1.5. Stochastic Gradient Descent¶
Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) is a simple yet very efficient approach to discriminative learning of linear classifiers under convex loss functions such as (linear) Support Vector Machines and Logistic Regression. Even though SGD has been around in the machine learning community for a long time, it has received a considerable amount of attention just recently in the context of large-scale learning.
SGD has been successfully applied to large-scale and sparse machine learning problems often encountered in text classification and natural language processing. Given that the data is sparse, the classifiers in this module easily scale to problems with more than 10^5 training examples and more than 10^5 features.
The advantages of Stochastic Gradient Descent are:
- Efficiency.
- Ease of implementation (lots of opportunities for code tuning).
The disadvantages of Stochastic Gradient Descent include:
- SGD requires a number of hyperparameters such as the regularization parameter and the number of iterations.
- SGD is sensitive to feature scaling.
1.5.1. Classification¶
Warning
Make sure you permute (shuffle) your training data before fitting the
model or use shuffle=True to shuffle after each iteration.
The class SGDClassifier implements a plain stochastic gradient
descent learning routine which supports different loss functions and
penalties for classification.
As other classifiers, SGD has to be fitted with two arrays: an array X of size [n_samples, n_features] holding the training samples, and an array Y of size [n_samples] holding the target values (class labels) for the training samples:
>>> from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier
>>> X = [[0., 0.], [1., 1.]]
>>> y = [0, 1]
>>> clf = SGDClassifier(loss="hinge", penalty="l2", max_iter=5)
>>> clf.fit(X, y)
SGDClassifier(alpha=0.0001, average=False, class_weight=None,
early_stopping=False, epsilon=0.1, eta0=0.0, fit_intercept=True,
l1_ratio=0.15, learning_rate='optimal', loss='hinge', max_iter=5,
n_iter_no_change=5, n_jobs=None, penalty='l2', power_t=0.5,
random_state=None, shuffle=True, tol=0.001,
validation_fraction=0.1, verbose=0, warm_start=False)
After being fitted, the model can then be used to predict new values:
>>> clf.predict([[2., 2.]])
array([1])
SGD fits a linear model to the training data. The member coef_ holds
the model parameters:
>>> clf.coef_
array([[9.9..., 9.9...]])
Member intercept_ holds the intercept (aka offset or bias):
>>> clf.intercept_
array([-9.9...])
Whether or not the model should use an intercept, i.e. a biased
hyperplane, is controlled by the parameter fit_intercept.
To get the signed distance to the hyperplane use SGDClassifier.decision_function:
>>> clf.decision_function([[2., 2.]])
array([29.6...])
The concrete loss function can be set via the loss
parameter. SGDClassifier supports the following loss functions:
loss="hinge": (soft-margin) linear Support Vector Machine,loss="modified_huber": smoothed hinge loss,loss="log": logistic regression,- and all regression losses below.
The first two loss functions are lazy, they only update the model parameters if an example violates the margin constraint, which makes training very efficient and may result in sparser models, even when L2 penalty is used.
Using loss="log" or loss="modified_huber" enables the
predict_proba method, which gives a vector of probability estimates
\(P(y|x)\) per sample \(x\):
>>> clf = SGDClassifier(loss="log", max_iter=5).fit(X, y)
>>> clf.predict_proba([[1., 1.]])
array([[0.00..., 0.99...]])
The concrete penalty can be set via the penalty parameter.
SGD supports the following penalties:
penalty="l2": L2 norm penalty oncoef_.penalty="l1": L1 norm penalty oncoef_.penalty="elasticnet": Convex combination of L2 and L1;(1 - l1_ratio) * L2 + l1_ratio * L1.
The default setting is penalty="l2". The L1 penalty leads to sparse
solutions, driving most coefficients to zero. The Elastic Net solves
some deficiencies of the L1 penalty in the presence of highly correlated
attributes. The parameter l1_ratio controls the convex combination
of L1 and L2 penalty.
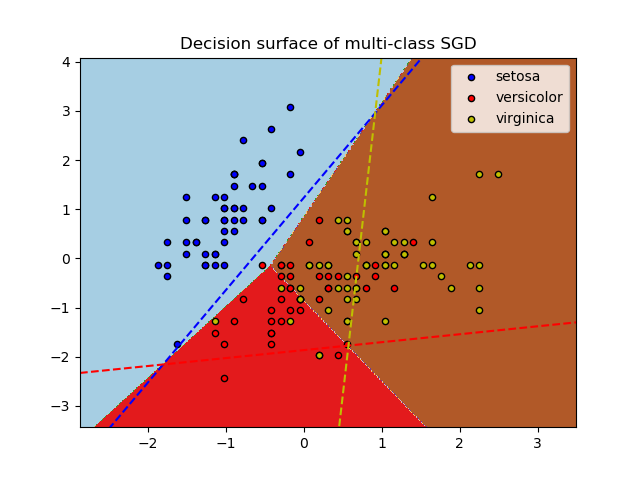
SGDClassifier supports multi-class classification by combining
multiple binary classifiers in a “one versus all” (OVA) scheme. For each
of the \(K\) classes, a binary classifier is learned that discriminates
between that and all other \(K-1\) classes. At testing time, we compute the
confidence score (i.e. the signed distances to the hyperplane) for each
classifier and choose the class with the highest confidence. The Figure
below illustrates the OVA approach on the iris dataset. The dashed
lines represent the three OVA classifiers; the background colors show
the decision surface induced by the three classifiers.
In the case of multi-class classification coef_ is a two-dimensional
array of shape=[n_classes, n_features] and intercept_ is a
one-dimensional array of shape=[n_classes]. The i-th row of coef_ holds
the weight vector of the OVA classifier for the i-th class; classes are
indexed in ascending order (see attribute classes_).
Note that, in principle, since they allow to create a probability model,
loss="log" and loss="modified_huber" are more suitable for
one-vs-all classification.
SGDClassifier supports both weighted classes and weighted
instances via the fit parameters class_weight and sample_weight. See
the examples below and the docstring of SGDClassifier.fit for
further information.
Examples:
SGDClassifier supports averaged SGD (ASGD). Averaging can be enabled
by setting `average=True`. ASGD works by averaging the coefficients
of the plain SGD over each iteration over a sample. When using ASGD
the learning rate can be larger and even constant leading on some
datasets to a speed up in training time.
For classification with a logistic loss, another variant of SGD with an
averaging strategy is available with Stochastic Average Gradient (SAG)
algorithm, available as a solver in LogisticRegression.
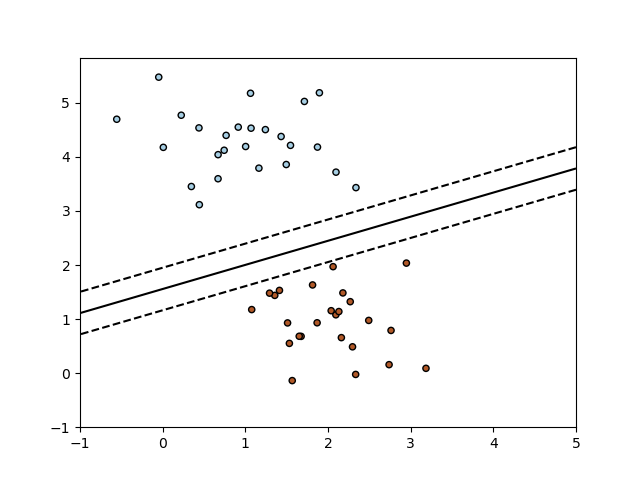
1.5.2. Regression¶
The class SGDRegressor implements a plain stochastic gradient
descent learning routine which supports different loss functions and
penalties to fit linear regression models. SGDRegressor is
well suited for regression problems with a large number of training
samples (> 10.000), for other problems we recommend Ridge,
Lasso, or ElasticNet.
The concrete loss function can be set via the loss
parameter. SGDRegressor supports the following loss functions:
loss="squared_loss": Ordinary least squares,loss="huber": Huber loss for robust regression,loss="epsilon_insensitive": linear Support Vector Regression.
The Huber and epsilon-insensitive loss functions can be used for
robust regression. The width of the insensitive region has to be
specified via the parameter epsilon. This parameter depends on the
scale of the target variables.
SGDRegressor supports averaged SGD as SGDClassifier.
Averaging can be enabled by setting `average=True`.
For regression with a squared loss and a l2 penalty, another variant of
SGD with an averaging strategy is available with Stochastic Average
Gradient (SAG) algorithm, available as a solver in Ridge.
1.5.3. Stochastic Gradient Descent for sparse data¶
Note
The sparse implementation produces slightly different results than the dense implementation due to a shrunk learning rate for the intercept.
There is built-in support for sparse data given in any matrix in a format supported by scipy.sparse. For maximum efficiency, however, use the CSR matrix format as defined in scipy.sparse.csr_matrix.
1.5.4. Complexity¶
The major advantage of SGD is its efficiency, which is basically linear in the number of training examples. If X is a matrix of size (n, p) training has a cost of \(O(k n \bar p)\), where k is the number of iterations (epochs) and \(\bar p\) is the average number of non-zero attributes per sample.
Recent theoretical results, however, show that the runtime to get some desired optimization accuracy does not increase as the training set size increases.
1.5.5. Stopping criterion¶
The classes SGDClassifier and SGDRegressor provide two
criteria to stop the algorithm when a given level of convergence is reached:
- With
early_stopping=True, the input data is split into a training set and a validation set. The model is then fitted on the training set, and the stopping criterion is based on the prediction score computed on the validation set. The size of the validation set can be changed with the parametervalidation_fraction.- With
early_stopping=False, the model is fitted on the entire input data and the stopping criterion is based on the objective function computed on the input data.
In both cases, the criterion is evaluated once by epoch, and the algorithm stops
when the criterion does not improve n_iter_no_change times in a row. The
improvement is evaluated with a tolerance tol, and the algorithm stops in
any case after a maximum number of iteration max_iter.
1.5.6. Tips on Practical Use¶
Stochastic Gradient Descent is sensitive to feature scaling, so it is highly recommended to scale your data. For example, scale each attribute on the input vector X to [0,1] or [-1,+1], or standardize it to have mean 0 and variance 1. Note that the same scaling must be applied to the test vector to obtain meaningful results. This can be easily done using
StandardScaler:from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler scaler = StandardScaler() scaler.fit(X_train) # Don't cheat - fit only on training data X_train = scaler.transform(X_train) X_test = scaler.transform(X_test) # apply same transformation to test dataIf your attributes have an intrinsic scale (e.g. word frequencies or indicator features) scaling is not needed.
Finding a reasonable regularization term \(\alpha\) is best done using
GridSearchCV, usually in the range10.0**-np.arange(1,7).Empirically, we found that SGD converges after observing approx. 10^6 training samples. Thus, a reasonable first guess for the number of iterations is
max_iter = np.ceil(10**6 / n), wherenis the size of the training set.If you apply SGD to features extracted using PCA we found that it is often wise to scale the feature values by some constant
csuch that the average L2 norm of the training data equals one.We found that Averaged SGD works best with a larger number of features and a higher eta0
References:
- “Efficient BackProp” Y. LeCun, L. Bottou, G. Orr, K. Müller - In Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade 1998.
1.5.7. Mathematical formulation¶
Given a set of training examples \((x_1, y_1), \ldots, (x_n, y_n)\) where \(x_i \in \mathbf{R}^m\) and \(y_i \in \{-1,1\}\), our goal is to learn a linear scoring function \(f(x) = w^T x + b\) with model parameters \(w \in \mathbf{R}^m\) and intercept \(b \in \mathbf{R}\). In order to make predictions, we simply look at the sign of \(f(x)\). A common choice to find the model parameters is by minimizing the regularized training error given by
where \(L\) is a loss function that measures model (mis)fit and \(R\) is a regularization term (aka penalty) that penalizes model complexity; \(\alpha > 0\) is a non-negative hyperparameter.
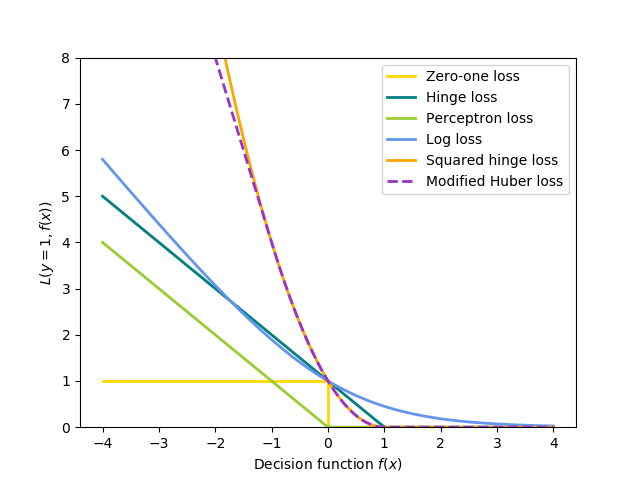
Different choices for \(L\) entail different classifiers such as
- Hinge: (soft-margin) Support Vector Machines.
- Log: Logistic Regression.
- Least-Squares: Ridge Regression.
- Epsilon-Insensitive: (soft-margin) Support Vector Regression.
All of the above loss functions can be regarded as an upper bound on the misclassification error (Zero-one loss) as shown in the Figure below.
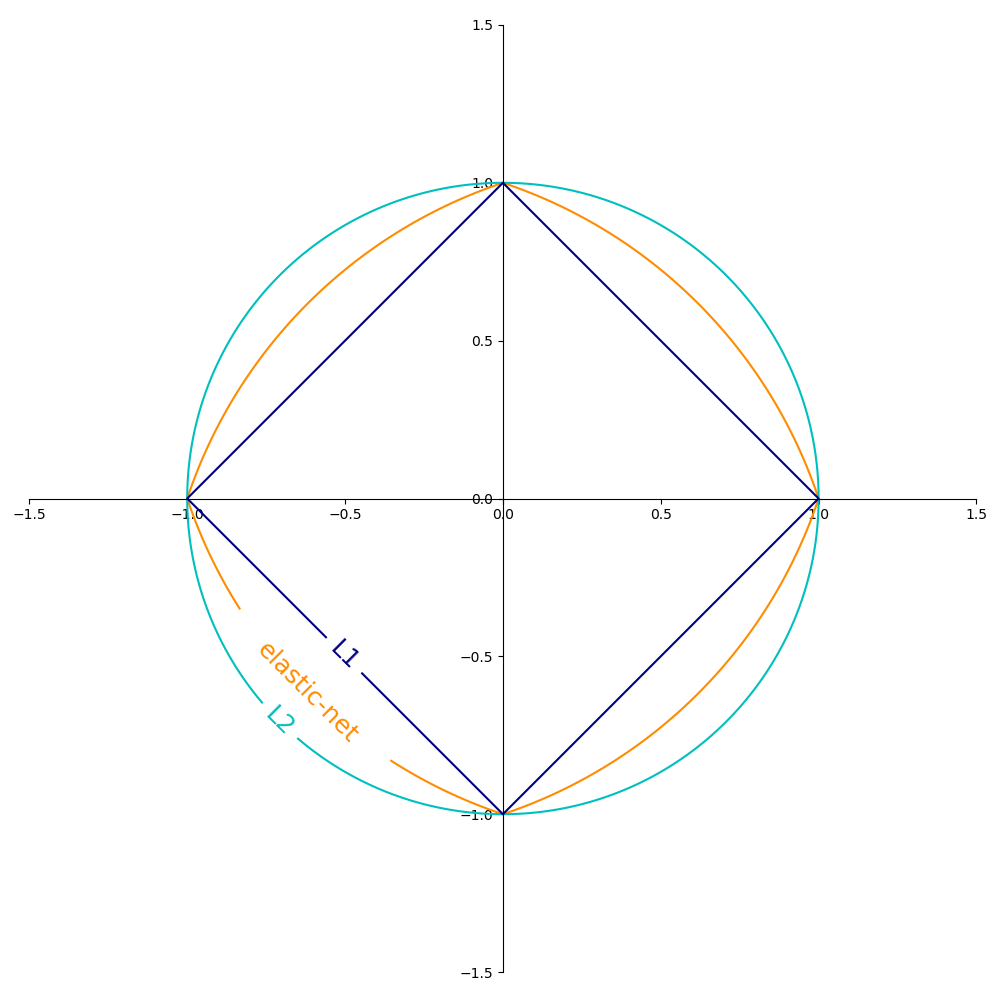
Popular choices for the regularization term \(R\) include:
- L2 norm: \(R(w) := \frac{1}{2} \sum_{i=1}^{n} w_i^2\),
- L1 norm: \(R(w) := \sum_{i=1}^{n} |w_i|\), which leads to sparse solutions.
- Elastic Net: \(R(w) := \frac{\rho}{2} \sum_{i=1}^{n} w_i^2 + (1-\rho) \sum_{i=1}^{n} |w_i|\), a convex combination of L2 and L1, where \(\rho\) is given by
1 - l1_ratio.
The Figure below shows the contours of the different regularization terms in the parameter space when \(R(w) = 1\).
1.5.7.1. SGD¶
Stochastic gradient descent is an optimization method for unconstrained optimization problems. In contrast to (batch) gradient descent, SGD approximates the true gradient of \(E(w,b)\) by considering a single training example at a time.
The class SGDClassifier implements a first-order SGD learning
routine. The algorithm iterates over the training examples and for each
example updates the model parameters according to the update rule given by
where \(\eta\) is the learning rate which controls the step-size in the parameter space. The intercept \(b\) is updated similarly but without regularization.
The learning rate \(\eta\) can be either constant or gradually decaying. For
classification, the default learning rate schedule (learning_rate='optimal')
is given by
where \(t\) is the time step (there are a total of n_samples * n_iter
time steps), \(t_0\) is determined based on a heuristic proposed by Léon Bottou
such that the expected initial updates are comparable with the expected
size of the weights (this assuming that the norm of the training samples is
approx. 1). The exact definition can be found in _init_t in BaseSGD.
For regression the default learning rate schedule is inverse scaling
(learning_rate='invscaling'), given by
where \(eta_0\) and \(power\_t\) are hyperparameters chosen by the
user via eta0 and power_t, resp.
For a constant learning rate use learning_rate='constant' and use eta0
to specify the learning rate.
For an adaptively decreasing learning rate, use learning_rate='adaptive'
and use eta0 to specify the starting learning rate. When the stopping
criterion is reached, the learning rate is divided by 5, and the algorithm
does not stop. The algorithm stops when the learning rate goes below 1e-6.
The model parameters can be accessed through the members coef_ and
intercept_:
- Member
coef_holds the weights \(w\)- Member
intercept_holds \(b\)
References:
- “Solving large scale linear prediction problems using stochastic gradient descent algorithms” T. Zhang - In Proceedings of ICML ‘04.
- “Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net” H. Zou, T. Hastie - Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B, 67 (2), 301-320.
- “Towards Optimal One Pass Large Scale Learning with Averaged Stochastic Gradient Descent” Xu, Wei
1.5.8. Implementation details¶
The implementation of SGD is influenced by the Stochastic Gradient SVM of Léon Bottou. Similar to SvmSGD, the weight vector is represented as the product of a scalar and a vector which allows an efficient weight update in the case of L2 regularization. In the case of sparse feature vectors, the intercept is updated with a smaller learning rate (multiplied by 0.01) to account for the fact that it is updated more frequently. Training examples are picked up sequentially and the learning rate is lowered after each observed example. We adopted the learning rate schedule from Shalev-Shwartz et al. 2007. For multi-class classification, a “one versus all” approach is used. We use the truncated gradient algorithm proposed by Tsuruoka et al. 2009 for L1 regularization (and the Elastic Net). The code is written in Cython.
References:
- “Stochastic Gradient Descent” L. Bottou - Website, 2010.
- “The Tradeoffs of Large Scale Machine Learning” L. Bottou - Website, 2011.
- “Pegasos: Primal estimated sub-gradient solver for svm” S. Shalev-Shwartz, Y. Singer, N. Srebro - In Proceedings of ICML ‘07.
- “Stochastic gradient descent training for l1-regularized log-linear models with cumulative penalty” Y. Tsuruoka, J. Tsujii, S. Ananiadou - In Proceedings of the AFNLP/ACL ‘09.