sklearn.linear_model.BayesianRidge¶
-
class
sklearn.linear_model.BayesianRidge(n_iter=300, tol=0.001, alpha_1=1e-06, alpha_2=1e-06, lambda_1=1e-06, lambda_2=1e-06, compute_score=False, fit_intercept=True, normalize=False, copy_X=True, verbose=False)[source]¶ Bayesian ridge regression
Fit a Bayesian ridge model and optimize the regularization parameters lambda (precision of the weights) and alpha (precision of the noise).
Read more in the User Guide.
Parameters: n_iter : int, optional
Maximum number of iterations. Default is 300.
tol : float, optional
Stop the algorithm if w has converged. Default is 1.e-3.
alpha_1 : float, optional
Hyper-parameter : shape parameter for the Gamma distribution prior over the alpha parameter. Default is 1.e-6
alpha_2 : float, optional
Hyper-parameter : inverse scale parameter (rate parameter) for the Gamma distribution prior over the alpha parameter. Default is 1.e-6.
lambda_1 : float, optional
Hyper-parameter : shape parameter for the Gamma distribution prior over the lambda parameter. Default is 1.e-6.
lambda_2 : float, optional
Hyper-parameter : inverse scale parameter (rate parameter) for the Gamma distribution prior over the lambda parameter. Default is 1.e-6
compute_score : boolean, optional
If True, compute the objective function at each step of the model. Default is False
fit_intercept : boolean, optional
whether to calculate the intercept for this model. If set to false, no intercept will be used in calculations (e.g. data is expected to be already centered). Default is True.
normalize : boolean, optional, default False
If True, the regressors X will be normalized before regression.
copy_X : boolean, optional, default True
If True, X will be copied; else, it may be overwritten.
verbose : boolean, optional, default False
Verbose mode when fitting the model.
Attributes: coef_ : array, shape = (n_features)
Coefficients of the regression model (mean of distribution)
alpha_ : float
estimated precision of the noise.
lambda_ : array, shape = (n_features)
estimated precisions of the weights.
scores_ : float
if computed, value of the objective function (to be maximized)
Notes
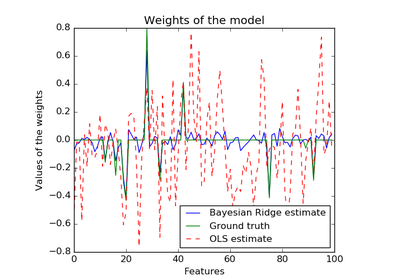
See examples/linear_model/plot_bayesian_ridge.py for an example.
Examples
>>> from sklearn import linear_model >>> clf = linear_model.BayesianRidge() >>> clf.fit([[0,0], [1, 1], [2, 2]], [0, 1, 2]) ... BayesianRidge(alpha_1=1e-06, alpha_2=1e-06, compute_score=False, copy_X=True, fit_intercept=True, lambda_1=1e-06, lambda_2=1e-06, n_iter=300, normalize=False, tol=0.001, verbose=False) >>> clf.predict([[1, 1]]) array([ 1.])
Methods
decision_function(*args, **kwargs)DEPRECATED: and will be removed in 0.19. fit(X, y)Fit the model get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator. predict(X)Predict using the linear model score(X, y[, sample_weight])Returns the coefficient of determination R^2 of the prediction. set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator. -
__init__(n_iter=300, tol=0.001, alpha_1=1e-06, alpha_2=1e-06, lambda_1=1e-06, lambda_2=1e-06, compute_score=False, fit_intercept=True, normalize=False, copy_X=True, verbose=False)[source]¶
-
decision_function(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ DEPRECATED: and will be removed in 0.19.
Decision function of the linear model.
Parameters: X : {array-like, sparse matrix}, shape = (n_samples, n_features)
Samples.
Returns: C : array, shape = (n_samples,)
Returns predicted values.
-
fit(X, y)[source]¶ Fit the model
Parameters: X : numpy array of shape [n_samples,n_features]
Training data
y : numpy array of shape [n_samples]
Target values
Returns: self : returns an instance of self.
-
get_params(deep=True)[source]¶ Get parameters for this estimator.
Parameters: deep: boolean, optional :
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
Returns: params : mapping of string to any
Parameter names mapped to their values.
-
predict(X)[source]¶ Predict using the linear model
Parameters: X : {array-like, sparse matrix}, shape = (n_samples, n_features)
Samples.
Returns: C : array, shape = (n_samples,)
Returns predicted values.
-
score(X, y, sample_weight=None)[source]¶ Returns the coefficient of determination R^2 of the prediction.
The coefficient R^2 is defined as (1 - u/v), where u is the regression sum of squares ((y_true - y_pred) ** 2).sum() and v is the residual sum of squares ((y_true - y_true.mean()) ** 2).sum(). Best possible score is 1.0 and it can be negative (because the model can be arbitrarily worse). A constant model that always predicts the expected value of y, disregarding the input features, would get a R^2 score of 0.0.
Parameters: X : array-like, shape = (n_samples, n_features)
Test samples.
y : array-like, shape = (n_samples) or (n_samples, n_outputs)
True values for X.
sample_weight : array-like, shape = [n_samples], optional
Sample weights.
Returns: score : float
R^2 of self.predict(X) wrt. y.
-
set_params(**params)[source]¶ Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as pipelines). The former have parameters of the form
<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.Returns: self :
-