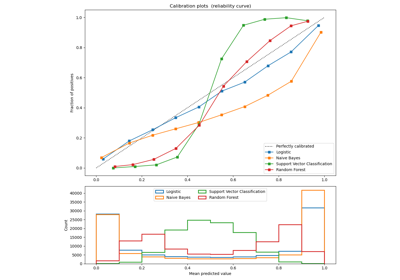
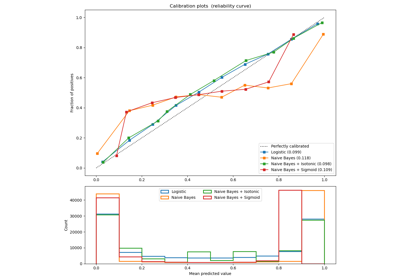
sklearn.calibration.calibration_curve¶
-
sklearn.calibration.calibration_curve(y_true, y_prob, *, normalize=False, n_bins=5, strategy='uniform')[source]¶ Compute true and predicted probabilities for a calibration curve.
The method assumes the inputs come from a binary classifier, and discretize the [0, 1] interval into bins.
Calibration curves may also be referred to as reliability diagrams.
Read more in the User Guide.
- Parameters
- y_truearray-like of shape (n_samples,)
True targets.
- y_probarray-like of shape (n_samples,)
Probabilities of the positive class.
- normalizebool, default=False
Whether y_prob needs to be normalized into the [0, 1] interval, i.e. is not a proper probability. If True, the smallest value in y_prob is linearly mapped onto 0 and the largest one onto 1.
- n_binsint, default=5
Number of bins to discretize the [0, 1] interval. A bigger number requires more data. Bins with no samples (i.e. without corresponding values in
y_prob) will not be returned, thus the returned arrays may have less thann_binsvalues.- strategy{‘uniform’, ‘quantile’}, default=’uniform’
Strategy used to define the widths of the bins.
- uniform
The bins have identical widths.
- quantile
The bins have the same number of samples and depend on
y_prob.
- Returns
- prob_truendarray of shape (n_bins,) or smaller
The proportion of samples whose class is the positive class, in each bin (fraction of positives).
- prob_predndarray of shape (n_bins,) or smaller
The mean predicted probability in each bin.
References
Alexandru Niculescu-Mizil and Rich Caruana (2005) Predicting Good Probabilities With Supervised Learning, in Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). See section 4 (Qualitative Analysis of Predictions).