Nearest Centroid Classification¶
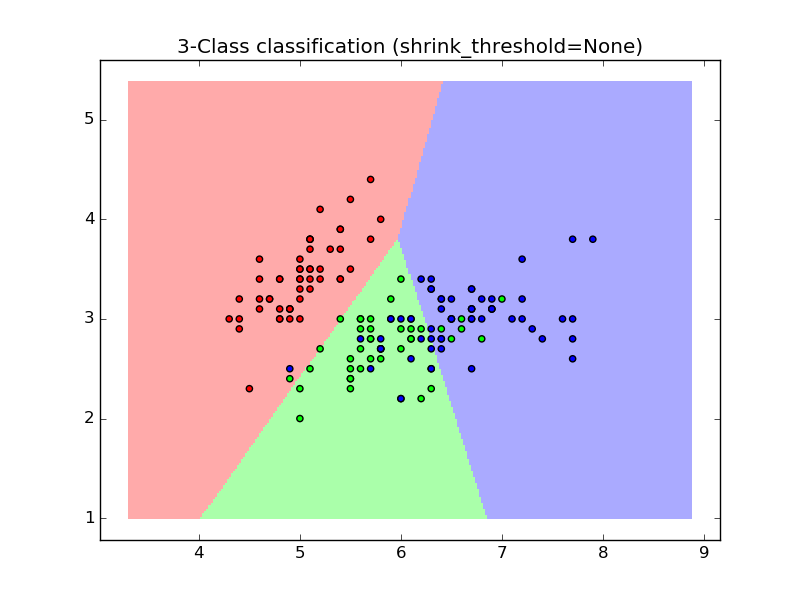
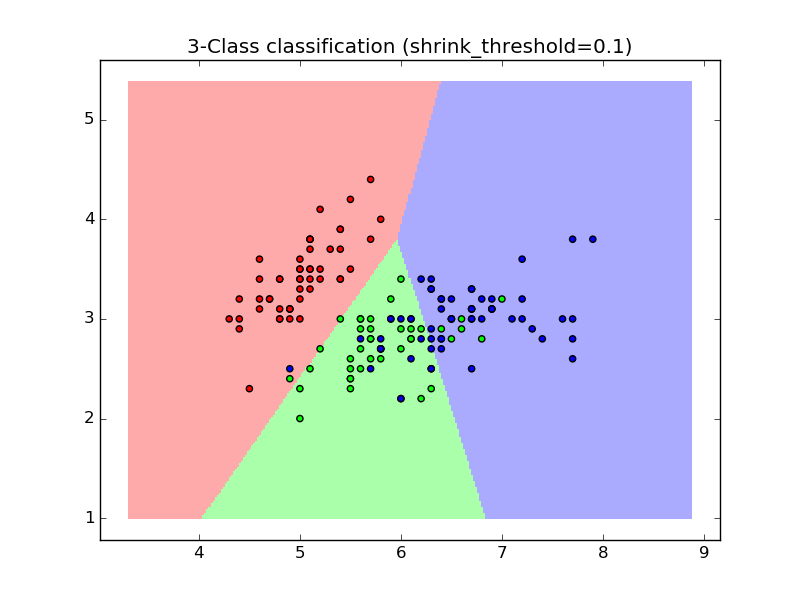
Sample usage of Nearest Centroid classification. It will plot the decision boundaries for each class.
Script output:
None 0.813333333333
0.1 0.813333333333
Python source code: plot_nearest_centroid.py
print(__doc__)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.neighbors import NearestCentroid
n_neighbors = 15
# import some data to play with
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, :2] # we only take the first two features. We could
# avoid this ugly slicing by using a two-dim dataset
y = iris.target
h = .02 # step size in the mesh
# Create color maps
cmap_light = ListedColormap(['#FFAAAA', '#AAFFAA', '#AAAAFF'])
cmap_bold = ListedColormap(['#FF0000', '#00FF00', '#0000FF'])
for shrinkage in [None, 0.1]:
# we create an instance of Neighbours Classifier and fit the data.
clf = NearestCentroid(shrink_threshold=shrinkage)
clf.fit(X, y)
y_pred = clf.predict(X)
print(shrinkage, np.mean(y == y_pred))
# Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each
# point in the mesh [x_min, m_max]x[y_min, y_max].
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure()
plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cmap_light)
# Plot also the training points
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap=cmap_bold)
plt.title("3-Class classification (shrink_threshold=%r)"
% shrinkage)
plt.axis('tight')
plt.show()
Total running time of the example: 0.16 seconds ( 0 minutes 0.16 seconds)