Note
Click here to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
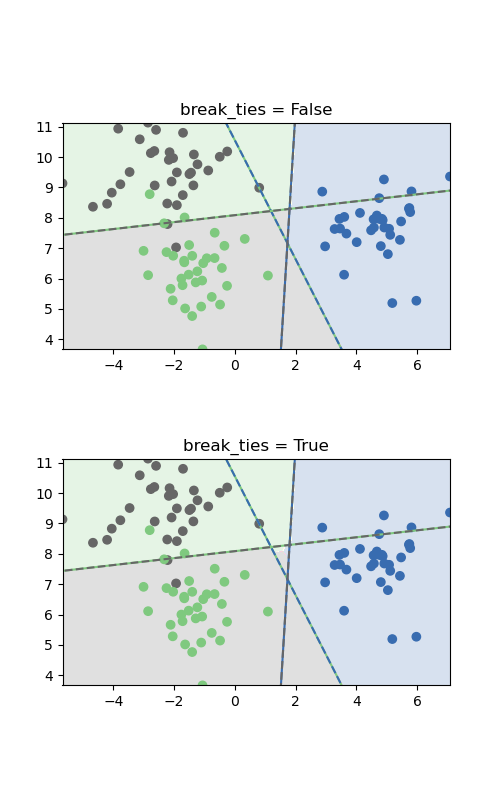
SVM Tie Breaking Example¶
Tie breaking is costly if decision_function_shape='ovr', and therefore it
is not enabled by default. This example illustrates the effect of the
break_ties parameter for a multiclass classification problem and
decision_function_shape='ovr'.
The two plots differ only in the area in the middle where the classes are
tied. If break_ties=False, all input in that area would be classified as
one class, whereas if break_ties=True, the tie-breaking mechanism will
create a non-convex decision boundary in that area.
print(__doc__)
# Code source: Andreas Mueller, Adrin Jalali
# License: BSD 3 clause
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
X, y = make_blobs(random_state=27)
fig, sub = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(5, 8))
titles = ("break_ties = False",
"break_ties = True")
for break_ties, title, ax in zip((False, True), titles, sub.flatten()):
svm = SVC(kernel="linear", C=1, break_ties=break_ties,
decision_function_shape='ovr').fit(X, y)
xlim = [X[:, 0].min(), X[:, 0].max()]
ylim = [X[:, 1].min(), X[:, 1].max()]
xs = np.linspace(xlim[0], xlim[1], 1000)
ys = np.linspace(ylim[0], ylim[1], 1000)
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(xs, ys)
pred = svm.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
colors = [plt.cm.Accent(i) for i in [0, 4, 7]]
points = ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap="Accent")
classes = [(0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2)]
line = np.linspace(X[:, 1].min() - 5, X[:, 1].max() + 5)
ax.imshow(-pred.reshape(xx.shape), cmap="Accent", alpha=.2,
extent=(xlim[0], xlim[1], ylim[1], ylim[0]))
for coef, intercept, col in zip(svm.coef_, svm.intercept_, classes):
line2 = -(line * coef[1] + intercept) / coef[0]
ax.plot(line2, line, "-", c=colors[col[0]])
ax.plot(line2, line, "--", c=colors[col[1]])
ax.set_xlim(xlim)
ax.set_ylim(ylim)
ax.set_title(title)
ax.set_aspect("equal")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.930 seconds)
