sklearn.preprocessing.KBinsDiscretizer¶
- class sklearn.preprocessing.KBinsDiscretizer(n_bins=5, *, encode='onehot', strategy='quantile', dtype=None)[source]¶
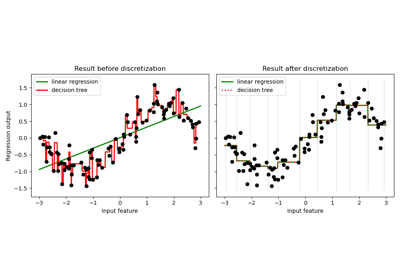
Bin continuous data into intervals.
Read more in the User Guide.
New in version 0.20.
- Parameters
- n_binsint or array-like of shape (n_features,), default=5
The number of bins to produce. Raises ValueError if
n_bins < 2.- encode{‘onehot’, ‘onehot-dense’, ‘ordinal’}, default=’onehot’
Method used to encode the transformed result.
‘onehot’: Encode the transformed result with one-hot encoding and return a sparse matrix. Ignored features are always stacked to the right.
‘onehot-dense’: Encode the transformed result with one-hot encoding and return a dense array. Ignored features are always stacked to the right.
‘ordinal’: Return the bin identifier encoded as an integer value.
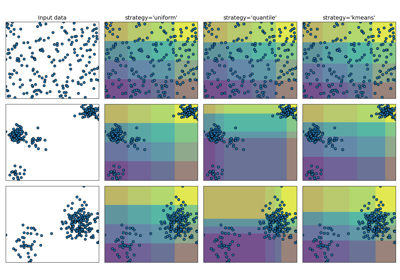
- strategy{‘uniform’, ‘quantile’, ‘kmeans’}, default=’quantile’
Strategy used to define the widths of the bins.
‘uniform’: All bins in each feature have identical widths.
‘quantile’: All bins in each feature have the same number of points.
‘kmeans’: Values in each bin have the same nearest center of a 1D k-means cluster.
- dtype{np.float32, np.float64}, default=None
The desired data-type for the output. If None, output dtype is consistent with input dtype. Only np.float32 and np.float64 are supported.
New in version 0.24.
- Attributes
- bin_edges_ndarray of ndarray of shape (n_features,)
The edges of each bin. Contain arrays of varying shapes
(n_bins_, )Ignored features will have empty arrays.- n_bins_ndarray of shape (n_features,), dtype=np.int_
Number of bins per feature. Bins whose width are too small (i.e., <= 1e-8) are removed with a warning.
- n_features_in_int
Number of features seen during fit.
New in version 0.24.
- feature_names_in_ndarray of shape (
n_features_in_,) Names of features seen during fit. Defined only when
Xhas feature names that are all strings.New in version 1.0.
See also
BinarizerClass used to bin values as
0or1based on a parameterthreshold.
Notes
In bin edges for feature
i, the first and last values are used only forinverse_transform. During transform, bin edges are extended to:np.concatenate([-np.inf, bin_edges_[i][1:-1], np.inf])
You can combine
KBinsDiscretizerwithColumnTransformerif you only want to preprocess part of the features.KBinsDiscretizermight produce constant features (e.g., whenencode = 'onehot'and certain bins do not contain any data). These features can be removed with feature selection algorithms (e.g.,VarianceThreshold).Examples
>>> from sklearn.preprocessing import KBinsDiscretizer >>> X = [[-2, 1, -4, -1], ... [-1, 2, -3, -0.5], ... [ 0, 3, -2, 0.5], ... [ 1, 4, -1, 2]] >>> est = KBinsDiscretizer(n_bins=3, encode='ordinal', strategy='uniform') >>> est.fit(X) KBinsDiscretizer(...) >>> Xt = est.transform(X) >>> Xt array([[ 0., 0., 0., 0.], [ 1., 1., 1., 0.], [ 2., 2., 2., 1.], [ 2., 2., 2., 2.]])
Sometimes it may be useful to convert the data back into the original feature space. The
inverse_transformfunction converts the binned data into the original feature space. Each value will be equal to the mean of the two bin edges.>>> est.bin_edges_[0] array([-2., -1., 0., 1.]) >>> est.inverse_transform(Xt) array([[-1.5, 1.5, -3.5, -0.5], [-0.5, 2.5, -2.5, -0.5], [ 0.5, 3.5, -1.5, 0.5], [ 0.5, 3.5, -1.5, 1.5]])
Methods
fit(X[, y])Fit the estimator.
fit_transform(X[, y])Fit to data, then transform it.
get_feature_names_out([input_features])Get output feature names.
get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator.
Transform discretized data back to original feature space.
set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator.
transform(X)Discretize the data.
- fit(X, y=None)[source]¶
Fit the estimator.
- Parameters
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Data to be discretized.
- yNone
Ignored. This parameter exists only for compatibility with
Pipeline.
- Returns
- selfobject
Returns the instance itself.
- fit_transform(X, y=None, **fit_params)[source]¶
Fit to data, then transform it.
Fits transformer to
Xandywith optional parametersfit_paramsand returns a transformed version ofX.- Parameters
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Input samples.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs), default=None
Target values (None for unsupervised transformations).
- **fit_paramsdict
Additional fit parameters.
- Returns
- X_newndarray array of shape (n_samples, n_features_new)
Transformed array.
- get_feature_names_out(input_features=None)[source]¶
Get output feature names.
- Parameters
- input_featuresarray-like of str or None, default=None
Input features.
If
input_featuresisNone, thenfeature_names_in_is used as feature names in. Iffeature_names_in_is not defined, then names are generated:[x0, x1, ..., x(n_features_in_)].If
input_featuresis an array-like, theninput_featuresmust matchfeature_names_in_iffeature_names_in_is defined.
- Returns
- feature_names_outndarray of str objects
Transformed feature names.
- get_params(deep=True)[source]¶
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- inverse_transform(Xt)[source]¶
Transform discretized data back to original feature space.
Note that this function does not regenerate the original data due to discretization rounding.
- Parameters
- Xtarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Transformed data in the binned space.
- Returns
- Xinvndarray, dtype={np.float32, np.float64}
Data in the original feature space.
- set_params(**params)[source]¶
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.