Note
Click here to download the full example code
Neighborhood Components Analysis Illustration¶
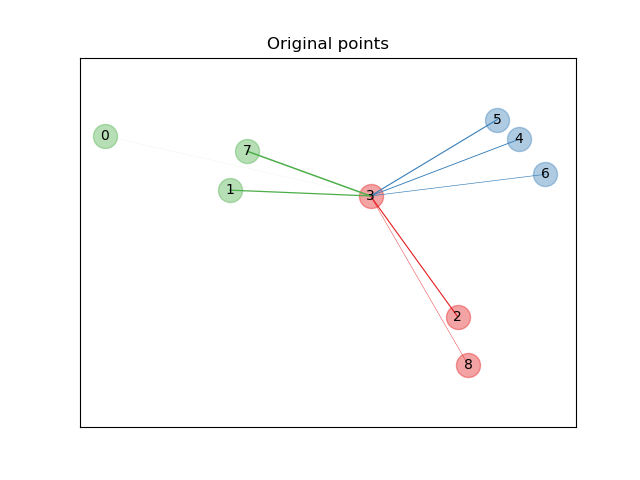
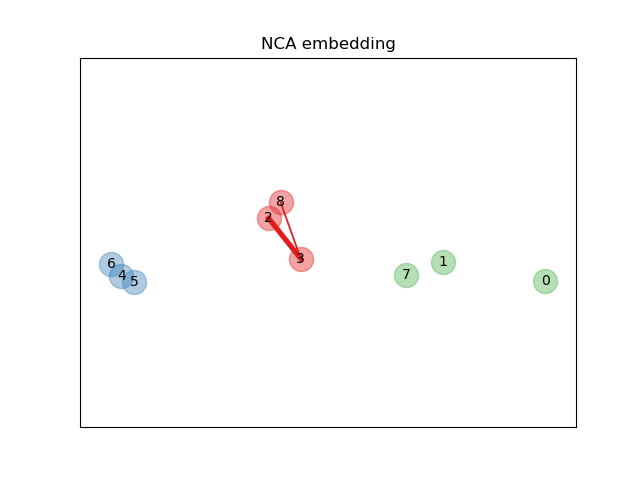
An example illustrating the goal of learning a distance metric that maximizes the nearest neighbors classification accuracy. The example is solely for illustration purposes. Please refer to the User Guide for more information.
# License: BSD 3 clause
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.neighbors import NeighborhoodComponentsAnalysis
from matplotlib import cm
from sklearn.utils.fixes import logsumexp
print(__doc__)
n_neighbors = 1
random_state = 0
# Create a tiny data set of 9 samples from 3 classes
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=9, n_features=2, n_informative=2,
n_redundant=0, n_classes=3, n_clusters_per_class=1,
class_sep=1.0, random_state=random_state)
# Plot the points in the original space
plt.figure()
ax = plt.gca()
# Draw the graph nodes
for i in range(X.shape[0]):
ax.text(X[i, 0], X[i, 1], str(i), va='center', ha='center')
ax.scatter(X[i, 0], X[i, 1], s=300, c=cm.Set1(y[i]), alpha=0.4)
def p_i(X, i):
diff_embedded = X[i] - X
dist_embedded = np.einsum('ij,ij->i', diff_embedded,
diff_embedded)
dist_embedded[i] = np.inf
# compute exponentiated distances (use the log-sum-exp trick to
# avoid numerical instabilities
exp_dist_embedded = np.exp(-dist_embedded -
logsumexp(-dist_embedded))
return exp_dist_embedded
def relate_point(X, i, ax):
pt_i = X[i]
for j, pt_j in enumerate(X):
thickness = p_i(X, i)
if i != j:
line = ([pt_i[0], pt_j[0]], [pt_i[1], pt_j[1]])
ax.plot(*line, c=cm.Set1(y[j]),
linewidth=5*thickness[j])
# we consider only point 3
i = 3
# Plot bonds linked to sample i in the original space
relate_point(X, i, ax)
ax.set_title("Original points")
ax.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.axis('equal')
# Learn an embedding with NeighborhoodComponentsAnalysis
nca = NeighborhoodComponentsAnalysis(max_iter=30, random_state=random_state)
nca = nca.fit(X, y)
# Plot the points after transformation with NeighborhoodComponentsAnalysis
plt.figure()
ax2 = plt.gca()
# Get the embedding and find the new nearest neighbors
X_embedded = nca.transform(X)
relate_point(X_embedded, i, ax2)
for i in range(len(X)):
ax2.text(X_embedded[i, 0], X_embedded[i, 1], str(i),
va='center', ha='center')
ax2.scatter(X_embedded[i, 0], X_embedded[i, 1], s=300, c=cm.Set1(y[i]),
alpha=0.4)
# Make axes equal so that boundaries are displayed correctly as circles
ax2.set_title("NCA embedding")
ax2.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax2.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
ax2.axis('equal')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.069 seconds)