Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
Recursive feature elimination with cross-validation¶
A Recursive Feature Elimination (RFE) example with automatic tuning of the number of features selected with cross-validation.
Data generation¶
We build a classification task using 3 informative features. The introduction of 2 additional redundant (i.e. correlated) features has the effect that the selected features vary depending on the cross-validation fold. The remaining features are non-informative as they are drawn at random.
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
X, y = make_classification(
n_samples=500,
n_features=15,
n_informative=3,
n_redundant=2,
n_repeated=0,
n_classes=8,
n_clusters_per_class=1,
class_sep=0.8,
random_state=0,
)
Model training and selection¶
We create the RFE object and compute the cross-validated scores. The scoring strategy “accuracy” optimizes the proportion of correctly classified samples.
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFECV
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
min_features_to_select = 1 # Minimum number of features to consider
clf = LogisticRegression()
cv = StratifiedKFold(5)
rfecv = RFECV(
estimator=clf,
step=1,
cv=cv,
scoring="accuracy",
min_features_to_select=min_features_to_select,
n_jobs=2,
)
rfecv.fit(X, y)
print(f"Optimal number of features: {rfecv.n_features_}")
Optimal number of features: 3
In the present case, the model with 3 features (which corresponds to the true generative model) is found to be the most optimal.
Plot number of features VS. cross-validation scores¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
n_scores = len(rfecv.cv_results_["mean_test_score"])
plt.figure()
plt.xlabel("Number of features selected")
plt.ylabel("Mean test accuracy")
plt.errorbar(
range(min_features_to_select, n_scores + min_features_to_select),
rfecv.cv_results_["mean_test_score"],
yerr=rfecv.cv_results_["std_test_score"],
)
plt.title("Recursive Feature Elimination \nwith correlated features")
plt.show()
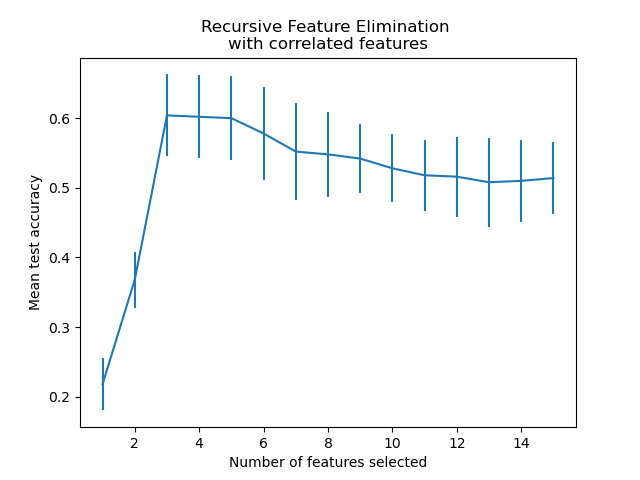
From the plot above one can further notice a plateau of equivalent scores (similar mean value and overlapping errorbars) for 3 to 5 selected features. This is the result of introducing correlated features. Indeed, the optimal model selected by the RFE can lie within this range, depending on the cross-validation technique. The test accuracy decreases above 5 selected features, this is, keeping non-informative features leads to over-fitting and is therefore detrimental for the statistical performance of the models.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.602 seconds)