sklearn.datasets.make_multilabel_classification¶
- sklearn.datasets.make_multilabel_classification(n_samples=100, n_features=20, *, n_classes=5, n_labels=2, length=50, allow_unlabeled=True, sparse=False, return_indicator='dense', return_distributions=False, random_state=None)[source]¶
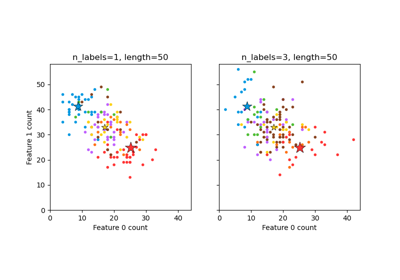
Generate a random multilabel classification problem.
- For each sample, the generative process is:
pick the number of labels: n ~ Poisson(n_labels)
n times, choose a class c: c ~ Multinomial(theta)
pick the document length: k ~ Poisson(length)
k times, choose a word: w ~ Multinomial(theta_c)
In the above process, rejection sampling is used to make sure that n is never zero or more than
n_classes, and that the document length is never zero. Likewise, we reject classes which have already been chosen.Read more in the User Guide.
- Parameters:
- n_samplesint, default=100
The number of samples.
- n_featuresint, default=20
The total number of features.
- n_classesint, default=5
The number of classes of the classification problem.
- n_labelsint, default=2
The average number of labels per instance. More precisely, the number of labels per sample is drawn from a Poisson distribution with
n_labelsas its expected value, but samples are bounded (using rejection sampling) byn_classes, and must be nonzero ifallow_unlabeledis False.- lengthint, default=50
The sum of the features (number of words if documents) is drawn from a Poisson distribution with this expected value.
- allow_unlabeledbool, default=True
If
True, some instances might not belong to any class.- sparsebool, default=False
If
True, return a sparse feature matrix.New in version 0.17: parameter to allow sparse output.
- return_indicator{‘dense’, ‘sparse’} or False, default=’dense’
If
'dense'returnYin the dense binary indicator format. If'sparse'returnYin the sparse binary indicator format.Falsereturns a list of lists of labels.- return_distributionsbool, default=False
If
True, return the prior class probability and conditional probabilities of features given classes, from which the data was drawn.- random_stateint, RandomState instance or None, default=None
Determines random number generation for dataset creation. Pass an int for reproducible output across multiple function calls. See Glossary.
- Returns:
- Xndarray of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The generated samples.
- Y{ndarray, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_classes)
The label sets. Sparse matrix should be of CSR format.
- p_cndarray of shape (n_classes,)
The probability of each class being drawn. Only returned if
return_distributions=True.- p_w_cndarray of shape (n_features, n_classes)
The probability of each feature being drawn given each class. Only returned if
return_distributions=True.