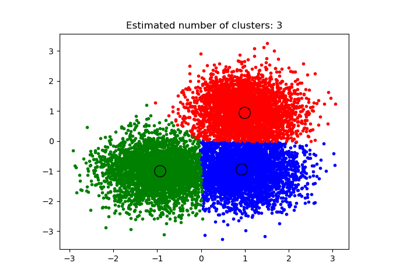
sklearn.cluster.MeanShift¶
- class sklearn.cluster.MeanShift(*, bandwidth=None, seeds=None, bin_seeding=False, min_bin_freq=1, cluster_all=True, n_jobs=None, max_iter=300)[source]¶
Mean shift clustering using a flat kernel.
Mean shift clustering aims to discover “blobs” in a smooth density of samples. It is a centroid-based algorithm, which works by updating candidates for centroids to be the mean of the points within a given region. These candidates are then filtered in a post-processing stage to eliminate near-duplicates to form the final set of centroids.
Seeding is performed using a binning technique for scalability.
Read more in the User Guide.
- Parameters:
- bandwidthfloat, default=None
Bandwidth used in the RBF kernel.
If not given, the bandwidth is estimated using sklearn.cluster.estimate_bandwidth; see the documentation for that function for hints on scalability (see also the Notes, below).
- seedsarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features), default=None
Seeds used to initialize kernels. If not set, the seeds are calculated by clustering.get_bin_seeds with bandwidth as the grid size and default values for other parameters.
- bin_seedingbool, default=False
If true, initial kernel locations are not locations of all points, but rather the location of the discretized version of points, where points are binned onto a grid whose coarseness corresponds to the bandwidth. Setting this option to True will speed up the algorithm because fewer seeds will be initialized. The default value is False. Ignored if seeds argument is not None.
- min_bin_freqint, default=1
To speed up the algorithm, accept only those bins with at least min_bin_freq points as seeds.
- cluster_allbool, default=True
If true, then all points are clustered, even those orphans that are not within any kernel. Orphans are assigned to the nearest kernel. If false, then orphans are given cluster label -1.
- n_jobsint, default=None
The number of jobs to use for the computation. This works by computing each of the n_init runs in parallel.
Nonemeans 1 unless in ajoblib.parallel_backendcontext.-1means using all processors. See Glossary for more details.- max_iterint, default=300
Maximum number of iterations, per seed point before the clustering operation terminates (for that seed point), if has not converged yet.
New in version 0.22.
- Attributes:
- cluster_centers_ndarray of shape (n_clusters, n_features)
Coordinates of cluster centers.
- labels_ndarray of shape (n_samples,)
Labels of each point.
- n_iter_int
Maximum number of iterations performed on each seed.
New in version 0.22.
- n_features_in_int
Number of features seen during fit.
New in version 0.24.
- feature_names_in_ndarray of shape (
n_features_in_,) Names of features seen during fit. Defined only when
Xhas feature names that are all strings.New in version 1.0.
See also
KMeansK-Means clustering.
Notes
Scalability:
Because this implementation uses a flat kernel and a Ball Tree to look up members of each kernel, the complexity will tend towards O(T*n*log(n)) in lower dimensions, with n the number of samples and T the number of points. In higher dimensions the complexity will tend towards O(T*n^2).
Scalability can be boosted by using fewer seeds, for example by using a higher value of min_bin_freq in the get_bin_seeds function.
Note that the estimate_bandwidth function is much less scalable than the mean shift algorithm and will be the bottleneck if it is used.
References
Dorin Comaniciu and Peter Meer, “Mean Shift: A robust approach toward feature space analysis”. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 2002. pp. 603-619.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.cluster import MeanShift >>> import numpy as np >>> X = np.array([[1, 1], [2, 1], [1, 0], ... [4, 7], [3, 5], [3, 6]]) >>> clustering = MeanShift(bandwidth=2).fit(X) >>> clustering.labels_ array([1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0]) >>> clustering.predict([[0, 0], [5, 5]]) array([1, 0]) >>> clustering MeanShift(bandwidth=2)
Methods
fit(X[, y])Perform clustering.
fit_predict(X[, y])Perform clustering on
Xand returns cluster labels.get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator.
predict(X)Predict the closest cluster each sample in X belongs to.
set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator.
- fit(X, y=None)[source]¶
Perform clustering.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Samples to cluster.
- yIgnored
Not used, present for API consistency by convention.
- Returns:
- selfobject
Fitted instance.
- fit_predict(X, y=None)[source]¶
Perform clustering on
Xand returns cluster labels.- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Input data.
- yIgnored
Not used, present for API consistency by convention.
- Returns:
- labelsndarray of shape (n_samples,), dtype=np.int64
Cluster labels.
- get_params(deep=True)[source]¶
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters:
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns:
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- predict(X)[source]¶
Predict the closest cluster each sample in X belongs to.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
New data to predict.
- Returns:
- labelsndarray of shape (n_samples,)
Index of the cluster each sample belongs to.
- set_params(**params)[source]¶
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters:
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
Examples using sklearn.cluster.MeanShift¶
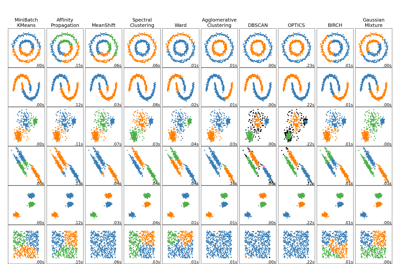
Comparing different clustering algorithms on toy datasets