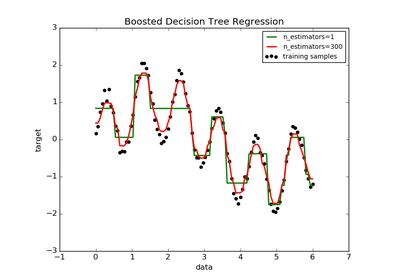
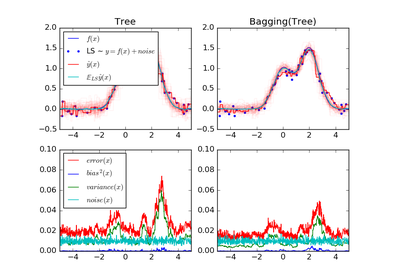
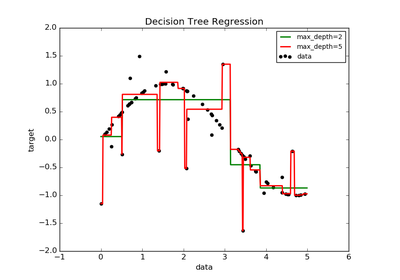
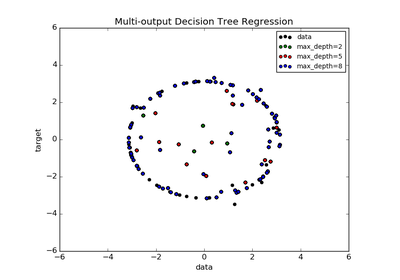
sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeRegressor¶
-
class
sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeRegressor(criterion='mse', splitter='best', max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2, min_samples_leaf=1, min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, max_features=None, random_state=None, max_leaf_nodes=None, presort=False)[source]¶ A decision tree regressor.
Read more in the User Guide.
Parameters: criterion : string, optional (default=”mse”)
The function to measure the quality of a split. The only supported criterion is “mse” for the mean squared error, which is equal to variance reduction as feature selection criterion.
splitter : string, optional (default=”best”)
The strategy used to choose the split at each node. Supported strategies are “best” to choose the best split and “random” to choose the best random split.
max_features : int, float, string or None, optional (default=None)
- The number of features to consider when looking for the best split:
- If int, then consider max_features features at each split.
- If float, then max_features is a percentage and int(max_features * n_features) features are considered at each split.
- If “auto”, then max_features=n_features.
- If “sqrt”, then max_features=sqrt(n_features).
- If “log2”, then max_features=log2(n_features).
- If None, then max_features=n_features.
Note: the search for a split does not stop until at least one valid partition of the node samples is found, even if it requires to effectively inspect more than
max_featuresfeatures.max_depth : int or None, optional (default=None)
The maximum depth of the tree. If None, then nodes are expanded until all leaves are pure or until all leaves contain less than min_samples_split samples. Ignored if
max_leaf_nodesis not None.min_samples_split : int, optional (default=2)
The minimum number of samples required to split an internal node.
min_samples_leaf : int, optional (default=1)
The minimum number of samples required to be at a leaf node.
min_weight_fraction_leaf : float, optional (default=0.)
The minimum weighted fraction of the input samples required to be at a leaf node.
max_leaf_nodes : int or None, optional (default=None)
Grow a tree with
max_leaf_nodesin best-first fashion. Best nodes are defined as relative reduction in impurity. If None then unlimited number of leaf nodes. If not None thenmax_depthwill be ignored.random_state : int, RandomState instance or None, optional (default=None)
If int, random_state is the seed used by the random number generator; If RandomState instance, random_state is the random number generator; If None, the random number generator is the RandomState instance used by np.random.
presort : bool, optional (default=False)
Whether to presort the data to speed up the finding of best splits in fitting. For the default settings of a decision tree on large datasets, setting this to true may slow down the training process. When using either a smaller dataset or a restricted depth, this may speed up the training.
Attributes: feature_importances_ : array of shape = [n_features]
The feature importances. The higher, the more important the feature. The importance of a feature is computed as the (normalized) total reduction of the criterion brought by that feature. It is also known as the Gini importance [R70].
max_features_ : int,
The inferred value of max_features.
n_features_ : int
The number of features when
fitis performed.n_outputs_ : int
The number of outputs when
fitis performed.tree_ : Tree object
The underlying Tree object.
See also
References
[R67] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decision_tree_learning [R68] L. Breiman, J. Friedman, R. Olshen, and C. Stone, “Classification and Regression Trees”, Wadsworth, Belmont, CA, 1984. [R69] T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani and J. Friedman. “Elements of Statistical Learning”, Springer, 2009. [R70] (1, 2) L. Breiman, and A. Cutler, “Random Forests”, http://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~breiman/RandomForests/cc_home.htm Examples
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_boston >>> from sklearn.cross_validation import cross_val_score >>> from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor >>> boston = load_boston() >>> regressor = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=0) >>> cross_val_score(regressor, boston.data, boston.target, cv=10) ... ... array([ 0.61..., 0.57..., -0.34..., 0.41..., 0.75..., 0.07..., 0.29..., 0.33..., -1.42..., -1.77...])
Methods
apply(X[, check_input])Returns the index of the leaf that each sample is predicted as. fit(X, y[, sample_weight, check_input, ...])Build a decision tree from the training set (X, y). fit_transform(X[, y])Fit to data, then transform it. get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator. predict(X[, check_input])Predict class or regression value for X. score(X, y[, sample_weight])Returns the coefficient of determination R^2 of the prediction. set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator. transform(*args, **kwargs)DEPRECATED: Support to use estimators as feature selectors will be removed in version 0.19. -
__init__(criterion='mse', splitter='best', max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2, min_samples_leaf=1, min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, max_features=None, random_state=None, max_leaf_nodes=None, presort=False)[source]¶
-
apply(X, check_input=True)[source]¶ Returns the index of the leaf that each sample is predicted as.
New in version 0.17.
Parameters: X : array_like or sparse matrix, shape = [n_samples, n_features]
The input samples. Internally, it will be converted to
dtype=np.float32and if a sparse matrix is provided to a sparsecsr_matrix.check_input : boolean, (default=True)
Allow to bypass several input checking. Don’t use this parameter unless you know what you do.
Returns: X_leaves : array_like, shape = [n_samples,]
For each datapoint x in X, return the index of the leaf x ends up in. Leaves are numbered within
[0; self.tree_.node_count), possibly with gaps in the numbering.
-
feature_importances_¶ Return the feature importances.
The importance of a feature is computed as the (normalized) total reduction of the criterion brought by that feature. It is also known as the Gini importance.
Returns: feature_importances_ : array, shape = [n_features]
-
fit(X, y, sample_weight=None, check_input=True, X_idx_sorted=None)[source]¶ Build a decision tree from the training set (X, y).
Parameters: X : array-like or sparse matrix, shape = [n_samples, n_features]
The training input samples. Internally, it will be converted to
dtype=np.float32and if a sparse matrix is provided to a sparsecsc_matrix.y : array-like, shape = [n_samples] or [n_samples, n_outputs]
The target values (class labels in classification, real numbers in regression). In the regression case, use
dtype=np.float64andorder='C'for maximum efficiency.sample_weight : array-like, shape = [n_samples] or None
Sample weights. If None, then samples are equally weighted. Splits that would create child nodes with net zero or negative weight are ignored while searching for a split in each node. In the case of classification, splits are also ignored if they would result in any single class carrying a negative weight in either child node.
check_input : boolean, (default=True)
Allow to bypass several input checking. Don’t use this parameter unless you know what you do.
X_idx_sorted : array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features], optional
The indexes of the sorted training input samples. If many tree are grown on the same dataset, this allows the ordering to be cached between trees. If None, the data will be sorted here. Don’t use this parameter unless you know what to do.
Returns: self : object
Returns self.
-
fit_transform(X, y=None, **fit_params)[source]¶ Fit to data, then transform it.
Fits transformer to X and y with optional parameters fit_params and returns a transformed version of X.
Parameters: X : numpy array of shape [n_samples, n_features]
Training set.
y : numpy array of shape [n_samples]
Target values.
Returns: X_new : numpy array of shape [n_samples, n_features_new]
Transformed array.
-
get_params(deep=True)[source]¶ Get parameters for this estimator.
Parameters: deep: boolean, optional :
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
Returns: params : mapping of string to any
Parameter names mapped to their values.
-
predict(X, check_input=True)[source]¶ Predict class or regression value for X.
For a classification model, the predicted class for each sample in X is returned. For a regression model, the predicted value based on X is returned.
Parameters: X : array-like or sparse matrix of shape = [n_samples, n_features]
The input samples. Internally, it will be converted to
dtype=np.float32and if a sparse matrix is provided to a sparsecsr_matrix.check_input : boolean, (default=True)
Allow to bypass several input checking. Don’t use this parameter unless you know what you do.
Returns: y : array of shape = [n_samples] or [n_samples, n_outputs]
The predicted classes, or the predict values.
-
score(X, y, sample_weight=None)[source]¶ Returns the coefficient of determination R^2 of the prediction.
The coefficient R^2 is defined as (1 - u/v), where u is the regression sum of squares ((y_true - y_pred) ** 2).sum() and v is the residual sum of squares ((y_true - y_true.mean()) ** 2).sum(). Best possible score is 1.0 and it can be negative (because the model can be arbitrarily worse). A constant model that always predicts the expected value of y, disregarding the input features, would get a R^2 score of 0.0.
Parameters: X : array-like, shape = (n_samples, n_features)
Test samples.
y : array-like, shape = (n_samples) or (n_samples, n_outputs)
True values for X.
sample_weight : array-like, shape = [n_samples], optional
Sample weights.
Returns: score : float
R^2 of self.predict(X) wrt. y.
-
set_params(**params)[source]¶ Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as pipelines). The former have parameters of the form
<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.Returns: self :
-
transform(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ DEPRECATED: Support to use estimators as feature selectors will be removed in version 0.19. Use SelectFromModel instead.
Reduce X to its most important features.
Usescoef_orfeature_importances_to determine the most important features. For models with acoef_for each class, the absolute sum over the classes is used.Parameters: X : array or scipy sparse matrix of shape [n_samples, n_features]
The input samples.
- threshold : string, float or None, optional (default=None)
The threshold value to use for feature selection. Features whose importance is greater or equal are kept while the others are discarded. If “median” (resp. “mean”), then the threshold value is the median (resp. the mean) of the feature importances. A scaling factor (e.g., “1.25*mean”) may also be used. If None and if available, the object attribute
thresholdis used. Otherwise, “mean” is used by default.
Returns: X_r : array of shape [n_samples, n_selected_features]
The input samples with only the selected features.