch, which approximates the feature map of the polynomial kernel:
K(X, Y) = (gamma * <X, Y> + coef0)^degree
by efficiently computing a Count Sketch of the outer product of a vector with itself using Fast Fourier Transforms (FFT). Read more in the User Guide.
New in version 0.24.
- Parameters
- gammafloat, default=1.0
Parameter of the polynomial kernel whose feature map will be approximated.
- degreeint, default=2
Degree of the polynomial kernel whose feature map will be approximated.
- coef0int, default=0
Constant term of the polynomial kernel whose feature map will be approximated.
- n_componentsint, default=100
Dimensionality of the output feature space. Usually, n_components should be greater than the number of features in input samples in order to achieve good performance. The optimal score / run time balance is typically achieved around n_components = 10 * n_features, but this depends on the specific dataset being used.
- random_stateint, RandomState instance, default=None
Determines random number generation for indexHash and bitHash initialization. Pass an int for reproducible results across multiple function calls. See Glossary.
- Attributes
- indexHash_ndarray of shape (degree, n_features), dtype=int64
Array of indexes in range [0, n_components) used to represent the 2-wise independent hash functions for Count Sketch computation.
- bitHash_ndarray of shape (degree, n_features), dtype=float32
Array with random entries in {+1, -1}, used to represent the 2-wise independent hash functions for Count Sketch computation.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.kernel_approximation import PolynomialCountSketch >>> from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier >>> X = [[0, 0], [1, 1], [1, 0], [0, 1]] >>> y = [0, 0, 1, 1] >>> ps = PolynomialCountSketch(degree=3, random_state=1) >>> X_features = ps.fit_transform(X) >>> clf = SGDClassifier(max_iter=10, tol=1e-3) >>> clf.fit(X_features, y) SGDClassifier(max_iter=10) >>> clf.score(X_features, y) 1.0
Methods
fit(X[, y])Fit the model with X.
fit_transform(X[, y])Fit to data, then transform it.
get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator.
set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator.
transform(X)Generate the feature map approximation for X.
-
fit(X, y=None)[source]¶ Fit the model with X.
Initializes the internal variables. The method needs no information about the distribution of data, so we only care about n_features in X.
- Parameters
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Training data, where n_samples in the number of samples and n_features is the number of features.
- Returns
- selfobject
Returns the transformer.
-
fit_transform(X, y=None, **fit_params)[source]¶ Fit to data, then transform it.
Fits transformer to
Xandywith optional parametersfit_paramsand returns a transformed version ofX.- Parameters
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Input samples.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs), default=None
Target values (None for unsupervised transformations).
- **fit_paramsdict
Additional fit parameters.
- Returns
- X_newndarray array of shape (n_samples, n_features_new)
Transformed array.
-
get_params(deep=True)[source]¶ Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
-
set_params(**params)[source]¶ Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.