Note
Click here to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
Comparison of Manifold Learning methods¶
An illustration of dimensionality reduction on the S-curve dataset with various manifold learning methods.
For a discussion and comparison of these algorithms, see the manifold module page
For a similar example, where the methods are applied to a sphere dataset, see Manifold Learning methods on a severed sphere
Note that the purpose of the MDS is to find a low-dimensional representation of the data (here 2D) in which the distances respect well the distances in the original high-dimensional space, unlike other manifold-learning algorithms, it does not seeks an isotropic representation of the data in the low-dimensional space.
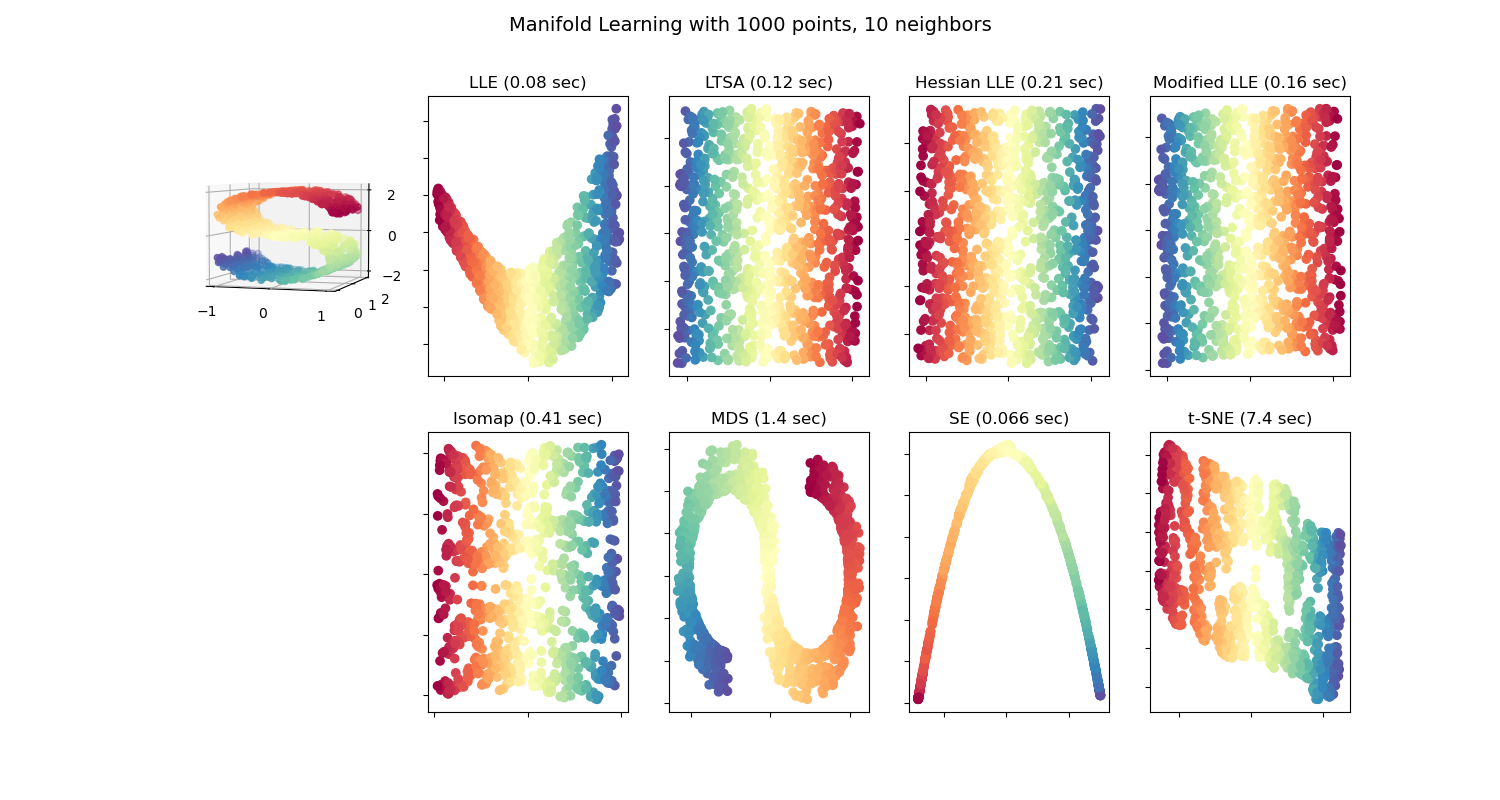
Out:
LLE: 0.08 sec
LTSA: 0.12 sec
Hessian LLE: 0.21 sec
Modified LLE: 0.16 sec
Isomap: 0.41 sec
MDS: 1.4 sec
SE: 0.066 sec
/home/circleci/project/sklearn/manifold/_t_sne.py:790: FutureWarning: The default learning rate in TSNE will change from 200.0 to 'auto' in 1.2.
warnings.warn(
/home/circleci/project/sklearn/manifold/_t_sne.py:982: FutureWarning: The PCA initialization in TSNE will change to have the standard deviation of PC1 equal to 1e-4 in 1.2. This will ensure better convergence.
warnings.warn(
t-SNE: 7.4 sec
# Author: Jake Vanderplas -- <vanderplas@astro.washington.edu>
from collections import OrderedDict
from functools import partial
from time import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from matplotlib.ticker import NullFormatter
from sklearn import manifold, datasets
# Next line to silence pyflakes. This import is needed.
Axes3D
n_points = 1000
X, color = datasets.make_s_curve(n_points, random_state=0)
n_neighbors = 10
n_components = 2
# Create figure
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 8))
fig.suptitle(
"Manifold Learning with %i points, %i neighbors" % (1000, n_neighbors), fontsize=14
)
# Add 3d scatter plot
ax = fig.add_subplot(251, projection="3d")
ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], X[:, 2], c=color, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
ax.view_init(4, -72)
# Set-up manifold methods
LLE = partial(
manifold.LocallyLinearEmbedding,
n_neighbors=n_neighbors,
n_components=n_components,
eigen_solver="auto",
)
methods = OrderedDict()
methods["LLE"] = LLE(method="standard")
methods["LTSA"] = LLE(method="ltsa")
methods["Hessian LLE"] = LLE(method="hessian")
methods["Modified LLE"] = LLE(method="modified")
methods["Isomap"] = manifold.Isomap(n_neighbors=n_neighbors, n_components=n_components)
methods["MDS"] = manifold.MDS(n_components, max_iter=100, n_init=1)
methods["SE"] = manifold.SpectralEmbedding(
n_components=n_components, n_neighbors=n_neighbors
)
methods["t-SNE"] = manifold.TSNE(n_components=n_components, init="pca", random_state=0)
# Plot results
for i, (label, method) in enumerate(methods.items()):
t0 = time()
Y = method.fit_transform(X)
t1 = time()
print("%s: %.2g sec" % (label, t1 - t0))
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 5, 2 + i + (i > 3))
ax.scatter(Y[:, 0], Y[:, 1], c=color, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
ax.set_title("%s (%.2g sec)" % (label, t1 - t0))
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(NullFormatter())
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(NullFormatter())
ax.axis("tight")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 10.330 seconds)
