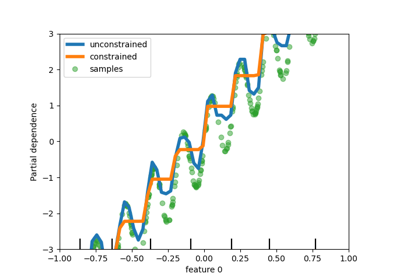
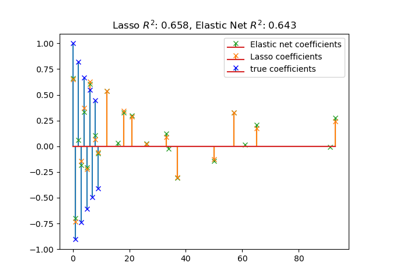
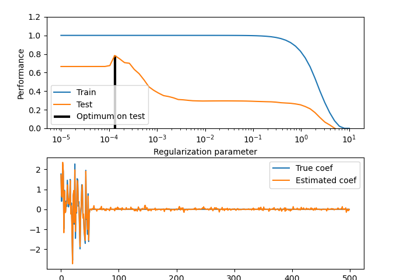
sklearn.linear_model.ElasticNet¶
-
class
sklearn.linear_model.ElasticNet(alpha=1.0, *, l1_ratio=0.5, fit_intercept=True, normalize=False, precompute=False, max_iter=1000, copy_X=True, tol=0.0001, warm_start=False, positive=False, random_state=None, selection='cyclic')[source]¶ Linear regression with combined L1 and L2 priors as regularizer.
Minimizes the objective function:
1 / (2 * n_samples) * ||y - Xw||^2_2 + alpha * l1_ratio * ||w||_1 + 0.5 * alpha * (1 - l1_ratio) * ||w||^2_2
If you are interested in controlling the L1 and L2 penalty separately, keep in mind that this is equivalent to:
a * L1 + b * L2
where:
alpha = a + b and l1_ratio = a / (a + b)
The parameter l1_ratio corresponds to alpha in the glmnet R package while alpha corresponds to the lambda parameter in glmnet. Specifically, l1_ratio = 1 is the lasso penalty. Currently, l1_ratio <= 0.01 is not reliable, unless you supply your own sequence of alpha.
Read more in the User Guide.
- Parameters
- alphafloat, default=1.0
Constant that multiplies the penalty terms. Defaults to 1.0. See the notes for the exact mathematical meaning of this parameter.
alpha = 0is equivalent to an ordinary least square, solved by theLinearRegressionobject. For numerical reasons, usingalpha = 0with theLassoobject is not advised. Given this, you should use theLinearRegressionobject.- l1_ratiofloat, default=0.5
The ElasticNet mixing parameter, with
0 <= l1_ratio <= 1. Forl1_ratio = 0the penalty is an L2 penalty.For l1_ratio = 1it is an L1 penalty. For0 < l1_ratio < 1, the penalty is a combination of L1 and L2.- fit_interceptbool, default=True
Whether the intercept should be estimated or not. If
False, the data is assumed to be already centered.- normalizebool, default=False
This parameter is ignored when
fit_interceptis set to False. If True, the regressors X will be normalized before regression by subtracting the mean and dividing by the l2-norm. If you wish to standardize, please usesklearn.preprocessing.StandardScalerbefore callingfiton an estimator withnormalize=False.- precomputebool or array-like of shape (n_features, n_features), default=False
Whether to use a precomputed Gram matrix to speed up calculations. The Gram matrix can also be passed as argument. For sparse input this option is always
Trueto preserve sparsity.- max_iterint, default=1000
The maximum number of iterations
- copy_Xbool, default=True
If
True, X will be copied; else, it may be overwritten.- tolfloat, default=1e-4
The tolerance for the optimization: if the updates are smaller than
tol, the optimization code checks the dual gap for optimality and continues until it is smaller thantol.- warm_startbool, default=False
When set to
True, reuse the solution of the previous call to fit as initialization, otherwise, just erase the previous solution. See the Glossary.- positivebool, default=False
When set to
True, forces the coefficients to be positive.- random_stateint, RandomState instance, default=None
The seed of the pseudo random number generator that selects a random feature to update. Used when
selection== ‘random’. Pass an int for reproducible output across multiple function calls. See Glossary.- selection{‘cyclic’, ‘random’}, default=’cyclic’
If set to ‘random’, a random coefficient is updated every iteration rather than looping over features sequentially by default. This (setting to ‘random’) often leads to significantly faster convergence especially when tol is higher than 1e-4.
- Attributes
- coef_ndarray of shape (n_features,) or (n_targets, n_features)
parameter vector (w in the cost function formula)
sparse_coef_sparse matrix of shape (n_features, 1) or (n_targets, n_features)sparse representation of the fitted
coef_- intercept_float or ndarray of shape (n_targets,)
independent term in decision function.
- n_iter_list of int
number of iterations run by the coordinate descent solver to reach the specified tolerance.
See also
ElasticNetCVElastic net model with best model selection by cross-validation.
SGDRegressorimplements elastic net regression with incremental training.
SGDClassifierimplements logistic regression with elastic net penalty (
SGDClassifier(loss="log", penalty="elasticnet")).
Notes
To avoid unnecessary memory duplication the X argument of the fit method should be directly passed as a Fortran-contiguous numpy array.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.linear_model import ElasticNet >>> from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
>>> X, y = make_regression(n_features=2, random_state=0) >>> regr = ElasticNet(random_state=0) >>> regr.fit(X, y) ElasticNet(random_state=0) >>> print(regr.coef_) [18.83816048 64.55968825] >>> print(regr.intercept_) 1.451... >>> print(regr.predict([[0, 0]])) [1.451...]
Methods
fit(X, y[, sample_weight, check_input])Fit model with coordinate descent.
get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator.
path(X, y, *[, l1_ratio, eps, n_alphas, …])Compute elastic net path with coordinate descent.
predict(X)Predict using the linear model.
score(X, y[, sample_weight])Return the coefficient of determination R^2 of the prediction.
set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator.
-
__init__(alpha=1.0, *, l1_ratio=0.5, fit_intercept=True, normalize=False, precompute=False, max_iter=1000, copy_X=True, tol=0.0001, warm_start=False, positive=False, random_state=None, selection='cyclic')[source]¶ Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
-
fit(X, y, sample_weight=None, check_input=True)[source]¶ Fit model with coordinate descent.
- Parameters
- X{ndarray, sparse matrix} of (n_samples, n_features)
Data
- y{ndarray, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_targets)
Target. Will be cast to X’s dtype if necessary
- sample_weightfloat or array-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None
Sample weight.
- check_inputbool, default=True
Allow to bypass several input checking. Don’t use this parameter unless you know what you do.
Notes
Coordinate descent is an algorithm that considers each column of data at a time hence it will automatically convert the X input as a Fortran-contiguous numpy array if necessary.
To avoid memory re-allocation it is advised to allocate the initial data in memory directly using that format.
-
get_params(deep=True)[source]¶ Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns
- paramsmapping of string to any
Parameter names mapped to their values.
-
static
path(X, y, *, l1_ratio=0.5, eps=0.001, n_alphas=100, alphas=None, precompute='auto', Xy=None, copy_X=True, coef_init=None, verbose=False, return_n_iter=False, positive=False, check_input=True, **params)[source]¶ Compute elastic net path with coordinate descent.
The elastic net optimization function varies for mono and multi-outputs.
For mono-output tasks it is:
1 / (2 * n_samples) * ||y - Xw||^2_2 + alpha * l1_ratio * ||w||_1 + 0.5 * alpha * (1 - l1_ratio) * ||w||^2_2
For multi-output tasks it is:
(1 / (2 * n_samples)) * ||Y - XW||^Fro_2 + alpha * l1_ratio * ||W||_21 + 0.5 * alpha * (1 - l1_ratio) * ||W||_Fro^2
Where:
||W||_21 = \sum_i \sqrt{\sum_j w_{ij}^2}
i.e. the sum of norm of each row.
Read more in the User Guide.
- Parameters
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Training data. Pass directly as Fortran-contiguous data to avoid unnecessary memory duplication. If
yis mono-output thenXcan be sparse.- y{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs)
Target values.
- l1_ratiofloat, default=0.5
Number between 0 and 1 passed to elastic net (scaling between l1 and l2 penalties).
l1_ratio=1corresponds to the Lasso.- epsfloat, default=1e-3
Length of the path.
eps=1e-3means thatalpha_min / alpha_max = 1e-3.- n_alphasint, default=100
Number of alphas along the regularization path.
- alphasndarray, default=None
List of alphas where to compute the models. If None alphas are set automatically.
- precompute‘auto’, bool or array-like of shape (n_features, n_features), default=’auto’
Whether to use a precomputed Gram matrix to speed up calculations. If set to
'auto'let us decide. The Gram matrix can also be passed as argument.- Xyarray-like of shape (n_features,) or (n_features, n_outputs), default=None
Xy = np.dot(X.T, y) that can be precomputed. It is useful only when the Gram matrix is precomputed.
- copy_Xbool, default=True
If
True, X will be copied; else, it may be overwritten.- coef_initndarray of shape (n_features, ), default=None
The initial values of the coefficients.
- verbosebool or int, default=False
Amount of verbosity.
- return_n_iterbool, default=False
Whether to return the number of iterations or not.
- positivebool, default=False
If set to True, forces coefficients to be positive. (Only allowed when
y.ndim == 1).- check_inputbool, default=True
Skip input validation checks, including the Gram matrix when provided assuming there are handled by the caller when check_input=False.
- **paramskwargs
Keyword arguments passed to the coordinate descent solver.
- Returns
- alphasndarray of shape (n_alphas,)
The alphas along the path where models are computed.
- coefsndarray of shape (n_features, n_alphas) or (n_outputs, n_features, n_alphas)
Coefficients along the path.
- dual_gapsndarray of shape (n_alphas,)
The dual gaps at the end of the optimization for each alpha.
- n_iterslist of int
The number of iterations taken by the coordinate descent optimizer to reach the specified tolerance for each alpha. (Is returned when
return_n_iteris set to True).
Notes
For an example, see examples/linear_model/plot_lasso_coordinate_descent_path.py.
-
predict(X)[source]¶ Predict using the linear model.
- Parameters
- Xarray_like or sparse matrix, shape (n_samples, n_features)
Samples.
- Returns
- Carray, shape (n_samples,)
Returns predicted values.
-
score(X, y, sample_weight=None)[source]¶ Return the coefficient of determination R^2 of the prediction.
The coefficient R^2 is defined as (1 - u/v), where u is the residual sum of squares ((y_true - y_pred) ** 2).sum() and v is the total sum of squares ((y_true - y_true.mean()) ** 2).sum(). The best possible score is 1.0 and it can be negative (because the model can be arbitrarily worse). A constant model that always predicts the expected value of y, disregarding the input features, would get a R^2 score of 0.0.
- Parameters
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Test samples. For some estimators this may be a precomputed kernel matrix or a list of generic objects instead, shape = (n_samples, n_samples_fitted), where n_samples_fitted is the number of samples used in the fitting for the estimator.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs)
True values for X.
- sample_weightarray-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None
Sample weights.
- Returns
- scorefloat
R^2 of self.predict(X) wrt. y.
Notes
The R2 score used when calling
scoreon a regressor usesmultioutput='uniform_average'from version 0.23 to keep consistent with default value ofr2_score. This influences thescoremethod of all the multioutput regressors (except forMultiOutputRegressor).
-
set_params(**params)[source]¶ Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as pipelines). The latter have parameters of the form
<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns
- selfobject
Estimator instance.
-
property
sparse_coef_¶ sparse representation of the fitted
coef_