Note
Click here to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
The Iris Dataset¶
This data sets consists of 3 different types of irises’ (Setosa, Versicolour, and Virginica) petal and sepal length, stored in a 150x4 numpy.ndarray
The rows being the samples and the columns being: Sepal Length, Sepal Width, Petal Length and Petal Width.
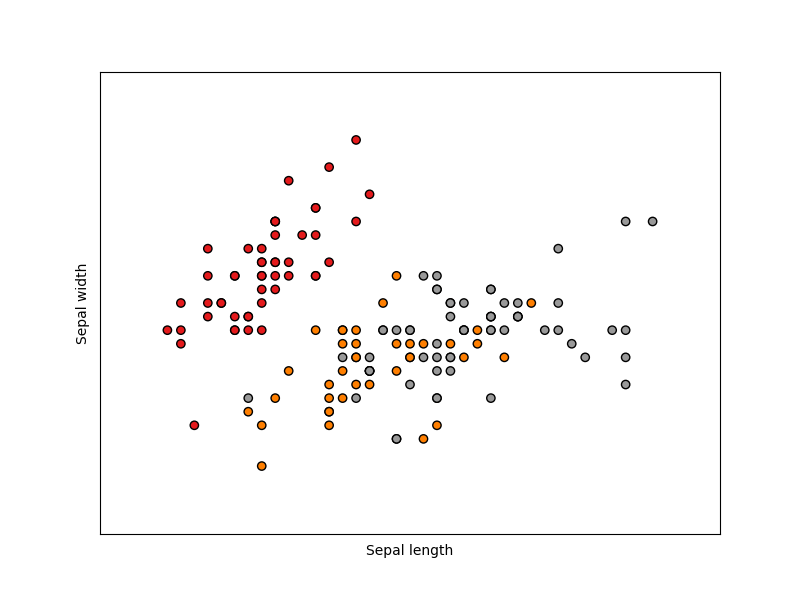
The below plot uses the first two features. See here for more information on this dataset.
# Code source: Gaël Varoquaux
# Modified for documentation by Jaques Grobler
# License: BSD 3 clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# unused but required import for doing 3d projections with matplotlib < 3.2
import mpl_toolkits.mplot3d # noqa: F401
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
# import some data to play with
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, :2] # we only take the first two features.
y = iris.target
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 0.5, X[:, 0].max() + 0.5
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 0.5, X[:, 1].max() + 0.5
plt.figure(2, figsize=(8, 6))
plt.clf()
# Plot the training points
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap=plt.cm.Set1, edgecolor="k")
plt.xlabel("Sepal length")
plt.ylabel("Sepal width")
plt.xlim(x_min, x_max)
plt.ylim(y_min, y_max)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
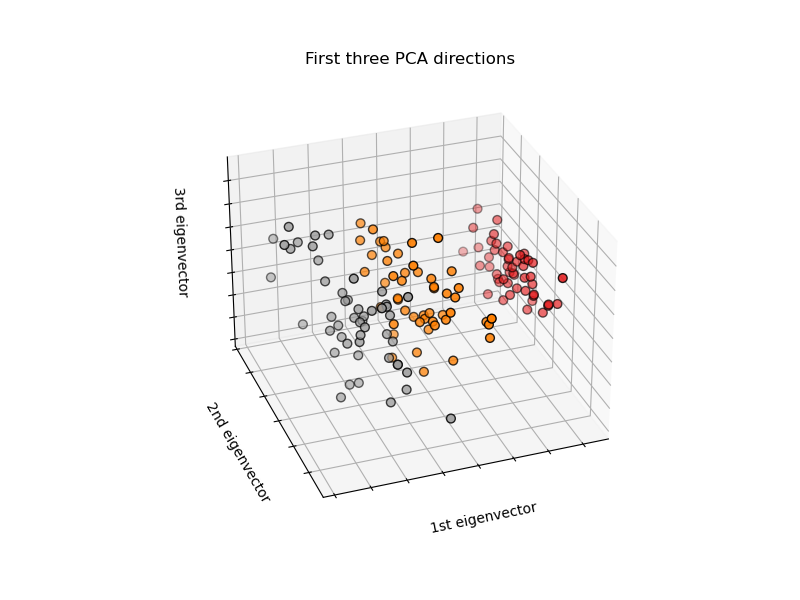
# To getter a better understanding of interaction of the dimensions
# plot the first three PCA dimensions
fig = plt.figure(1, figsize=(8, 6))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection="3d", elev=-150, azim=110)
X_reduced = PCA(n_components=3).fit_transform(iris.data)
ax.scatter(
X_reduced[:, 0],
X_reduced[:, 1],
X_reduced[:, 2],
c=y,
cmap=plt.cm.Set1,
edgecolor="k",
s=40,
)
ax.set_title("First three PCA directions")
ax.set_xlabel("1st eigenvector")
ax.xaxis.set_ticklabels([])
ax.set_ylabel("2nd eigenvector")
ax.yaxis.set_ticklabels([])
ax.set_zlabel("3rd eigenvector")
ax.zaxis.set_ticklabels([])
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.174 seconds)