Anomaly detection with Local Outlier Factor (LOF)¶
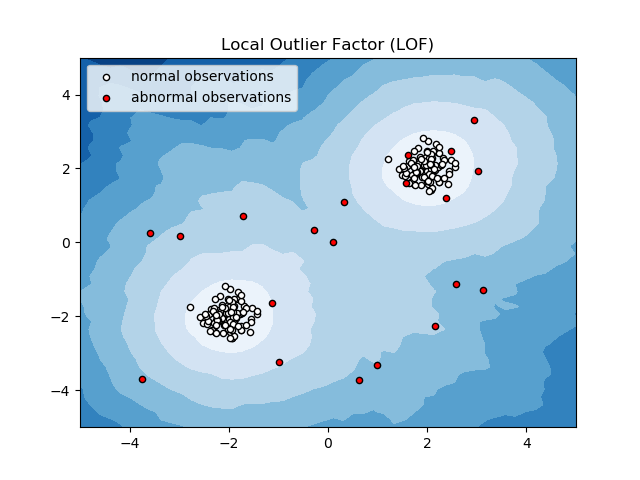
This example presents the Local Outlier Factor (LOF) estimator. The LOF algorithm is an unsupervised outlier detection method which computes the local density deviation of a given data point with respect to its neighbors. It considers as outlier samples that have a substantially lower density than their neighbors.
The number of neighbors considered, (parameter n_neighbors) is typically chosen 1) greater than the minimum number of objects a cluster has to contain, so that other objects can be local outliers relative to this cluster, and 2) smaller than the maximum number of close by objects that can potentially be local outliers. In practice, such informations are generally not available, and taking n_neighbors=20 appears to work well in general.
print(__doc__)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.neighbors import LocalOutlierFactor
np.random.seed(42)
# Generate train data
X = 0.3 * np.random.randn(100, 2)
# Generate some abnormal novel observations
X_outliers = np.random.uniform(low=-4, high=4, size=(20, 2))
X = np.r_[X + 2, X - 2, X_outliers]
# fit the model
clf = LocalOutlierFactor(n_neighbors=20)
y_pred = clf.fit_predict(X)
y_pred_outliers = y_pred[200:]
# plot the level sets of the decision function
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-5, 5, 50), np.linspace(-5, 5, 50))
Z = clf._decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.title("Local Outlier Factor (LOF)")
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Blues_r)
a = plt.scatter(X[:200, 0], X[:200, 1], c='white',
edgecolor='k', s=20)
b = plt.scatter(X[200:, 0], X[200:, 1], c='red',
edgecolor='k', s=20)
plt.axis('tight')
plt.xlim((-5, 5))
plt.ylim((-5, 5))
plt.legend([a, b],
["normal observations",
"abnormal observations"],
loc="upper left")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.056 seconds)

