Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
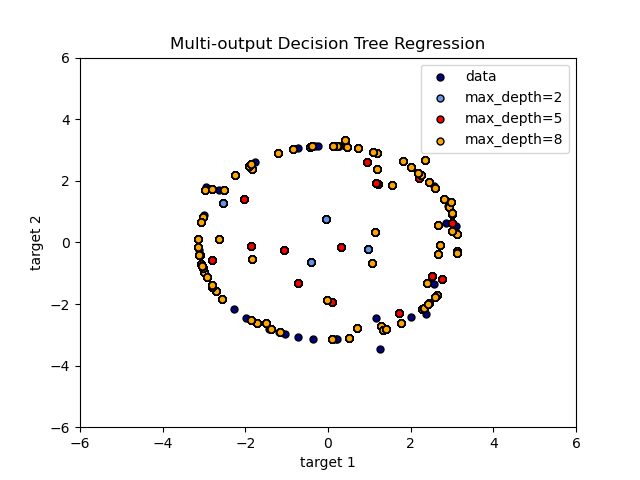
Multi-output Decision Tree Regression¶
An example to illustrate multi-output regression with decision tree.
The decision trees is used to predict simultaneously the noisy x and y observations of a circle given a single underlying feature. As a result, it learns local linear regressions approximating the circle.
We can see that if the maximum depth of the tree (controlled by the
max_depth parameter) is set too high, the decision trees learn too fine
details of the training data and learn from the noise, i.e. they overfit.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
# Create a random dataset
rng = np.random.RandomState(1)
X = np.sort(200 * rng.rand(100, 1) - 100, axis=0)
y = np.array([np.pi * np.sin(X).ravel(), np.pi * np.cos(X).ravel()]).T
y[::5, :] += 0.5 - rng.rand(20, 2)
# Fit regression model
regr_1 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=2)
regr_2 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=5)
regr_3 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=8)
regr_1.fit(X, y)
regr_2.fit(X, y)
regr_3.fit(X, y)
# Predict
X_test = np.arange(-100.0, 100.0, 0.01)[:, np.newaxis]
y_1 = regr_1.predict(X_test)
y_2 = regr_2.predict(X_test)
y_3 = regr_3.predict(X_test)
# Plot the results
plt.figure()
s = 25
plt.scatter(y[:, 0], y[:, 1], c="navy", s=s, edgecolor="black", label="data")
plt.scatter(
y_1[:, 0],
y_1[:, 1],
c="cornflowerblue",
s=s,
edgecolor="black",
label="max_depth=2",
)
plt.scatter(y_2[:, 0], y_2[:, 1], c="red", s=s, edgecolor="black", label="max_depth=5")
plt.scatter(
y_3[:, 0], y_3[:, 1], c="orange", s=s, edgecolor="black", label="max_depth=8"
)
plt.xlim([-6, 6])
plt.ylim([-6, 6])
plt.xlabel("target 1")
plt.ylabel("target 2")
plt.title("Multi-output Decision Tree Regression")
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.242 seconds)