Note
Click here to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
Gradient Boosting regression¶
Demonstrate Gradient Boosting on the Boston housing dataset.
This example fits a Gradient Boosting model with least squares loss and 500 regression trees of depth 4.
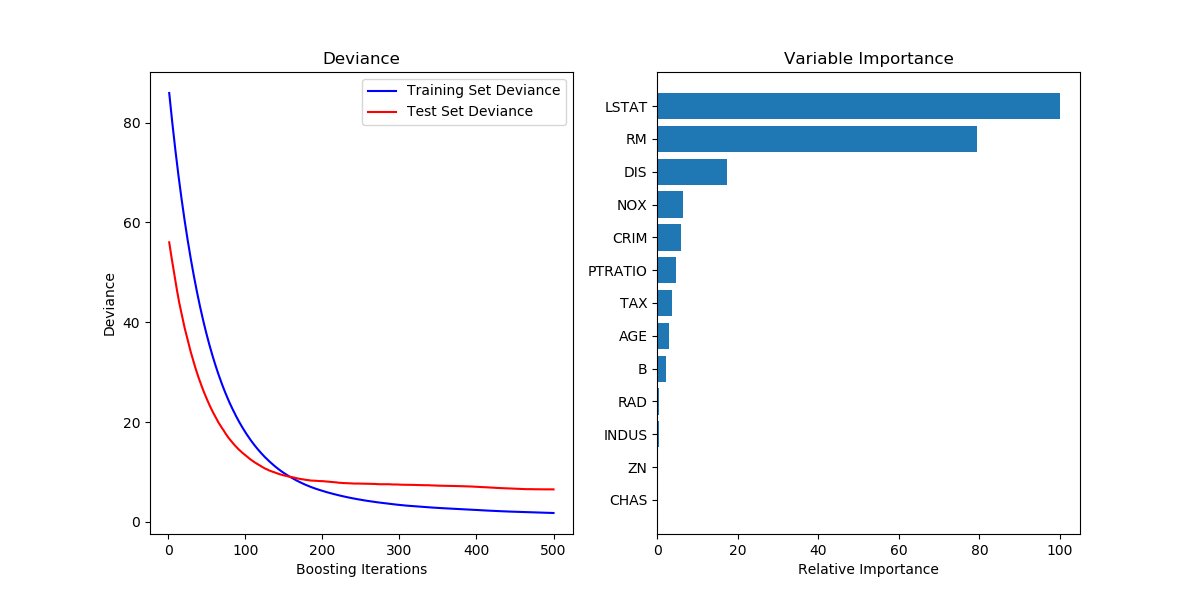
Out:
MSE: 6.4961
print(__doc__)
# Author: Peter Prettenhofer <peter.prettenhofer@gmail.com>
#
# License: BSD 3 clause
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import ensemble
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# #############################################################################
# Load data
boston = datasets.load_boston()
X, y = shuffle(boston.data, boston.target, random_state=13)
X = X.astype(np.float32)
offset = int(X.shape[0] * 0.9)
X_train, y_train = X[:offset], y[:offset]
X_test, y_test = X[offset:], y[offset:]
# #############################################################################
# Fit regression model
params = {'n_estimators': 500, 'max_depth': 4, 'min_samples_split': 2,
'learning_rate': 0.01, 'loss': 'ls'}
clf = ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(**params)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, clf.predict(X_test))
print("MSE: %.4f" % mse)
# #############################################################################
# Plot training deviance
# compute test set deviance
test_score = np.zeros((params['n_estimators'],), dtype=np.float64)
for i, y_pred in enumerate(clf.staged_predict(X_test)):
test_score[i] = clf.loss_(y_test, y_pred)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.title('Deviance')
plt.plot(np.arange(params['n_estimators']) + 1, clf.train_score_, 'b-',
label='Training Set Deviance')
plt.plot(np.arange(params['n_estimators']) + 1, test_score, 'r-',
label='Test Set Deviance')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.xlabel('Boosting Iterations')
plt.ylabel('Deviance')
# #############################################################################
# Plot feature importance
feature_importance = clf.feature_importances_
# make importances relative to max importance
feature_importance = 100.0 * (feature_importance / feature_importance.max())
sorted_idx = np.argsort(feature_importance)
pos = np.arange(sorted_idx.shape[0]) + .5
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.barh(pos, feature_importance[sorted_idx], align='center')
plt.yticks(pos, boston.feature_names[sorted_idx])
plt.xlabel('Relative Importance')
plt.title('Variable Importance')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.998 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 8 MB
