sklearn.ensemble.AdaBoostClassifier¶
- class sklearn.ensemble.AdaBoostClassifier(base_estimator=None, *, n_estimators=50, learning_rate=1.0, algorithm='SAMME.R', random_state=None)[source]¶
An AdaBoost classifier.
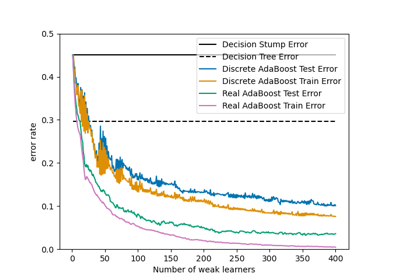
An AdaBoost [1] classifier is a meta-estimator that begins by fitting a classifier on the original dataset and then fits additional copies of the classifier on the same dataset but where the weights of incorrectly classified instances are adjusted such that subsequent classifiers focus more on difficult cases.
This class implements the algorithm known as AdaBoost-SAMME [2].
Read more in the User Guide.
New in version 0.14.
- Parameters:
- base_estimatorobject, default=None
The base estimator from which the boosted ensemble is built. Support for sample weighting is required, as well as proper
classes_andn_classes_attributes. IfNone, then the base estimator isDecisionTreeClassifierinitialized withmax_depth=1.- n_estimatorsint, default=50
The maximum number of estimators at which boosting is terminated. In case of perfect fit, the learning procedure is stopped early. Values must be in the range
[1, inf).- learning_ratefloat, default=1.0
Weight applied to each classifier at each boosting iteration. A higher learning rate increases the contribution of each classifier. There is a trade-off between the
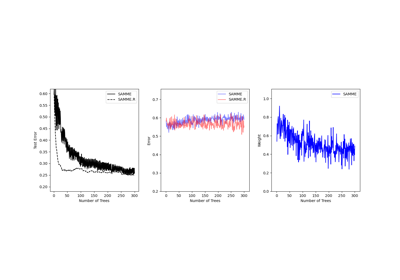
learning_rateandn_estimatorsparameters. Values must be in the range(0.0, inf).- algorithm{‘SAMME’, ‘SAMME.R’}, default=’SAMME.R’
If ‘SAMME.R’ then use the SAMME.R real boosting algorithm.
base_estimatormust support calculation of class probabilities. If ‘SAMME’ then use the SAMME discrete boosting algorithm. The SAMME.R algorithm typically converges faster than SAMME, achieving a lower test error with fewer boosting iterations.- random_stateint, RandomState instance or None, default=None
Controls the random seed given at each
base_estimatorat each boosting iteration. Thus, it is only used whenbase_estimatorexposes arandom_state. Pass an int for reproducible output across multiple function calls. See Glossary.
- Attributes:
- base_estimator_estimator
The base estimator from which the ensemble is grown.
- estimators_list of classifiers
The collection of fitted sub-estimators.
- classes_ndarray of shape (n_classes,)
The classes labels.
- n_classes_int
The number of classes.
- estimator_weights_ndarray of floats
Weights for each estimator in the boosted ensemble.
- estimator_errors_ndarray of floats
Classification error for each estimator in the boosted ensemble.
feature_importances_ndarray of shape (n_features,)The impurity-based feature importances.
- n_features_in_int
Number of features seen during fit.
New in version 0.24.
- feature_names_in_ndarray of shape (
n_features_in_,) Names of features seen during fit. Defined only when
Xhas feature names that are all strings.New in version 1.0.
See also
AdaBoostRegressorAn AdaBoost regressor that begins by fitting a regressor on the original dataset and then fits additional copies of the regressor on the same dataset but where the weights of instances are adjusted according to the error of the current prediction.
GradientBoostingClassifierGB builds an additive model in a forward stage-wise fashion. Regression trees are fit on the negative gradient of the binomial or multinomial deviance loss function. Binary classification is a special case where only a single regression tree is induced.
sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeClassifierA non-parametric supervised learning method used for classification. Creates a model that predicts the value of a target variable by learning simple decision rules inferred from the data features.
References
[1]Y. Freund, R. Schapire, “A Decision-Theoretic Generalization of on-Line Learning and an Application to Boosting”, 1995.
[2]Zhu, H. Zou, S. Rosset, T. Hastie, “Multi-class AdaBoost”, 2009.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier >>> from sklearn.datasets import make_classification >>> X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=4, ... n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, ... random_state=0, shuffle=False) >>> clf = AdaBoostClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=0) >>> clf.fit(X, y) AdaBoostClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=0) >>> clf.predict([[0, 0, 0, 0]]) array([1]) >>> clf.score(X, y) 0.983...
Methods
Compute the decision function of
X.fit(X, y[, sample_weight])Build a boosted classifier from the training set (X, y).
get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator.
predict(X)Predict classes for X.
Predict class log-probabilities for X.
Predict class probabilities for X.
score(X, y[, sample_weight])Return the mean accuracy on the given test data and labels.
set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator.
Compute decision function of
Xfor each boosting iteration.Return staged predictions for X.
Predict class probabilities for X.
staged_score(X, y[, sample_weight])Return staged scores for X, y.
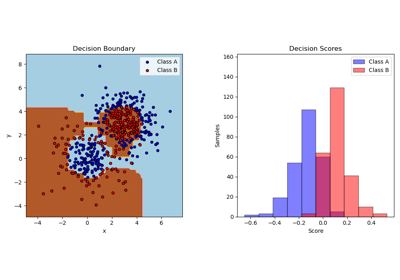
- decision_function(X)[source]¶
Compute the decision function of
X.- Parameters:
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The training input samples. Sparse matrix can be CSC, CSR, COO, DOK, or LIL. COO, DOK, and LIL are converted to CSR.
- Returns:
- scorendarray of shape of (n_samples, k)
The decision function of the input samples. The order of outputs is the same of that of the classes_ attribute. Binary classification is a special cases with
k == 1, otherwisek==n_classes. For binary classification, values closer to -1 or 1 mean more like the first or second class inclasses_, respectively.
- property feature_importances_¶
The impurity-based feature importances.
The higher, the more important the feature. The importance of a feature is computed as the (normalized) total reduction of the criterion brought by that feature. It is also known as the Gini importance.
Warning: impurity-based feature importances can be misleading for high cardinality features (many unique values). See
sklearn.inspection.permutation_importanceas an alternative.- Returns:
- feature_importances_ndarray of shape (n_features,)
The feature importances.
- fit(X, y, sample_weight=None)[source]¶
Build a boosted classifier from the training set (X, y).
- Parameters:
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The training input samples. Sparse matrix can be CSC, CSR, COO, DOK, or LIL. COO, DOK, and LIL are converted to CSR.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,)
The target values (class labels).
- sample_weightarray-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None
Sample weights. If None, the sample weights are initialized to
1 / n_samples.
- Returns:
- selfobject
Fitted estimator.
- get_params(deep=True)[source]¶
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters:
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns:
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- predict(X)[source]¶
Predict classes for X.
The predicted class of an input sample is computed as the weighted mean prediction of the classifiers in the ensemble.
- Parameters:
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The training input samples. Sparse matrix can be CSC, CSR, COO, DOK, or LIL. COO, DOK, and LIL are converted to CSR.
- Returns:
- yndarray of shape (n_samples,)
The predicted classes.
- predict_log_proba(X)[source]¶
Predict class log-probabilities for X.
The predicted class log-probabilities of an input sample is computed as the weighted mean predicted class log-probabilities of the classifiers in the ensemble.
- Parameters:
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The training input samples. Sparse matrix can be CSC, CSR, COO, DOK, or LIL. COO, DOK, and LIL are converted to CSR.
- Returns:
- pndarray of shape (n_samples, n_classes)
The class probabilities of the input samples. The order of outputs is the same of that of the classes_ attribute.
- predict_proba(X)[source]¶
Predict class probabilities for X.
The predicted class probabilities of an input sample is computed as the weighted mean predicted class probabilities of the classifiers in the ensemble.
- Parameters:
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The training input samples. Sparse matrix can be CSC, CSR, COO, DOK, or LIL. COO, DOK, and LIL are converted to CSR.
- Returns:
- pndarray of shape (n_samples, n_classes)
The class probabilities of the input samples. The order of outputs is the same of that of the classes_ attribute.
- score(X, y, sample_weight=None)[source]¶
Return the mean accuracy on the given test data and labels.
In multi-label classification, this is the subset accuracy which is a harsh metric since you require for each sample that each label set be correctly predicted.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Test samples.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs)
True labels for
X.- sample_weightarray-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None
Sample weights.
- Returns:
- scorefloat
Mean accuracy of
self.predict(X)wrt.y.
- set_params(**params)[source]¶
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters:
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
- staged_decision_function(X)[source]¶
Compute decision function of
Xfor each boosting iteration.This method allows monitoring (i.e. determine error on testing set) after each boosting iteration.
- Parameters:
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The training input samples. Sparse matrix can be CSC, CSR, COO, DOK, or LIL. COO, DOK, and LIL are converted to CSR.
- Yields:
- scoregenerator of ndarray of shape (n_samples, k)
The decision function of the input samples. The order of outputs is the same of that of the classes_ attribute. Binary classification is a special cases with
k == 1, otherwisek==n_classes. For binary classification, values closer to -1 or 1 mean more like the first or second class inclasses_, respectively.
- staged_predict(X)[source]¶
Return staged predictions for X.
The predicted class of an input sample is computed as the weighted mean prediction of the classifiers in the ensemble.
This generator method yields the ensemble prediction after each iteration of boosting and therefore allows monitoring, such as to determine the prediction on a test set after each boost.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The input samples. Sparse matrix can be CSC, CSR, COO, DOK, or LIL. COO, DOK, and LIL are converted to CSR.
- Yields:
- ygenerator of ndarray of shape (n_samples,)
The predicted classes.
- staged_predict_proba(X)[source]¶
Predict class probabilities for X.
The predicted class probabilities of an input sample is computed as the weighted mean predicted class probabilities of the classifiers in the ensemble.
This generator method yields the ensemble predicted class probabilities after each iteration of boosting and therefore allows monitoring, such as to determine the predicted class probabilities on a test set after each boost.
- Parameters:
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The training input samples. Sparse matrix can be CSC, CSR, COO, DOK, or LIL. COO, DOK, and LIL are converted to CSR.
- Yields:
- pgenerator of ndarray of shape (n_samples,)
The class probabilities of the input samples. The order of outputs is the same of that of the classes_ attribute.
- staged_score(X, y, sample_weight=None)[source]¶
Return staged scores for X, y.
This generator method yields the ensemble score after each iteration of boosting and therefore allows monitoring, such as to determine the score on a test set after each boost.
- Parameters:
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The training input samples. Sparse matrix can be CSC, CSR, COO, DOK, or LIL. COO, DOK, and LIL are converted to CSR.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,)
Labels for X.
- sample_weightarray-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None
Sample weights.
- Yields:
- zfloat
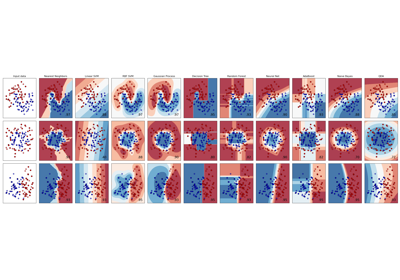
Examples using sklearn.ensemble.AdaBoostClassifier¶
Plot the decision surfaces of ensembles of trees on the iris dataset