Decision Tree Regression with AdaBoost¶
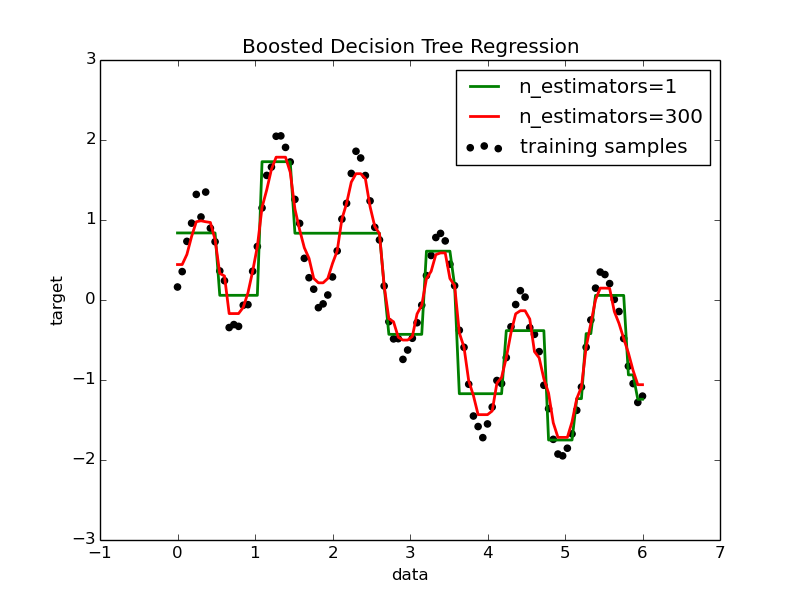
A decision tree is boosted using the AdaBoost.R2 [1] algorithm on a 1D sinusoidal dataset with a small amount of Gaussian noise. 299 boosts (300 decision trees) is compared with a single decision tree regressor. As the number of boosts is increased the regressor can fit more detail.
| [1] |
|
Python source code: plot_adaboost_regression.py
print(__doc__)
# Author: Noel Dawe <noel.dawe@gmail.com>
#
# License: BSD 3 clause
# importing necessary libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostRegressor
# Create the dataset
rng = np.random.RandomState(1)
X = np.linspace(0, 6, 100)[:, np.newaxis]
y = np.sin(X).ravel() + np.sin(6 * X).ravel() + rng.normal(0, 0.1, X.shape[0])
# Fit regression model
clf_1 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=4)
clf_2 = AdaBoostRegressor(DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=4),
n_estimators=300, random_state=rng)
clf_1.fit(X, y)
clf_2.fit(X, y)
# Predict
y_1 = clf_1.predict(X)
y_2 = clf_2.predict(X)
# Plot the results
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(X, y, c="k", label="training samples")
plt.plot(X, y_1, c="g", label="n_estimators=1", linewidth=2)
plt.plot(X, y_2, c="r", label="n_estimators=300", linewidth=2)
plt.xlabel("data")
plt.ylabel("target")
plt.title("Boosted Decision Tree Regression")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Total running time of the example: 0.44 seconds ( 0 minutes 0.44 seconds)

