sklearn.inspection.DecisionBoundaryDisplay¶
- class sklearn.inspection.DecisionBoundaryDisplay(*, xx0, xx1, response, xlabel=None, ylabel=None)[source]¶
Decisions boundary visualization.
It is recommended to use
from_estimatorto create aDecisionBoundaryDisplay. All parameters are stored as attributes.Read more in the User Guide.
New in version 1.1.
- Parameters:
- xx0ndarray of shape (grid_resolution, grid_resolution)
First output of
meshgrid.- xx1ndarray of shape (grid_resolution, grid_resolution)
Second output of
meshgrid.- responsendarray of shape (grid_resolution, grid_resolution)
Values of the response function.
- xlabelstr, default=None
Default label to place on x axis.
- ylabelstr, default=None
Default label to place on y axis.
- Attributes:
- surface_matplotlib
QuadContourSetorQuadMesh If
plot_methodis ‘contour’ or ‘contourf’,surface_is aQuadContourSet. Ifplot_methodis ‘pcolormesh’,surface_is aQuadMesh.- ax_matplotlib Axes
Axes with confusion matrix.
- figure_matplotlib Figure
Figure containing the confusion matrix.
- surface_matplotlib
See also
DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimatorPlot decision boundary given an estimator.
Examples
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> import numpy as np >>> from sklearn.datasets import load_iris >>> from sklearn.inspection import DecisionBoundaryDisplay >>> from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier >>> iris = load_iris() >>> feature_1, feature_2 = np.meshgrid( ... np.linspace(iris.data[:, 0].min(), iris.data[:, 0].max()), ... np.linspace(iris.data[:, 1].min(), iris.data[:, 1].max()) ... ) >>> grid = np.vstack([feature_1.ravel(), feature_2.ravel()]).T >>> tree = DecisionTreeClassifier().fit(iris.data[:, :2], iris.target) >>> y_pred = np.reshape(tree.predict(grid), feature_1.shape) >>> display = DecisionBoundaryDisplay( ... xx0=feature_1, xx1=feature_2, response=y_pred ... ) >>> display.plot() <...> >>> display.ax_.scatter( ... iris.data[:, 0], iris.data[:, 1], c=iris.target, edgecolor="black" ... ) <...> >>> plt.show()
Methods
from_estimator(estimator, X, *[, ...])Plot decision boundary given an estimator.
plot([plot_method, ax, xlabel, ylabel])Plot visualization.
- classmethod from_estimator(estimator, X, *, grid_resolution=100, eps=1.0, plot_method='contourf', response_method='auto', xlabel=None, ylabel=None, ax=None, **kwargs)[source]¶
Plot decision boundary given an estimator.
Read more in the User Guide.
- Parameters:
- estimatorobject
Trained estimator used to plot the decision boundary.
- X{array-like, sparse matrix, dataframe} of shape (n_samples, 2)
Input data that should be only 2-dimensional.
- grid_resolutionint, default=100
Number of grid points to use for plotting decision boundary. Higher values will make the plot look nicer but be slower to render.
- epsfloat, default=1.0
Extends the minimum and maximum values of X for evaluating the response function.
- plot_method{‘contourf’, ‘contour’, ‘pcolormesh’}, default=’contourf’
Plotting method to call when plotting the response. Please refer to the following matplotlib documentation for details:
contourf,contour,pcolormesh.- response_method{‘auto’, ‘predict_proba’, ‘decision_function’, ‘predict’}, default=’auto’
Specifies whether to use predict_proba, decision_function, predict as the target response. If set to ‘auto’, the response method is tried in the following order: decision_function, predict_proba, predict. For multiclass problems, predict is selected when
response_method="auto".- xlabelstr, default=None
The label used for the x-axis. If
None, an attempt is made to extract a label fromXif it is a dataframe, otherwise an empty string is used.- ylabelstr, default=None
The label used for the y-axis. If
None, an attempt is made to extract a label fromXif it is a dataframe, otherwise an empty string is used.- axMatplotlib axes, default=None
Axes object to plot on. If
None, a new figure and axes is created.- **kwargsdict
Additional keyword arguments to be passed to the
plot_method.
- Returns:
- display
DecisionBoundaryDisplay Object that stores the result.
- display
See also
DecisionBoundaryDisplayDecision boundary visualization.
ConfusionMatrixDisplay.from_estimatorPlot the confusion matrix given an estimator, the data, and the label.
ConfusionMatrixDisplay.from_predictionsPlot the confusion matrix given the true and predicted labels.
Examples
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> from sklearn.datasets import load_iris >>> from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression >>> from sklearn.inspection import DecisionBoundaryDisplay >>> iris = load_iris() >>> X = iris.data[:, :2] >>> classifier = LogisticRegression().fit(X, iris.target) >>> disp = DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimator( ... classifier, X, response_method="predict", ... xlabel=iris.feature_names[0], ylabel=iris.feature_names[1], ... alpha=0.5, ... ) >>> disp.ax_.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=iris.target, edgecolor="k") <...> >>> plt.show()
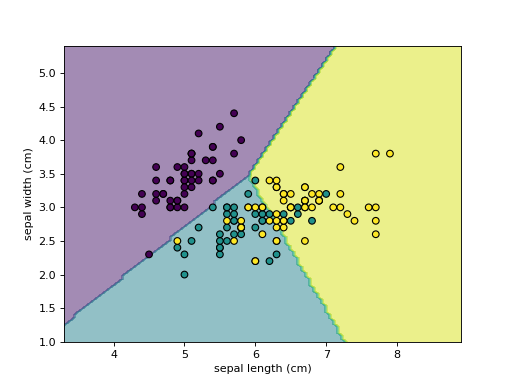
- plot(plot_method='contourf', ax=None, xlabel=None, ylabel=None, **kwargs)[source]¶
Plot visualization.
- Parameters:
- plot_method{‘contourf’, ‘contour’, ‘pcolormesh’}, default=’contourf’
Plotting method to call when plotting the response. Please refer to the following matplotlib documentation for details:
contourf,contour,pcolormesh.- axMatplotlib axes, default=None
Axes object to plot on. If
None, a new figure and axes is created.- xlabelstr, default=None
Overwrite the x-axis label.
- ylabelstr, default=None
Overwrite the y-axis label.
- **kwargsdict
Additional keyword arguments to be passed to the
plot_method.
- Returns:
- display:
DecisionBoundaryDisplay Object that stores computed values.
- display: