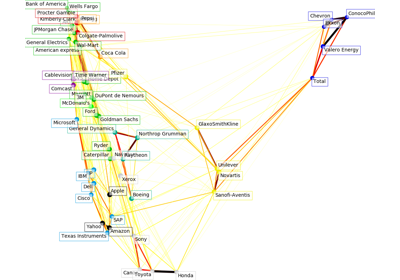
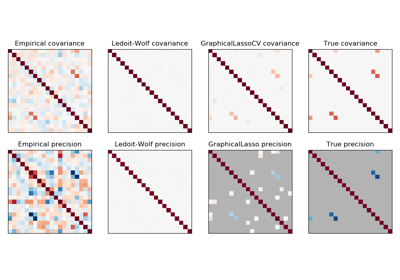
sklearn.covariance.GraphicalLassoCV¶
-
class
sklearn.covariance.GraphicalLassoCV(alphas=4, n_refinements=4, cv=’warn’, tol=0.0001, enet_tol=0.0001, max_iter=100, mode=’cd’, n_jobs=None, verbose=False, assume_centered=False)[source]¶ Sparse inverse covariance w/ cross-validated choice of the l1 penalty.
See glossary entry for cross-validation estimator.
Read more in the User Guide.
Parameters: - alphas : integer, or list positive float, optional
If an integer is given, it fixes the number of points on the grids of alpha to be used. If a list is given, it gives the grid to be used. See the notes in the class docstring for more details.
- n_refinements : strictly positive integer
The number of times the grid is refined. Not used if explicit values of alphas are passed.
- cv : int, cross-validation generator or an iterable, optional
Determines the cross-validation splitting strategy. Possible inputs for cv are:
- None, to use the default 3-fold cross-validation,
- integer, to specify the number of folds.
- CV splitter,
- An iterable yielding (train, test) splits as arrays of indices.
For integer/None inputs
KFoldis used.Refer User Guide for the various cross-validation strategies that can be used here.
Changed in version 0.20:
cvdefault value if None will change from 3-fold to 5-fold in v0.22.- tol : positive float, optional
The tolerance to declare convergence: if the dual gap goes below this value, iterations are stopped.
- enet_tol : positive float, optional
The tolerance for the elastic net solver used to calculate the descent direction. This parameter controls the accuracy of the search direction for a given column update, not of the overall parameter estimate. Only used for mode=’cd’.
- max_iter : integer, optional
Maximum number of iterations.
- mode : {‘cd’, ‘lars’}
The Lasso solver to use: coordinate descent or LARS. Use LARS for very sparse underlying graphs, where number of features is greater than number of samples. Elsewhere prefer cd which is more numerically stable.
- n_jobs : int or None, optional (default=None)
number of jobs to run in parallel.
Nonemeans 1 unless in ajoblib.parallel_backendcontext.-1means using all processors. See Glossary for more details.- verbose : boolean, optional
If verbose is True, the objective function and duality gap are printed at each iteration.
- assume_centered : boolean
If True, data are not centered before computation. Useful when working with data whose mean is almost, but not exactly zero. If False, data are centered before computation.
Attributes: - location_ : array-like, shape (n_features,)
Estimated location, i.e. the estimated mean.
- covariance_ : numpy.ndarray, shape (n_features, n_features)
Estimated covariance matrix.
- precision_ : numpy.ndarray, shape (n_features, n_features)
Estimated precision matrix (inverse covariance).
- alpha_ : float
Penalization parameter selected.
- cv_alphas_ : list of float
All penalization parameters explored.
- grid_scores_ : 2D numpy.ndarray (n_alphas, n_folds)
Log-likelihood score on left-out data across folds.
- n_iter_ : int
Number of iterations run for the optimal alpha.
See also
Notes
The search for the optimal penalization parameter (alpha) is done on an iteratively refined grid: first the cross-validated scores on a grid are computed, then a new refined grid is centered around the maximum, and so on.
One of the challenges which is faced here is that the solvers can fail to converge to a well-conditioned estimate. The corresponding values of alpha then come out as missing values, but the optimum may be close to these missing values.
Examples
>>> import numpy as np >>> from sklearn.covariance import GraphicalLassoCV >>> true_cov = np.array([[0.8, 0.0, 0.2, 0.0], ... [0.0, 0.4, 0.0, 0.0], ... [0.2, 0.0, 0.3, 0.1], ... [0.0, 0.0, 0.1, 0.7]]) >>> np.random.seed(0) >>> X = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean=[0, 0, 0, 0], ... cov=true_cov, ... size=200) >>> cov = GraphicalLassoCV(cv=5).fit(X) >>> np.around(cov.covariance_, decimals=3) array([[0.816, 0.051, 0.22 , 0.017], [0.051, 0.364, 0.018, 0.036], [0.22 , 0.018, 0.322, 0.094], [0.017, 0.036, 0.094, 0.69 ]]) >>> np.around(cov.location_, decimals=3) array([0.073, 0.04 , 0.038, 0.143])
Methods
error_norm(self, comp_cov[, norm, scaling, …])Computes the Mean Squared Error between two covariance estimators. fit(self, X[, y])Fits the GraphicalLasso covariance model to X. get_params(self[, deep])Get parameters for this estimator. get_precision(self)Getter for the precision matrix. mahalanobis(self, X)Computes the squared Mahalanobis distances of given observations. score(self, X_test[, y])Computes the log-likelihood of a Gaussian data set with self.covariance_as an estimator of its covariance matrix.set_params(self, \*\*params)Set the parameters of this estimator. -
__init__(self, alphas=4, n_refinements=4, cv=’warn’, tol=0.0001, enet_tol=0.0001, max_iter=100, mode=’cd’, n_jobs=None, verbose=False, assume_centered=False)[source]¶
-
error_norm(self, comp_cov, norm=’frobenius’, scaling=True, squared=True)[source]¶ Computes the Mean Squared Error between two covariance estimators. (In the sense of the Frobenius norm).
Parameters: - comp_cov : array-like, shape = [n_features, n_features]
The covariance to compare with.
- norm : str
The type of norm used to compute the error. Available error types: - ‘frobenius’ (default): sqrt(tr(A^t.A)) - ‘spectral’: sqrt(max(eigenvalues(A^t.A)) where A is the error
(comp_cov - self.covariance_).- scaling : bool
If True (default), the squared error norm is divided by n_features. If False, the squared error norm is not rescaled.
- squared : bool
Whether to compute the squared error norm or the error norm. If True (default), the squared error norm is returned. If False, the error norm is returned.
Returns: - The Mean Squared Error (in the sense of the Frobenius norm) between
selfandcomp_covcovariance estimators.
-
fit(self, X, y=None)[source]¶ Fits the GraphicalLasso covariance model to X.
Parameters: - X : ndarray, shape (n_samples, n_features)
Data from which to compute the covariance estimate
- y : (ignored)
-
get_params(self, deep=True)[source]¶ Get parameters for this estimator.
Parameters: - deep : boolean, optional
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
Returns: - params : mapping of string to any
Parameter names mapped to their values.
-
get_precision(self)[source]¶ Getter for the precision matrix.
Returns: - precision_ : array-like
The precision matrix associated to the current covariance object.
-
mahalanobis(self, X)[source]¶ Computes the squared Mahalanobis distances of given observations.
Parameters: - X : array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features]
The observations, the Mahalanobis distances of the which we compute. Observations are assumed to be drawn from the same distribution than the data used in fit.
Returns: - dist : array, shape = [n_samples,]
Squared Mahalanobis distances of the observations.
-
score(self, X_test, y=None)[source]¶ Computes the log-likelihood of a Gaussian data set with
self.covariance_as an estimator of its covariance matrix.Parameters: - X_test : array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features]
Test data of which we compute the likelihood, where n_samples is the number of samples and n_features is the number of features. X_test is assumed to be drawn from the same distribution than the data used in fit (including centering).
- y
not used, present for API consistence purpose.
Returns: - res : float
The likelihood of the data set with
self.covariance_as an estimator of its covariance matrix.
-
set_params(self, **params)[source]¶ Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as pipelines). The latter have parameters of the form
<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.Returns: - self