sklearn.covariance.ShrunkCovariance¶
- class sklearn.covariance.ShrunkCovariance(*, store_precision=True, assume_centered=False, shrinkage=0.1)[source]¶
Covariance estimator with shrinkage.
Read more in the User Guide.
- Parameters:
- store_precisionbool, default=True
Specify if the estimated precision is stored.
- assume_centeredbool, default=False
If True, data will not be centered before computation. Useful when working with data whose mean is almost, but not exactly zero. If False, data will be centered before computation.
- shrinkagefloat, default=0.1
Coefficient in the convex combination used for the computation of the shrunk estimate. Range is [0, 1].
- Attributes:
- covariance_ndarray of shape (n_features, n_features)
Estimated covariance matrix
- location_ndarray of shape (n_features,)
Estimated location, i.e. the estimated mean.
- precision_ndarray of shape (n_features, n_features)
Estimated pseudo inverse matrix. (stored only if store_precision is True)
- n_features_in_int
Number of features seen during fit.
New in version 0.24.
- feature_names_in_ndarray of shape (
n_features_in_,) Names of features seen during fit. Defined only when
Xhas feature names that are all strings.New in version 1.0.
See also
EllipticEnvelopeAn object for detecting outliers in a Gaussian distributed dataset.
EmpiricalCovarianceMaximum likelihood covariance estimator.
GraphicalLassoSparse inverse covariance estimation with an l1-penalized estimator.
GraphicalLassoCVSparse inverse covariance with cross-validated choice of the l1 penalty.
LedoitWolfLedoitWolf Estimator.
MinCovDetMinimum Covariance Determinant (robust estimator of covariance).
OASOracle Approximating Shrinkage Estimator.
Notes
The regularized covariance is given by:
(1 - shrinkage) * cov + shrinkage * mu * np.identity(n_features)
where mu = trace(cov) / n_features
Examples
>>> import numpy as np >>> from sklearn.covariance import ShrunkCovariance >>> from sklearn.datasets import make_gaussian_quantiles >>> real_cov = np.array([[.8, .3], ... [.3, .4]]) >>> rng = np.random.RandomState(0) >>> X = rng.multivariate_normal(mean=[0, 0], ... cov=real_cov, ... size=500) >>> cov = ShrunkCovariance().fit(X) >>> cov.covariance_ array([[0.7387..., 0.2536...], [0.2536..., 0.4110...]]) >>> cov.location_ array([0.0622..., 0.0193...])
Methods
error_norm(comp_cov[, norm, scaling, squared])Compute the Mean Squared Error between two covariance estimators.
fit(X[, y])Fit the shrunk covariance model to X.
get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator.
Getter for the precision matrix.
mahalanobis(X)Compute the squared Mahalanobis distances of given observations.
score(X_test[, y])Compute the log-likelihood of
X_testunder the estimated Gaussian model.set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator.
- error_norm(comp_cov, norm='frobenius', scaling=True, squared=True)[source]¶
Compute the Mean Squared Error between two covariance estimators.
- Parameters:
- comp_covarray-like of shape (n_features, n_features)
The covariance to compare with.
- norm{“frobenius”, “spectral”}, default=”frobenius”
The type of norm used to compute the error. Available error types: - ‘frobenius’ (default): sqrt(tr(A^t.A)) - ‘spectral’: sqrt(max(eigenvalues(A^t.A)) where A is the error
(comp_cov - self.covariance_).- scalingbool, default=True
If True (default), the squared error norm is divided by n_features. If False, the squared error norm is not rescaled.
- squaredbool, default=True
Whether to compute the squared error norm or the error norm. If True (default), the squared error norm is returned. If False, the error norm is returned.
- Returns:
- resultfloat
The Mean Squared Error (in the sense of the Frobenius norm) between
selfandcomp_covcovariance estimators.
- fit(X, y=None)[source]¶
Fit the shrunk covariance model to X.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Training data, where
n_samplesis the number of samples andn_featuresis the number of features.- yIgnored
Not used, present for API consistency by convention.
- Returns:
- selfobject
Returns the instance itself.
- get_params(deep=True)[source]¶
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters:
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns:
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- get_precision()[source]¶
Getter for the precision matrix.
- Returns:
- precision_array-like of shape (n_features, n_features)
The precision matrix associated to the current covariance object.
- mahalanobis(X)[source]¶
Compute the squared Mahalanobis distances of given observations.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The observations, the Mahalanobis distances of the which we compute. Observations are assumed to be drawn from the same distribution than the data used in fit.
- Returns:
- distndarray of shape (n_samples,)
Squared Mahalanobis distances of the observations.
- score(X_test, y=None)[source]¶
Compute the log-likelihood of
X_testunder the estimated Gaussian model.The Gaussian model is defined by its mean and covariance matrix which are represented respectively by
self.location_andself.covariance_.- Parameters:
- X_testarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Test data of which we compute the likelihood, where
n_samplesis the number of samples andn_featuresis the number of features.X_testis assumed to be drawn from the same distribution than the data used in fit (including centering).- yIgnored
Not used, present for API consistency by convention.
- Returns:
- resfloat
The log-likelihood of
X_testwithself.location_andself.covariance_as estimators of the Gaussian model mean and covariance matrix respectively.
- set_params(**params)[source]¶
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters:
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
Examples using sklearn.covariance.ShrunkCovariance¶
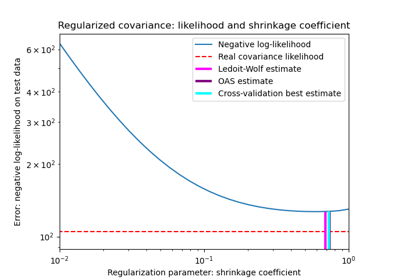
Shrinkage covariance estimation: LedoitWolf vs OAS and max-likelihood
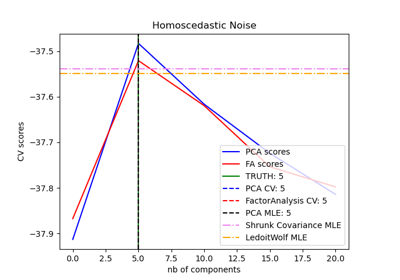
Model selection with Probabilistic PCA and Factor Analysis (FA)
